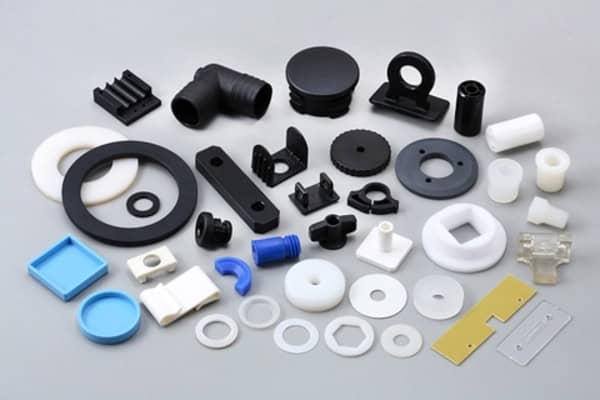
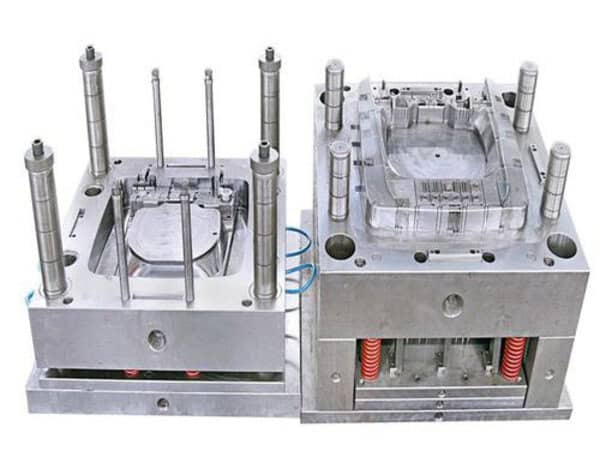
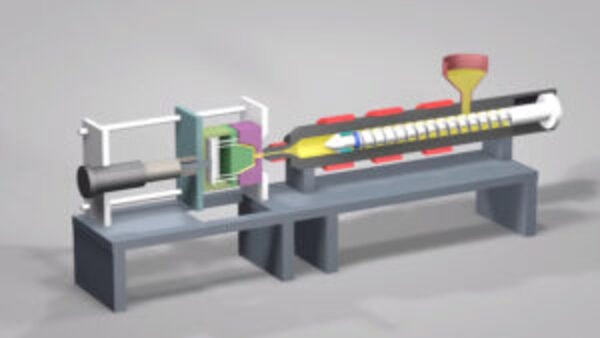
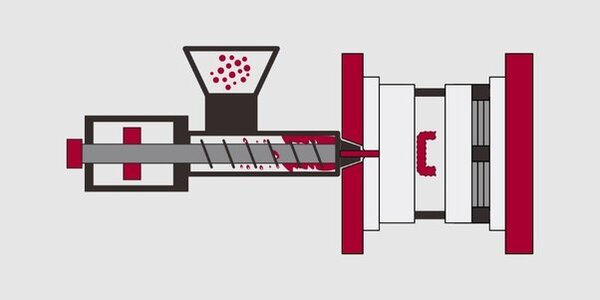
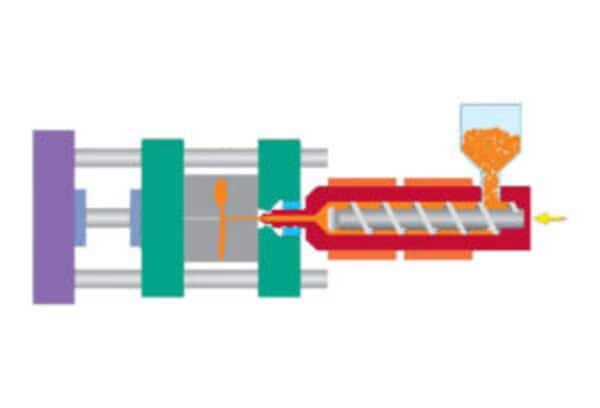
Micro injection molding enables precise manufacturing of extremely small, intricate components, widely used across electronics, medical devices, and automotive industries.
