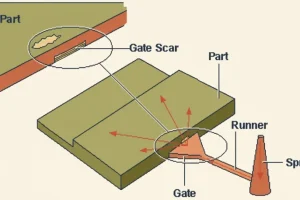
– Low-volume injection molding bridges the gap between 3D printing and mass production (100–10,000 units).
– Utilizing aluminum tooling or Master Unit Die (MUD) systems can reduce upfront costs by 40–60%.
– It allows for the use of production-grade thermoplastics, ensuring functional verification before scaling.
– Ideal for “bridge tooling” to accelerate time-to-market while steel molds are being fabricated.
What Is Small Batch Injection Molding?
Small batch injection molding, also referred to as малосерийное литье под давлением1 (LVIM), is a specialized manufacturing process designed to produce plastic parts in quantities ranging typically from 100 to 10,000 units. Unlike traditional high-volume molding, which prioritizes cycle time optimization over millions of cycles using hardened steel molds, LVIM prioritizes flexibility, low upfront capital expenditure (CapEx), and speed.
For startups, this method offers a critical "startup manufacturing solution2," allowing for market testing and functional validation using real engineering-grade materials—such as Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) or Polycarbonate (PC)—without the prohibitive cost of P20 or H13 steel tooling.
Low-volume injection molding allows for the use of the exact same engineering-grade resins as mass production.Правда
Unlike 3D printing which often uses simulants, LVIM uses standard thermoplastic pellets, ensuring identical mechanical and chemical properties to the final product.
Low-volume molding always requires lower per-unit costs than 3D printing regardless of quantity.Ложь
For extremely low quantities (e.g., under 50 units), industrial 3D printing is often cheaper due to the elimination of tooling costs entirely.
How Do Tooling Parameters Differ for Low Volume Production Runs?
To achieve cost efficiency, the parameters for low volume production runs differ significantly from mass production standards. The focus shifts from mold longevity to mold fabrication speed and cost.
| Параметр | Low-Volume (Soft Tooling) | High-Volume (Hard Tooling) | Примечание |
|---|---|---|---|
| Материал пресс-формы | Aluminum (7075-T6) or Pre-hardened Steel (P20) | Hardened Steel (H13, S7, 420 SS) | Aluminum machines 2x-3x faster than steel. |
| Expected Mold Life | 1,000 – 10,000 shots | 100,000 – 1,000,000+ shots | Soft tooling degrades faster under high pressure/abrasive glass fibers. |
| Каналы охлаждения | Straight, simple lines | Conformal, complex circuits | Simple cooling reduces mold cost but may extend cycle time slightly. |
| Автоматизация | Manual insert loading / Part removal | Fully automated / Robot extraction | Manual operation removes the need for expensive ejection automation design. |
| Допуски | ±0.127 mm (±0.005 in) | ±0.050 mm (±0.002 in) | Tighter tolerances require EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), increasing cost. |

What Are the Strategic Steps for Short Run Molding?
Реализация short run molding cost3 strategy requires a shift in the Проектирование для производства (DFM)4 approach.
-
Material Selection & Verification:
Choose the final production resin. If the goal is on-demand manufacturing, ensure the material is readily available in smaller quantities (some suppliers have high Minimum Order Quantities or MOQs). -
Simplified DFM Analysis:
Modify part geometry to remove complex undercuts or side-actions.- Strategy: Use "shut-offs" (where mold faces meet) to create holes rather than sliding cores. Sliding cores increase tooling costs by 15-30%.
-
Tooling Fabrication (CNC vs. EDM):
Opt for Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining over Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) wherever possible. CNC is faster and cheaper for cutting aluminum molds. -
Master Unit Die (MUD) Implementation:
Utilize a MUD system. This involves a standard mold base frame that sits in the press, where only the smaller core and cavity inserts are custom-machined. This allows you to pay only for the inserts, not the entire mold base. -
Нет. Качество детали (размеры, чистота поверхности, свойства материала) идентично серийному производству. "Низкая" относится только к долговечности инструмента и количеству произведённых деталей, а не к точности детали.
Even in low volume, T0 (first shots) samples are critical. Review for flash, sink marks, or warpage. Since the mold is softer, modifications (removing metal) are easier than with hardened steel.
