– A typical injection molding cycle takes 15–60 seconds, but total production time includes mold setup (2–8 hours), sampling, and ramp-up.
– Cooling time accounts for 60–80% of the total cycle, making it the biggest lever for speed optimization.
– In our factory, optimizing cooling channels and gate design has cut cycle times by 20–35% on existing molds.
– Total project lead time from design to mass production typically ranges from 4–12 weeks depending on part complexity.
How Long Does Injection Molding Actually Take?
Injection molding production time depends on two very different scales: the cycle time for each individual shot (typically 15–60 seconds) and the project lead time from concept to mass production (typically 4–12 weeks). At ZetarMold, clients often ask “how long will it take?” — and the honest answer requires understanding both timescales.

The per-part cycle time1 breaks down into four phases: injection (1–5 seconds), packing (3–10 seconds), cooling (10–40 seconds), and mold open/eject/close (3–8 seconds). The total determines your hourly output rate and unit economics.
What Are the Key Phases of Injection Molding Cycle Time?
Each cycle consists of four sequential phases. Understanding how long each takes — and what controls it — is essential for optimization.
| Phase | Typical Duration | Key Variables | % of Total Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection (fill) | 1–5 s | Part volume, injection speed, number of gates | 5–15% |
| Packing (holding) | 3–10 s | Gate freeze time, holding pressure profile | 10–20% |
| Cooling | 10–40 s | Wall thickness, mold temperature, coolant flow | 60–80% |
| Mold open/eject/close | 3–8 s | Machine dry cycle, ejection complexity | 5–15% |
“Faster injection speed always means shorter cycle time.”False
While faster injection reduces fill time by a few seconds, it can create quality issues like jetting, burn marks, or flash that require slower overall cycles. Since cooling dominates cycle time (60–80%), injection speed has minimal impact on total throughput compared to cooling optimization.
“Reducing wall thickness by 10% can cut cooling time — and total cycle — by approximately 20%.”True
Cooling time scales roughly with the square of wall thickness. A 10% reduction in wall thickness (e.g., 2.5 mm to 2.25 mm) reduces cooling time by approximately 19%, which translates directly into shorter cycles and higher hourly output.
What Factors Determine Total Project Lead Time?
Beyond the per-shot cycle, the total time from project start to mass production involves several major milestones.
| Phase | Duration | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
| DFM review | 2–5 days | Design for manufacturability analysis, material selection |
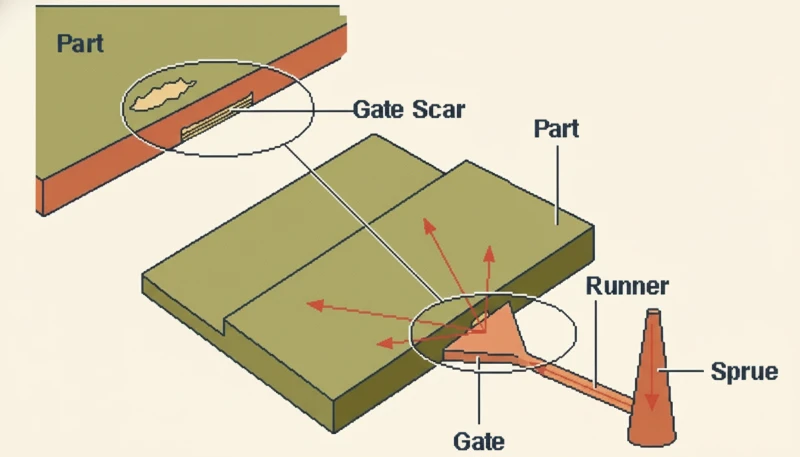
| Mold design | 5–10 days | 3D mold design, cooling layout, gate placement |
| Mold manufacturing | 3–6 weeks | CNC machining, EDM, assembly, polishing |
| Trial molding (T1) | 1–2 days | First samples, dimensional inspection |
| Mold revision | 3–7 days | Steel-safe modifications based on T1 results |
| T2/T3 trials | 1–3 days each | Validation samples, process documentation |
| Production ramp-up | 1–3 days | Establish stable process, quality confirmation |
At ZetarMold, we typically deliver T1 samples within 25–35 days for standard complexity molds. Complex multi-cavity or hot runner molds may extend to 45–60 days.
How Can You Reduce Cooling Time — the Biggest Time Consumer?
Since cooling accounts for 60–80% of cycle time, it offers the greatest opportunity for time reduction. In our production facility, we have achieved 20–35% cycle time reductions through cooling optimization alone.
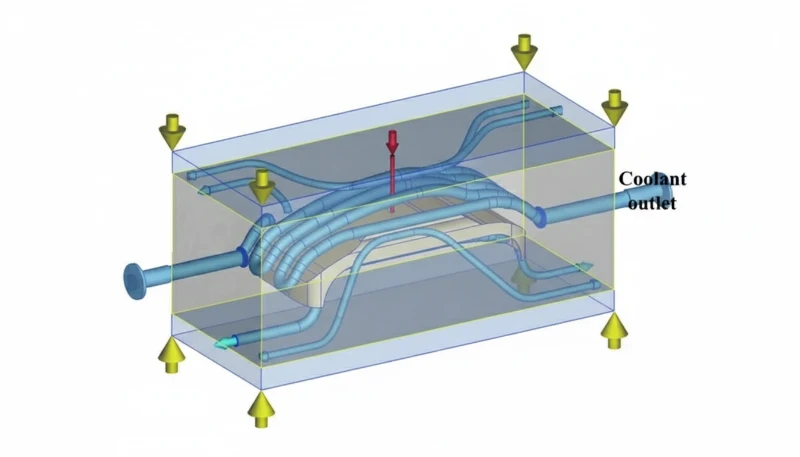
Proven cooling optimization strategies:
- Conformal cooling2 — 3D-printed cooling channels that follow part contours reduce cooling time by 25–40% compared to straight-drilled channels.
- BeCu inserts — Beryllium copper’s thermal conductivity (3–5× steel) accelerates heat removal in thick or hard-to-cool areas.
- Turbulent flow — Ensuring Reynolds number >10,000 in cooling circuits improves heat transfer efficiency by 3–5×.
- Mold temperature controllers — Precise ±1°C temperature control prevents over-cooling (which wastes time) and under-cooling (which causes defects).
What Machine and Automation Choices Affect Production Speed?
The injection molding machine itself and the level of automation significantly impact throughput.

