– MUD inserts significantly reduce tooling costs by sharing a common mold base (frame).
– Design For Manufacturing (DFM) must strictly adhere to the specific “real estate” limits of the chosen MUD frame series (e.g., 08/09, 84/90).
– Cooling layouts are the primary constraint; water lines must route within the insert without interfering with the standardized frame mounting or ejection.
– Gating options are restricted by the fixed sprue location of the Master Unit Die frame.
What is a Master Unit Die (MUD) Insert?
A Master Unit Die (MUD) system involves a standard, reusable mold frame (the "master" base) that remains in the injection molding machine, and interchangeable "companion" inserts that contain the cavity and core geometry. This approach allows manufacturers to swap only the inserts rather than the entire heavy mold base, facilitating rapid changeovers (often under 10 minutes) and reducing tooling costs1 by up to 66%.
However, designing for MUD requires a different approach than standalone custom mold bases. Engineers must fit all mechanical requirements—cooling, ejection, and parting locks—within a strictly defined volumetric envelope.
MUD Insert Quick Specifications
| Cecha | Opis |
|---|---|
| Component Name | Master Unit Die (MUD)2 Insert / Quick-Change Insert |
| Primary Standard | DME Standard (North America), HASCO (Europe equivalents) |
| Material Commonality | P20, 718H, NAK80, H13, S7, or Aluminum (QC-10) for prototypes |
| Typical Cost Savings | 40%–60% vs. Standard Mold Base |
| Changeover Time | 5–10 minutes |
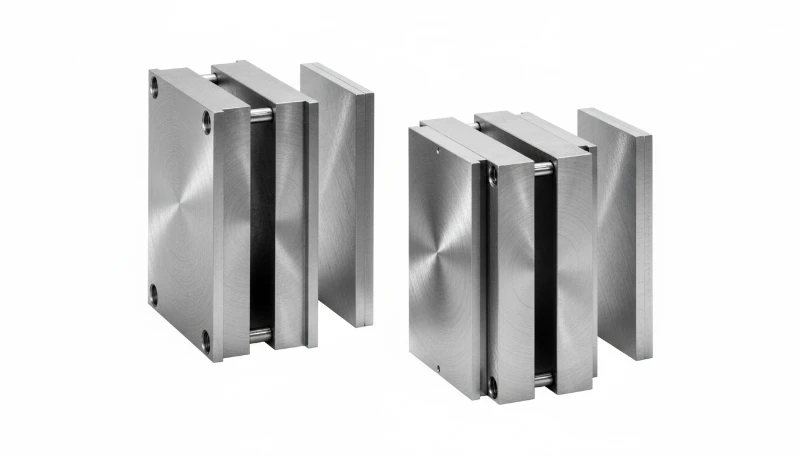

What are the Standard MUD Insert Dimensions and Constraints?
When executing MUD mold design guide3 principles, the first step is selecting the correct frame series. The insert must fit within the pocket of the frame. The table below outlines the most common MUD frame series and their dimensional constraints.
Common MUD Frame Series and Constraints Table
| Frame Series | Appx. Insert Size (w x l) | Max Part Depth | Typical Clamp Tonnage | Najlepsze dla |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08/09 (U-Frame) | 8.375" x 9.0" | 2.50" | 30–75 Tons | Small precision parts, micro-molding, single cavity. |
| 84/90 (T-Style) | 8.4" x 9.0" | 3.00" | 50–110 Tons | Standard small components, 1–2 cavities. |
| 10/12 (H-Frame) | 10.0" x 12.0" | 3.50" | 75–150 Tons | Medium parts, multi-cavity small parts. |
| 11/14 (Double) | (2) 11.0" x 14.0" | 4.00" | 150–250 Tons | High-volume production with dual inserts. |
Uwaga: Dimensions listed are nominal. Designers must consult specific vendor CAD data for exact usable "steel safe" areas, as mounting bolt locations reduce the effective cavity area.
MUD inserts allow for unlimited cooling channel placement because the frame is external.Fałsz
MUD inserts have severe cooling constraints because water lines must enter/exit through specific clearance areas to avoid the frame structure and ejector system.
Standardizing on a specific MUD frame series reduces setup time and inventory complexity.Prawda
Using a consistent frame size (e.g., all 08/09) allows a factory to keep the frame in the press and only swap inserts, maximizing uptime.
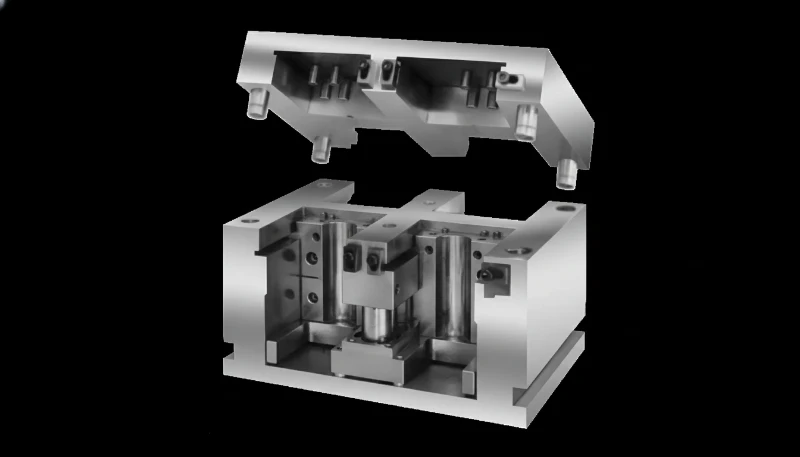
How Should Part Geometry be Optimized for MUD Frames?
Injection molding design constraints for MUD systems differ from standard tooling. The goal of DFM for MUD is to ensure the part fits the insert without compromising structural integrity or cooling efficiency.
Step-by-Step Optimization Process
- Establish the "Live" Area:
Determine the usable steel area. Subtract the space required for the mounting rails (usually 0.5" to 1.0" on the sides) and leader pin bushings. The part cavity must sit centrally to balance injection pressure. - Verify Ejection Stroke:
MUD frames have fixed ejector plate travel. Ensure the part requires an ejection stroke less than the frame’s maximum limit (e.g., an 08/09 frame may limit ejection to 1.5 inches). If the part is deeper, it cannot run in that MUD frame. - Check Cooling Line Access:
Unlike custom molds where water manifolds can be placed anywhere, MUD inserts4 usually require water lines to enter and exit from the top or bottom of the insert (vertical orientation). Side access is often blocked by the master frame rails. - Steel Safe Wall Thickness:
Ensure there is at least 0.5" to 0.75" of steel between the cavity edge and the insert edge to prevent "blowing out" the side of the insert under high injection pressures.