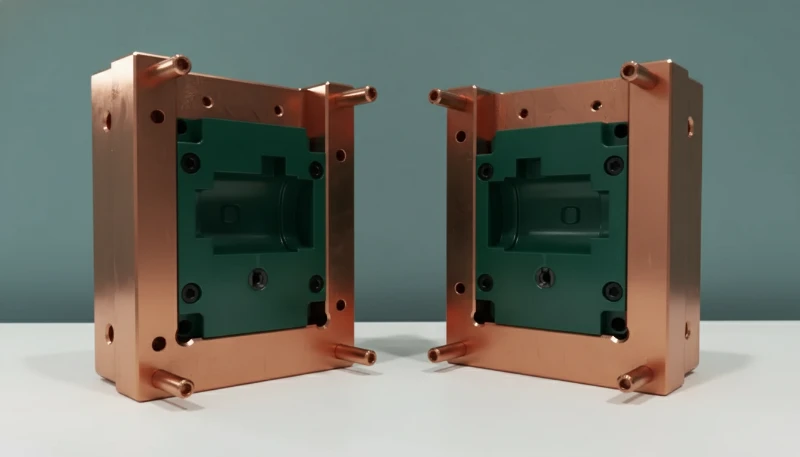
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Low-Volume Molding?
| Характеристика | Преимущества | Недостатки |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Structure | Tooling costs are 40-60% lower than production steel molds. | Per-unit price is higher due to amortization of setup fees over fewer parts. |
| Time-to-Market | Molds can be cut in 5-15 days. | Slower than 3D printing (which takes hours/days). |
| Качество | Production-grade surface finish (SPI standards) and material properties. | Aluminum molds are susceptible to damage if mishandled; limits use of abrasive glass-filled nylons. |
| Гибкость | Design changes are cheaper to implement in aluminum. | Not suitable for high-volume scaling without building new tooling. |
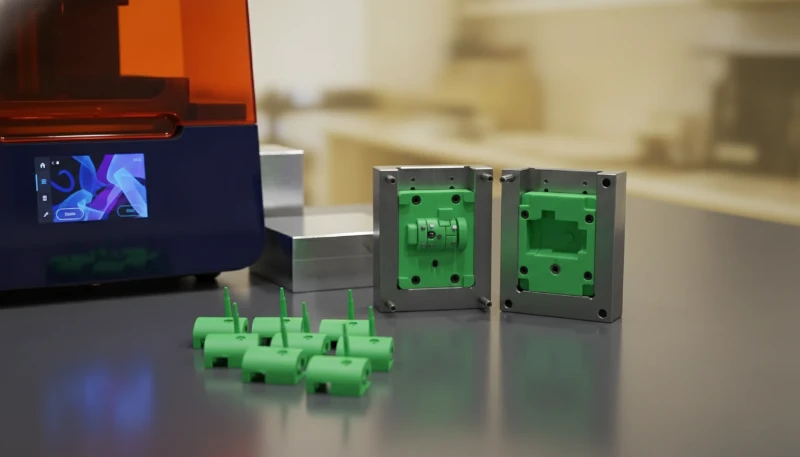
What Strategies Can Optimize On-Demand Manufacturing Costs?
To maximize the value of производство по требованию5, technical buyers should leverage specific design and procurement strategies.
- Use Standard Mold Bases: Request standard ISO or MUD bases. Avoiding custom mold bases saves significant steel costs and shipping weight.
- Texturing Hierarchy: Avoid chemical etching for texturing on low-volume molds unless necessary. Bead blasting is a cheaper alternative that provides a matte finish sufficient for non-cosmetic parts.
- Family Molds: If you require multiple small parts (e.g., a housing top and bottom) made of the same material, use a family mold. This places multiple different cavities in one mold base, producing a full set of parts in a single cycle.
- Surface Finish Rationalization: Do not specify an SPI-A2 (high polish) finish if SPI-B3 (paper finish) or SPI-C1 (stone finish) will suffice. Polishing is labor-intensive and costly.
Aluminum molds offer superior heat dissipation compared to tool steel, potentially reducing cycle times.Правда
Aluminum's thermal conductivity is roughly 4-5 times higher than tool steel, allowing parts to cool and eject faster, which benefits cycle time.
You cannot use abrasive materials like Glass-Filled Nylon (PA66-GF30) in low-volume aluminum molds.Ложь
You can use abrasive materials, but the mold life will be significantly reduced (e.g., down to 500-1,000 shots) due to faster erosion of the gate and runner systems.