Machine selection factors:
- All-electric vs. hydraulic — All-electric machines have 15–20% faster dry cycles (mold open/close) and more precise repeatability.
- Clamp tonnage matching — An oversized machine wastes energy and has slower movements. Matching tonnage to actual need improves speed.
- Multi-cavity molds — Doubling cavities doubles output per cycle. We commonly run 4–16 cavity molds for high-volume parts.
Automation impact:
- Robotic part removal — Reduces mold-open time by 1–3 seconds per cycle vs. gravity drop.
- In-mold labeling (IML) — Combines decoration with molding, eliminating a secondary operation.
- Automated quality inspection — Vision systems check parts in real-time without stopping production.
“Multi-cavity molds always reduce per-part production time proportionally.”False
While multi-cavity molds increase parts per cycle, they also require longer cooling times (more heat to remove), higher clamp tonnage, and more complex balancing. A 4-cavity mold typically produces 3.2–3.6× the output of a single-cavity mold — not 4×. Filling imbalance can further reduce the efficiency gain.
“All-electric injection molding machines can deliver 15–20% faster cycle times than equivalent hydraulic machines.”True
All-electric machines use servo motors that move the clamp and screw simultaneously (parallel motion), while hydraulic machines often perform these sequentially. This parallel operation, combined with faster acceleration and deceleration, typically saves 15–20% on total cycle time.
How Do You Calculate Production Time for a Specific Project?
Here is the formula we use at ZetarMold to estimate total production time for a given order quantity:
Production time = Setup time + (Order quantity ÷ Cavities × Cycle time) + Quality checks + Planned downtime
Example calculation for 100,000 parts:
- Setup time: 4 hours
- Cycle time: 30 seconds
- Mold cavities: 4
- Production shots: 100,000 ÷ 4 = 25,000 shots
- Pure molding time: 25,000 × 30s = 750,000s = 208 hours
- Efficiency factor (85%): 208 ÷ 0.85 = 245 hours ≈ 10.2 days (24h operation)
- Add setup + QC: ~11 days total
Need a precise production timeline for your project? Contact ZetarMold for a detailed quotation including mold lead time and production scheduling.

FAQ
What is the fastest possible injection molding cycle time?
For thin-wall parts (0.5–1.0 mm) in fast-cooling materials like PP, cycle times as low as 3–6 seconds are achievable with optimized cooling and high-speed machines. Standard parts with 1.5–2.5 mm walls typically run 20–40 seconds.
How long does it take to change molds between production runs?
Mold changeover typically takes 2–8 hours including installation, water/hydraulic connections, and process setup. With quick mold change (QMC) systems, this can be reduced to 30–60 minutes. We use standardized mold bases to minimize changeover time.
Does part color affect production time?
Color changes require purging the barrel, which adds 15–60 minutes depending on the machine size and color contrast (light-to-dark is faster than dark-to-light). The actual molding cycle time is unaffected by color.
How does mold flow analysis help predict production time?
Mold flow simulation predicts fill time, packing time, and cooling time with ±5–10% accuracy before the mold is built. This allows engineers to optimize gate location, cooling layout, and process parameters to minimize cycle time at the design stage.
What is the typical scrap rate in injection molding production?
Well-optimized processes achieve 0.5–2% scrap rates. During initial production ramp-up, scrap may reach 5–10% for the first 50–100 shots while the process stabilizes. At ZetarMold, we target less than 1% scrap for steady-state production.
Summary

Injection molding production time operates on two scales: the per-part cycle (15–60 seconds) dominated by cooling time, and the project timeline (4–12 weeks) driven by mold manufacturing. The most effective strategies for reducing production time focus on cooling optimization, proper machine selection, and automation. At ZetarMold, we engineer every project for both speed and quality — because in manufacturing, time is money, and quality is reputation.
-
Cycle time is the total elapsed time from the start of one injection molding shot to the start of the next, including injection, packing, cooling, mold opening, part ejection, and mold closing. ↩
-
Conformal cooling uses cooling channels that follow the contour of the part geometry — typically produced by 3D metal printing — to achieve more uniform and faster heat extraction than conventional straight-drilled cooling lines. ↩
-
Draft angle is the slight taper (typically 0.5–3°) applied to vertical walls of a molded part that allows it to release cleanly from the mold during ejection without scraping or sticking. ↩