Micro injection molding produces highly detailed miniature parts with exceptional precision, using minimal material. This process is essential in medical, automotive, and electronic fields, where miniaturization and accuracy are crucial. Key advantages include reduced material waste and the ability to create complex, high-quality parts at scale.
While micro injection molding offers unique benefits, understanding the process, materials, and equipment is key to optimizing production for tiny, intricate parts. Read on to explore how mastering these factors can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of your manufacturing operations.
Micro injection molding allows for the creation of extremely small, detailed parts with minimal material.True
The precision of micro injection molding enables production of intricate parts, often as small as a few millimeters, with exceptional detail.
Micro injection molding only works with specific types of plastics.False
While micro injection molding often uses specialized thermoplastics, many materials can be adapted for use, making the process versatile for different applications.
What is the Micro Injection Molding Process?
Micro injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity as small as a few millimeters, typically using specialized machines. It is used for producing small, complex parts with high precision. The process offers faster cycle times and better material usage, making it efficient for high-volume production of miniature components.
Micro molding is a super specialized form of injection molding that focuses on making really tiny parts. The process involves making a hole that matches the shape of the part you want.
Micro-structured steel or aluminum molds are made with super precise machines that use computer programs and electricity to cut the metal with really tiny tolerances. This method can make parts that weigh less than a gram and are only a few millimeters big.
What are the Key Points of Micro Injection Molding Mold Processing?
Micro injection molding involves using small, highly detailed molds to produce tiny, intricate parts with precise dimensions. The key points include fast cycle times, reduced material waste, and high production consistency. This method is ideal for manufacturing small, complex components like micro gears and connectors.

There are usually two trends in mold processing for micro injection molding: the first is to use mirror spark machine processing. In order to ensure high precision, it is best to use graphite electrodes for EDM, because the loss of graphite electrodes is much smaller than that of ordinary copper electrodes.
The second, more common processing method is to use electroforming molds. The electroforming process can ensure very high precision, but the disadvantage is that the processing cycle is long, each hole must be processed independently, and if there is slight damage during production that cannot be repaired, the damaged hole can only be replaced.
In terms of molds, mold temperature1is also a very important parameter for micro injection molding. Facing high-end customers, the current more common practice is to borrow the concept of high-gloss injection molding and introduce a rapid heating and cooling system.
In theory, high mold temperature is very helpful for micro injection molding, such as preventing thin-wall filling difficulties and material shortages. However, too high mold temperature will bring new problems, such as extended cycle and shrinkage and deformation after mold opening.
So, it’s very important to introduce a new mold temperature control system. When we do injection molding, we can raise the mold temperature (it can be higher than the melting point of the plastic we’re using) so that the melt can fill the cavity quickly, to prevent the melt from dropping too fast during the filling process and causing incomplete filling; and then when we demold, we can quickly lower the mold temperature, keep it at a temperature slightly lower than the plastic’s thermal deformation temperature, and then open the mold and eject.
Also, because micro injection molding is a milligram-level product, even if the product is optimized and improved, the mass ratio of the product and the material in the gating system is still 1:10 when using a conventional gating2 system to mold the product. Only less than 10% of the material is injected into the micro product, resulting in a large amount of gating system condensate, so micro injection molding should use a hot runner gating system.
What are the Key points in Selecting Materials for Micro Injection Molding?
The key factors in selecting materials for micro injection molding include material flow characteristics, shrinkage rates, thermal stability, and moldability. High-performance polymers like PEEK, PPS, and PEI are commonly used for their strength, stability, and low shrinkage. The choice of material directly impacts part quality, cycle time, and production costs in the micro molding process.
When it comes to picking materials, it’s best to start with some general engineering plastics that have low viscosity and good thermal stability.
We choose low-viscosity materials because they flow easily when they’re melted. That means they don’t put up much resistance as they flow through the whole system, so they fill the mold quickly and smoothly. They don’t cool down much as they flow, either. If they did, they’d form cold joints in the product. They don’t stretch much as they flow, either, so the product comes out pretty much the same all over.
If you choose high-viscosity plastics, not only will the filling be slow, but the feeding time will be long. The shear flow caused by the feeding will easily orient the chain molecules along the shear flow direction.