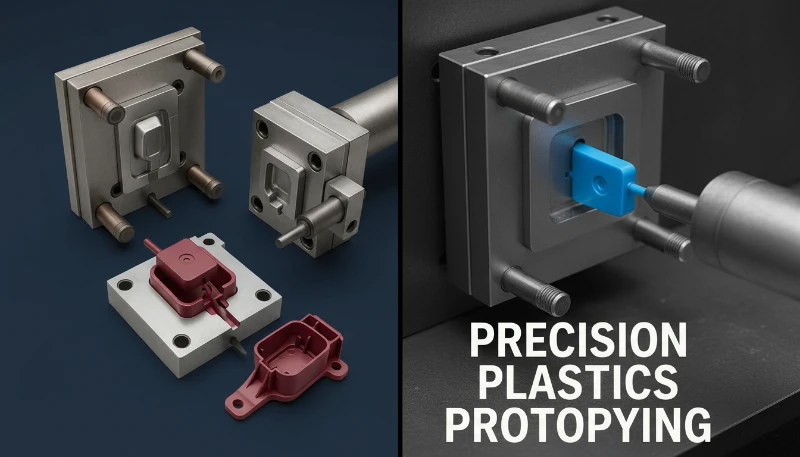
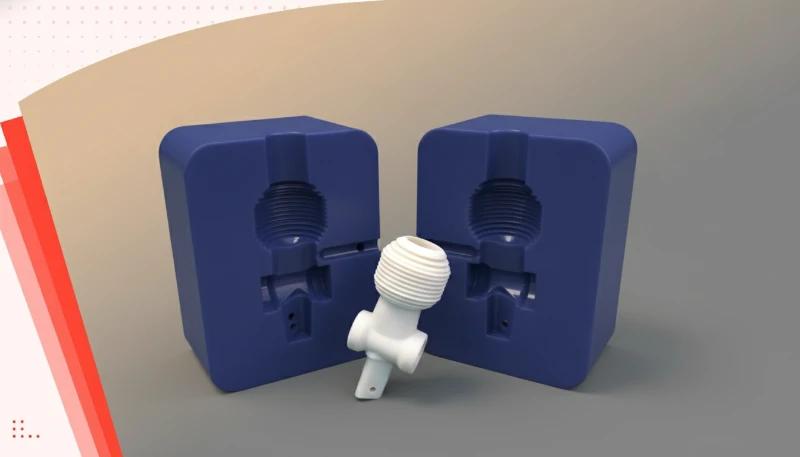
Where Is Low-Volume Injection Molding Applied?
- Medical Device Clinical Trials: Producing ISO 13485 compliant parts6 for testing before committing to Class 101 production molds.
- Automotive Aftermarket: Creating replacement clips, housings, or gears for discontinued vehicle models where demand is finite.
- IoT Hardware Startups: Launching a beta version of a consumer electronic device (1,000 units) for Kickstarter backers.
- Bridge Tooling: Running production on soft tooling to supply the assembly line while waiting 8-12 weeks for the high-capacity hardened steel mold to be completed.

Часто задаваемые вопросы (FAQ)
Q1: What is the typical crossover point between 3D printing and small batch injection molding?
Generally, once you exceed 50–100 units, injection molding becomes more cost-effective than industrial SLA or SLS 3D printing, primarily because the material cost of injection molding pellets is significantly lower than printing resins.
Q2: Can low-volume aluminum molds be used for high-temperature materials7 like PEEK?
Yes, but with caution. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) requires high mold temperatures (160°C+). Aluminum can handle this, but thermal expansion must be calculated carefully to maintain tolerances, and the mold life will be short.
Q3: How long does it take to manufacture a low-volume mold?
Lead times for startup manufacturing solutions involving simple aluminum tooling8 are typically 2 to 4 weeks, compared to 8 to 12 weeks for complex steel production molds.
Q4: Does "low volume" mean lower quality?
No. The part quality (dimensions, surface finish, material properties) is identical to mass production. The "low" refers only to the durability of the tool and the quantity produced, not the part fidelity.
Узнайте, как алюминиевая оснастка может значительно снизить первоначальные затраты и повысить эффективность производства.
If demand exceeds the life of the soft tool, you must invest in a hard steel mold. However, the aluminum mold served its purpose by validating the design and funding the expensive mold through initial sales.
Резюме
Is low-volume injection molding cost-effective for your startup? Yes, provided your production needs fall within the 100 to 5,000 unit window. By utilizing aluminum tooling, simple cooling strategies, and производство по требованию principles, startups can achieve production-grade quality at a fraction of the traditional tooling cost. This approach mitigates risk, allowing for design iteration and market validation before significant capital is tied up in steel tooling.
-
Explore how low-volume injection molding can provide cost-effective solutions for startups looking to validate their products. ↩
-
Find out how startup manufacturing solutions can help new businesses test their products effectively. ↩
-
Explore the key factors that influence the costs associated with short run molding. ↩
-
Learn how DFM can optimize the manufacturing process and reduce costs. ↩
-
Find out how on-demand manufacturing can provide flexibility and cost savings for startups. ↩
-
Learn about the importance of ISO 13485 compliance in medical device manufacturing. ↩
-
Understand the considerations when working with high-temperature materials like PEEK in molding. ↩
-
Learn how aluminum tooling can significantly lower upfront costs and improve production efficiency. ↩