What are the Best Gating Strategies for MUD Inserts?
Gating for MUD requires strategic planning because the sprue bushing location is fixed in the master frame. You cannot move the sprue to a different location relative to the machine nozzle.
1. Edge Gating (Most Common)
- Design: The runner travels from the center sprue (in the frame) to the parting line of the insert.
- Constraint: The runner system consumes valuable cavity space.
- Najlepsze dla: Flat parts, multi-cavity layouts.
2. Sub-Gating (Tunnel Gates)
- Design: Self-shearing gates that tunnel below the parting line.
- Constraint: Requires sufficient vertical space (Z-height) in the insert for the runner to flex and eject. If the MUD insert is too thin, the runner may stick.
- Najlepsze dla: Automatic operation without operator gate trimming.
3. Hot Tip / Hot Sprue
- Design: Direct injection into the part or runner.
- Constraint: While possible, integrating hot runner manifolds into small MUD inserts is complex and expensive, negating the low-cost benefit of MUD. Single hot drops are feasible but require careful wire routing through the frame.
- Najlepsze dla: High-volume medical or consumer electronics parts.
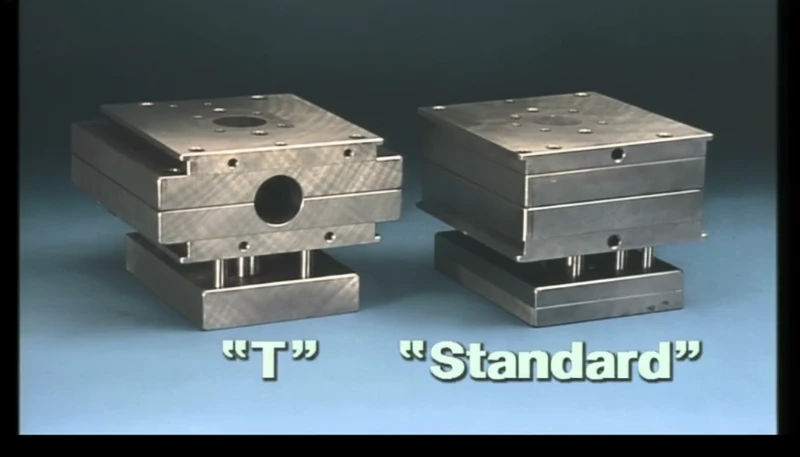