In this case, the orientation state will be frozen when cooled below the softening point, and this frozen orientation to a certain extent will easily cause internal stress in the product, and even cause stress cracking or warping3deformation of the product.
The reason we need plastics to be thermally stable is because they can easily degrade from being in the hot runner for a long time or from being sheared by the screw, especially if they’re heat-sensitive plastics.
Even if you have a really short cycle time, the small shot size of the material means it’s going to spend a relatively long time in the gating system, and that’s going to cause a lot of degradation of the plastic. So heat-sensitive plastics are not good for micro molding.
What are the Equipment Requirements for Micro Injection Molding?
Key equipment requirements for micro injection molding include high-precision injection molding machines, micro tooling, and tight temperature control. These machines must handle small volumes of material with extreme accuracy, and tooling must be capable of creating intricate features at a microscopic scale. Commonly used materials include specialized resins such as liquid silicone rubber (LSR) or thermoplastics.
Micro plasticizing device, using a short screw with an L/D ratio of about 15 and a screw diameter in the range of 12-18mm to avoid the risk of degradation and deterioration of raw materials; high-precision injection volume control system to achieve the most reasonable and accurate projection volume control.
The ideal injection speed control system ensures that the injection molding process can be fully and perfectly transmitted; precise mold temperature control helps to reasonably guarantee the molding quality of the melt in each part between complex structures; the mold has a vacuum function, which has more accurate dimensional stability and injection auxiliary functions for micro products.
Nozzle that seals itself to prevent drooling and inconsistent injection volume; precise and gentle A flexible clamping system to protect the precision mold and injection molding conditions.
What are the Key Points of Micro Injection Molding Process?
Micro injection molding involves the use of specialized machines to inject tiny amounts of material into molds with very fine details. This process is crucial for producing parts with high dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances. It reduces waste and is cost-effective for small-batch production.
Micro injection molding needs high-speed injection capability and high injection pressure4
, higher melt temperature within the allowable range, and the mold wall temperature needs to be precisely controlled. These conditions are necessary, and large runners and large gate designs are required in mold development so that the melt has a more reliable flow channel and switching capability in the cavity.
Perfect auxiliary equipment: It is very important to use high-precision mold guide devices, mold evacuation systems, runner collectors and product removal mechanical devices, as well as automatic gate removal systems and automatic activation mold cleaning systems, and even effective product packaging and processing systems.
What are the Characteristics of Micro Injection Molding Process?
Micro injection molding uses specialized molds and equipment to produce tiny, complex parts with tight tolerances. It is commonly used in electronics, medical devices, and automotive applications. The process reduces material waste, improves precision, and allows for high-volume production of micro-sized components.
Microinjection molded products are characterized by their small size, unique shape, and intricate functional areas. Typically, these products range in size from a few microns to a few centimeters, with aspect ratios between 1 and 100. Some functional areas require high strength, high finish, high transparency, and so on.
To achieve these features with high reproducibility, special requirements must be met during the process. Specifically, to ensure proper filling, high injection speeds and pressures (up to hundreds or thousands of kg/cm2) are required. The material temperature should be as high as possible within the allowable range, and the mold wall temperature should also be controlled at the high end.
To get a big shot size, you need big runners and big gates. That way, you can control the polymer as it flows and not mess it up. You need a special mold with a split heater and cooler to control the mold temperature. For example, you need a high mold temperature when you fill the mold and a low mold temperature when you cool the mold.
So, you need two oil systems with different temperatures to heat and cool the mold when you fill and cool the mold. To control the process and handle and package the parts, you need better mold sensors, better mold guides, a way to get the air out of the mold, a way to collect the runners, a way to get the parts out of the mold, a way to get rid of the gate, and a way to clean the mold every cycle. You need all this stuff to make good parts and collect them.
When it comes to materials, many of the same materials that are used for macro molding can also be used for micro molding. Some of the materials that are used in micro injection molding include: POM, PC, PMMA, PA, LCP, PEI, and silicone rubber. Acrylic5
, acrylamide, and siloxane-based materials have also been used in reaction injection applications.
