The molding cycle of injection molding consists of mold closing time, filling time, holding time, cooling time, and demolding time. Among them, cooling time accounts for the largest proportion, about 70% ~ 80%.
Therefore, cooling time will directly affect the molding cycle and output of plastic products. In the demoulding stage, the cooling temperature of plastic products should be lower than the thermal conductivity deformation temperature of plastic products.
To prevent the plastic products from residual stress damage caused by relaxation or warping and molding deformation caused by an external force.

What is injection molding cooling time?
Injection molding cooling time usually refers to the time between the plastic melt filling the injection mold cavity and the time when the mold can be opened to remove the product.
Can open the mold to take out the time standard that makes a piece, often with make a piece already sufficient solidify, have a certain intensity and rigid prevail when opening a molded top, do not send deformation craze.
Even if the same plastic is used for plastic injection molding, its cooling time varies with the thickness of the wall, the temperature of the molten plastic, the demoulding temperature of the molding part, and the temperature of the injection mold.
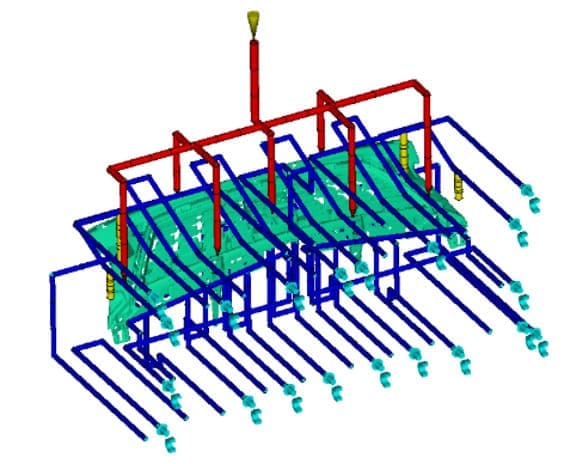
How is Cooling Time Calculated in Plastic Injection Molding?
Cooling time can be calculated by using an equation that incorporates wall thickness and a measurement known as thermal diffusivity – which quantifies the plastic’s thermal conductivity, density, and energy requirements to raise its temperature.
The estimated time also depends on the type of thermoplastic, as each has different melting and molding temperatures.

Injection molding cooling time reference
1. The temperature of the center layer of the thickest part of the wall of the plastic injection molded part, and the time needed to cool down to the temperature below the thermal deformation of the plastic;
2. The average temperature in the section of the plastic injection processing part, and the time required by cooling to the specified mold temperature of the product;
3. The temperature of the center layer of the thickest part of the wall of crystalline plastic molding parts, the time needed to cool down to below its melting point, or the time required to reach the specified crystallization percentage.
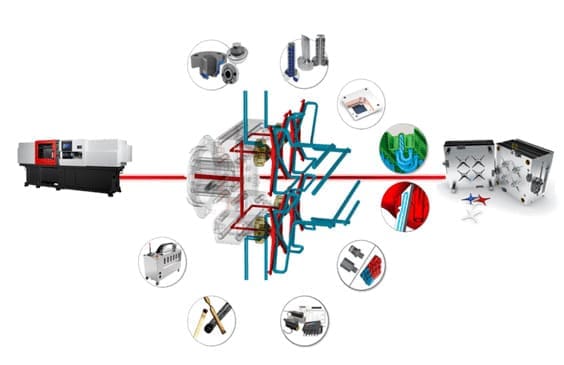
Factors affecting the cooling time of injection molding
Estimating cooling time for injection molding can be complex, as it depends on various factors such as the material used, size and shape of the part, wall thickness, actual melt temperature, and mold temperature.
1. Type of plastic used
In general, materials with lower melting points will solidify faster than those with higher melting points.
2. Mold size and shape
3. Wall thickness of injection molded parts
Smaller parts with thinner walls will cool faster than larger parts with thicker walls.
4. Mold temperature
The lower mold temperature causes the material to cool faster.
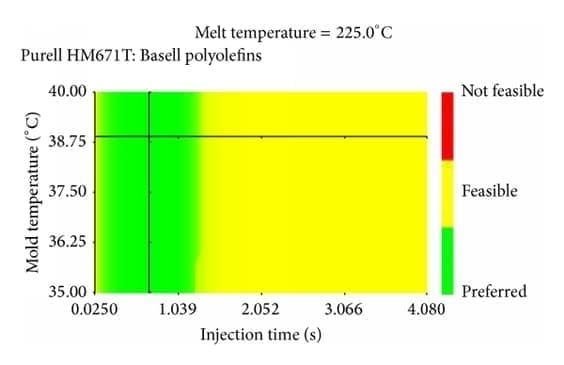
5. Speed of injection molding cycle time
The larger the injection molding machine, the longer the cooling time.
Each of these factors affects the time it takes plastic to cool and solidify. By taking all these factors into account, the cooling time for a particular injection molding process can be calculated.
In addition, the progress of the cooling process must be closely monitored to ensure that molded parts meet all quality requirements.

Why is cooldown time important?
Estimating the cooling time of an injection molded part is important for several reasons. First, it ensures uniform cooling channels in cavity temperature sensors, thus preventing warping and deformation.
In addition, it helps avoid stress fractures and other defects that may occur if the cooling process is not controlled properly.
Finally, by accurately predicting cooling times, production can be scheduled more efficiently and parts can be completed on time.
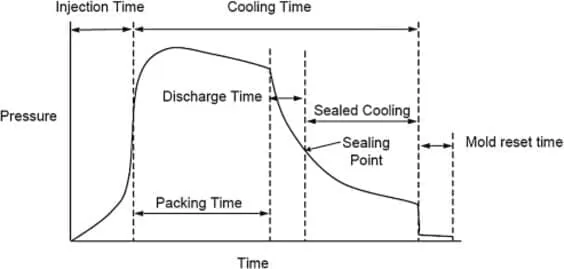
Many factors must be considered when estimating the cooling time, including the size and shape of the part, the materials used, and the die design.
With experience, most engineers have a good sense of how these factors will affect the cooling time of a particular part.
However, there are also software programs that can help make more accurate predictions. In any case, accurate estimation of cooling time is an important part of successful plastic injection molding.

What happens when the cooling time for injection molding is insufficient?
It is very important to estimate the cooling circuit fill time of injection molding parts to ensure the correct process.
If the cooling time is too short, the molten plastic may not have enough time to cool and solidify properly.
At this time, the ejection product is still soft. The problems that are prone to occur include ejection deformation, microcosm, and product warpage, resulting in poor quality parts.
However, if it is cooled too long, the plastic can cool unevenly, causing warping or other defects.
Estimating the cooling time can be difficult because it depends on many factors, such as the size and shape of the part, the type of plastic used, and the ambient temperature.
By using proven methods for cooling line design, warp and cooling time are minimized. The mold is also fully instrumented with cavity pressure sensors at post gate and end of fill in conjunction with in-cavity temperature sensors. However, some general guidelines can help ensure that the cooling time is adequate.

Summary
Although estimating cooling times can be difficult, it is important to ensure that plastic parts are adequately tensile test bar cooled.
However, defects can occur if the cooling time is too long. For more information on cooling time and other factors that affect the quality of molded plastic parts, please contact ZetarMold. We are happy to discuss your specific needs and find a solution that meets your requirements.