What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using MUD Inserts?
To determine if MUD insert dimensions and limitations fit your project, review this comparative analysis.
| Cecha | Zalety | Wady |
|---|---|---|
| Koszt | Insert costs are 50–66% lower than full mold bases (only buying cavity/core steel). | Initial purchase of the Master Frame is required (one-time cost). |
| Czas realizacji | Faster machining; inserts are stock items and easy to handle (CNC time reduced). | Limited by the availability of the specific frame size in the shop. |
| Przechowywanie | Inserts are small and lightweight; shelves can hold dozens of tools. | Lost parts risk; small inserts are easier to misplace than 500lb molds. |
| Wydajność | Quick changeovers increase machine uptime. | Cooling limitations: Difficult to achieve conformal cooling or complex baffles in tight spaces. |
MUD inserts are strictly for prototyping and cannot handle production volumes.Fałsz
MUD inserts made from hardened steel (H13/S7) run millions of cycles; the system is standard for high-mix, low-volume production as well as mass production of small parts.
Using MUD inserts requires verifying that the injection machine's ejector pattern matches the MUD frame.Prawda
The MUD frame connects to the machine ejection; if the pattern (knockout holes) doesn't align, the ejection system will not function.
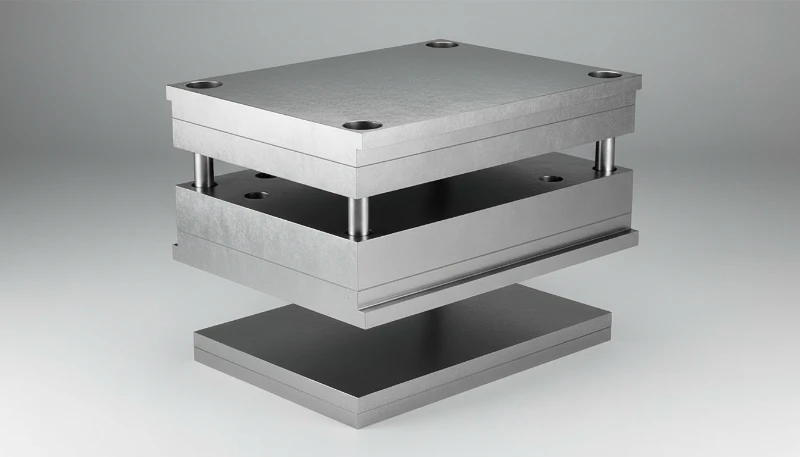

When Should Manufacturers Use MUD Systems?
The decision to use a MUD system is usually driven by part size and production volume mix.
1. Prototyping and Pilot Runs
For NPI (New Product Introduction), using an aluminum MUD insert allows for testing geometry with minimal investment. If the design fails, only the small insert is scrapped, not a whole mold base.
2. High-Mix, Low-Volume Production
Facilities producing hundreds of different SKUs in small batches (e.g., 500–5,000 parts per run) benefit most. The 5-minute changeover time reduces the downtime penalty usually associated with short runs.
3. Family Molds
Different versions of a similar part (e.g., Left and Right buttons) can be run by simply swapping the cavity insert while keeping the same runner profile in the frame.
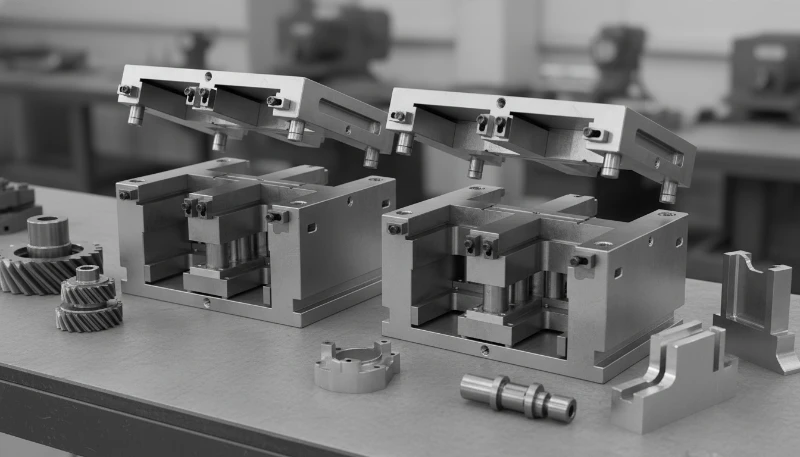