What are the Benefits of Micro Injection Molding?
Micro injection molding allows for the creation of ultra-small, intricate components with exceptional accuracy. It minimizes material waste, reduces cycle times, and supports mass production of tiny, complex parts. Key benefits include cost savings, increased production speed, and the ability to manufacture intricate designs at a small scale.
Micro molding technology has a lot of advantages when it comes to precision, processing, and cost. There are a lot of benefits to this process, and here are some of the important ones:
Precision and Complexity
This advanced injection molding technology is really good at making things that are really precise and have a lot of shapes. You can make really small and delicate parts with really tight tolerances. You can use advanced processing technologies like CNC and EDM to make really small cores, cavities6, and features with really good precision.
This precision is really important in the medical device, electronics, and micro-optics industries because even a little bit of difference can make a big difference in how well something works. This technology makes sure that you can make the same thing over and over again, so you can make really precise and reliable plastic parts.
Material Selection and Compatibility
The program also supports a wide range of materials, including high-performance polymers7 and engineering thermoplastics. These materials have great mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and thermal stability.
Different materials can be combined to make parts that are perfect for specific uses. You can choose materials that work well with the human body, materials that conduct electricity, materials that can handle high temperatures, and more. You can pick the right materials to make sure your micromolded parts do what they’re supposed to do.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Unlike traditional injection molding, micromolding offers significant cost advantages. It requires smaller and less expensive tools, which saves costs. For example, the required clamping force is reduced, allowing the use of smaller and less expensive machines. As a result, micromolding costs can be reduced by about 40% compared to full-size mold costs.
Also, the process cuts production costs by cutting cycle time. The process uses micro molds, usually made of aluminum, which makes processing faster and cheaper. Compact barrels, fewer mold cavities8
, and smaller flow channels also help cut costs. All these things together make micromolding cost-effective. The small size of micro parts also means you use materials efficiently, so you don’t waste much.
It also allows for the integration of multiple steps such as assembly or overmolding into a single production cycle. This process consolidation improves efficiency and reduces overall manufacturing time. With optimized micromolding molds and automation capabilities, the technology can achieve faster cycle times, increased productivity, and cost-effectiveness.
What are the Applications of Micro Injection Molding?
Micro injection molding is used to manufacture tiny, complex components with high precision. Common applications include medical devices, electronics, automotive, and consumer goods. Key advantages include reduced material waste, faster cycle times, and the ability to produce intricate designs that traditional molding techniques cannot achieve.
This process is useful in a lot of applications, especially when size and precision are important. Its ability to produce small, complex plastic parts with the highest precision has paved the way for innovative advancements in the following industries:
Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry needs to be super accurate in what it does, and it often needs to use really complicated machines. This is what medical device manufacturing is all about. It’s about making things like drug delivery devices, diagnostic systems, catheters, optical and hearing aid components, and so on.
This technology is especially good for making instruments that are used in surgeries where they don’t have to cut you open very much, like neurosurgery and aortic treatments. It’s also getting used more and more for making microfluidic systems for medical applications. That’s why the medical industry is using this technology more and more.
Electronic and Electrical Industry
As electronic devices get smaller, the electronics industry needs to be more precise. Microinjection molding is great for making lots of different electronic parts. One example is micro-optics. It makes things like lasers, smartphones, lenses, prisms, and more.
It also makes microelectronic parts like connectors, plugs, switches, computer chips, and more. These parts can be used in computers, phones, music players, and other small electronics.
MEMS also rely on micromolding technology. There is an increasing demand for advanced molding technology in the manufacturing process. For example, research on biomedical MEMS and the application of next-gen sequencing have significantly increased the demand for MEMS.
Automotive and Aerospace Industries
The importance of this molding technology is evident in the manufacturing of automotive parts, which often require lightweight and compact designs. It can be used to produce a variety of automotive parts. These include engine components, brakes, and other related parts like gaskets, clips, door lock mechanisms, switches, buttons, and micro plastic gears.
What are the Challenges of Micro Injection Molding?
Micro injection molding involves creating tiny, high-precision parts used in industries like medical devices, electronics, and automotive. The key challenges include maintaining uniform material flow, controlling part shrinkage, and minimizing defects like warping and short shots. Advancements in equipment and material science are addressing these issues to improve consistency and efficiency.
Micro molding is a real challenge. You have to control the mold and the material flow. You have to control the quality. You have to be able to scale it. Let’s talk about some of the challenges.
Tooling and Mold Design Complexity
Getting it right is critical in mold making and micro molding. Even a tiny misalignment in the injection mold design can have a big impact on the quality of small plastic parts. When you’re micro molding liquid silicone rubber, you need even more precision when you mix materials, add colors, and dose accurately to make sure the process is stable and repeatable.
Building the mold is a big engineering challenge, mostly because of the mold design. The mold design has to have certain things in it to make sure the mold halves line up right and the part comes out right. The mold design also has to make sure the parts are good and the mold lasts a long time so you can make a lot of parts. That’s because a normal micro injection mold is supposed to make millions of parts before it’s done.
Material Flow and Injection Molding Parameters
Getting the material to flow right is key. The small size of the mold cavity and the thin walls of micro parts can make it tough to fill the mold right. You have to think about injection speed, pressure, temperature, and gate design to make sure the material flows the same way every time.
Balanced cavity pressure in micro injection molds makes sure the filling is the same every time. Good valve gate technology and a well-balanced cold plate keep you from getting short shots or not filling all the way. Cavity temperature affects how the material solidifies and how the part molds. Proper nozzle cooling helps you go from cooling during filling to heating during curing.
If you have the space, direct gating is the best. If you don’t have the space, you can use other types of gates like film gates, edge gates, or tunnel gates. Overflow helps make sure the part is completely filled and helps get rid of trapped air. Runners help you do things like slit, mark, print, package, and assemble, which makes your workflow better.
Quality Control and Inspection of Micro Components
Micro components are so small that it’s hard to see if they’re messed up or the right size. You might need special machines to take pictures of them or measure them to see if they’re messed up.
You also need to have really good quality control. That means you need to watch the process and use math to make sure you’re making good parts all the time.
Scalability and Output Considerations
While the technology is well suited for small-scale production of micro components, scaling up production can be challenging. In addition, the selection of suitable materials and the availability of sufficient quantities of raw materials also affect the scalability of the process.
Therefore, designers and engineers must carefully evaluate cycle time, mold durability, and machine capacity. This will help ensure efficient and cost-effective production of large volumes.
Conclusion
So, in conclusion, while traditional injection molding has its advantages, it may not be suitable for certain applications. This has led to the emergence of a more precise and compact solution called micro injection molding. Its many advantages and versatile applications make it a key part of many industries to effectively meet new market challenges.
If you want to make it in the world of micro molding, you need precision tooling, advanced technology, and optimized manufacturing processes. That’s where Zetar Mold comes in. We offer comprehensive injection molding services that use the latest technology to turn your ideas into reality. Our experienced engineering team will give you the confidence you need to know you’re getting the best manufacturing solution for your project.
Get in touch with us today to start your molding journey with Zetar Mold. Let’s work together to make your vision a reality!
-
Learn about The Role Of Mold Temperature In Injection Molding: Mold temperature refers to the surface temperature of the mold cavity and core. ↩
-
Learn about TYPES OF GATES FOR INJECTION MOLDING: The injection molding gate is the entry point for the molten plastic into the mold cavity. ↩
-
Learn about Warpage Analysis And Solutions | Injection Molding Defects: Warpage in injection molding refers to when the shape of the injection-molded product deviates from the shape of the mold cavity. ↩
-
Learn about Understanding Injection Speed And Injection Pressure: at the same injection speed, higher injection pressure improves the plastic’s flow capability…… ↩
-
Learn about Acrylic Injection Molding: Acrylic is a clear and commonly used injection molding plastic. ↩
-
Learn about What is core and cavity in injection molding : The core and cavity are the two halves of the mold. ↩
-
Learn about High-performance plastics : High performance plastics have ideal mechanical properties and high chemical stability. ↩
-
Learn about Mold Cavity: Types, Difference, Advantages : The mold cavity is a crucial component in the production of metal parts. ↩