What Practical Troubleshooting Tips Apply to MUD Mold Design?
Experienced mold designers use the following "insider" strategies to avoid common pitfalls in MUD tooling.
- The "Water Jumper" Problem: In MUD frames, water lines often need to "jump" from the A-side to the B-side externally. Wskazówka: Use recessed quick-disconnect fittings or counterbore the hose channels so they do not get crushed when the mold closes or during storage.
- Support Pillars are Missing: MUD frames often lack the central support pillars found in custom mold bases. Wskazówka: If the part has a large projected area, calculate the deflection carefully. You may need to add localized support pillars within the insert itself if space permits, or reduce injection pressure.
- Guide Pin Wear: Because the frame stays in the press, the leader pins and bushings wear out over years of use, affecting the alignment of new inserts. Wskazówka: Implement a PM (Preventative Maintenance) schedule to replace frame bushings every 50,000 cycles or annually.
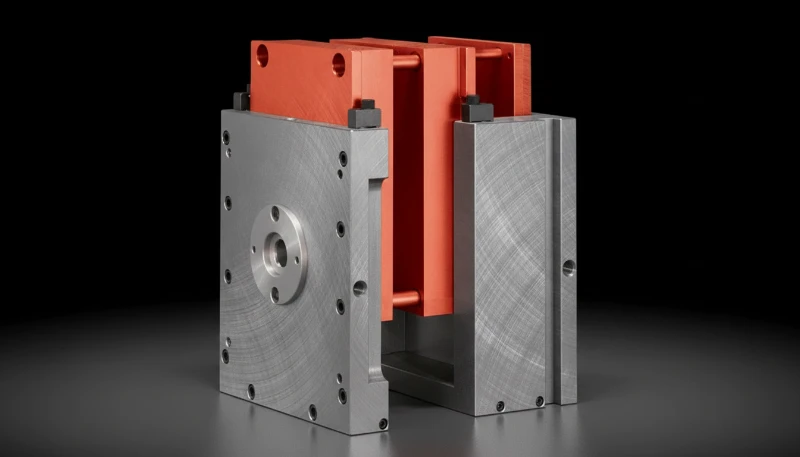

FAQ: Common Questions about MUD Mold Design
Q: Can I use a 3-plate mold design5 with a MUD frame?
A: Generally, no. Standard MUD frames are 2-plate systems. While complex custom modifications can simulate 3-plate stripping, it defeats the "standard and cheap" purpose of MUD.
Q: Are MUD inserts limited to aluminum?
A: No. MUD inserts can be machined from any tool steel, including P20, H13, S7, or Stainless Steel (420SS). The material choice depends on the resin abrasiveness and target cycle count.
Q: What is the maximum temperature for MUD inserts?
A: This depends on the frame. Standard frames handle typical engineering plastics (up to 250°C/480°F). For high-temperature materials like PEEK, the frame requires insulation boards to prevent heat transfer to the machine platens.
Q: Can I use slides and lifters in a MUD insert?
A: Yes, but space is the limiting factor. Mechanical slides must fit within the insert boundaries and not extend beyond the frame rails when the mold is open. Hydraulic slides are difficult to implement due to space.
Q: How does MUD gating differ from conventional gating?
A: The sprue location is fixed. You cannot move the sprue bushing. Therefore, your runner design must always route from that fixed center point to your cavities, which may result in longer runners for off-center parts.
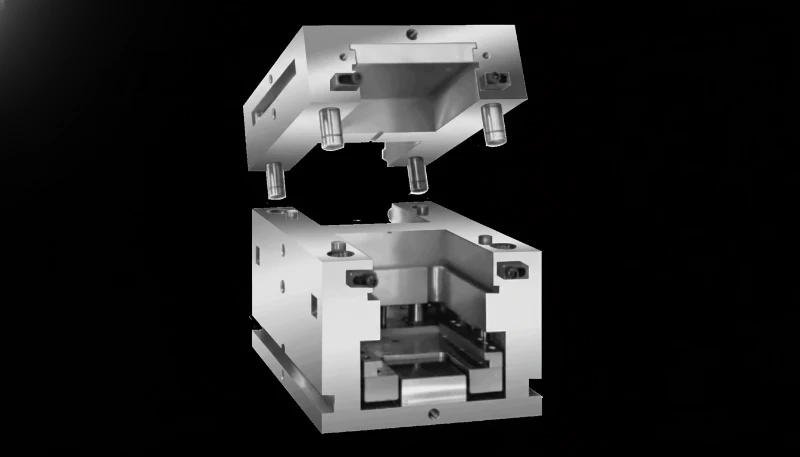

Wnioski
Master Unit Die (MUD) systems offer a powerful solution for reducing tooling costs and shortening lead times, but they impose strict physical boundaries on the designer. By adhering to MUD mold design guide best practices—specifically respecting the MUD insert dimensions, optimizing cooling within tight spaces, and verifying ejection limits—manufacturers can leverage this system for both prototyping and long-term production. The key to success lies in early DFM for MUD analysis, ensuring the part geometry fits the "real estate" of the standard frame before steel is cut.
-
Explore strategies for minimizing tooling costs in manufacturing, including the use of MUD systems. ↩
-
Get insights into the MUD system and how it revolutionizes the injection molding process. ↩
-
Explore essential guidelines for effective MUD mold design to ensure successful manufacturing. ↩
-
Explore how MUD inserts can significantly reduce tooling costs and improve efficiency in manufacturing. ↩
-
Explore the features and benefits of 3-plate mold designs in injection molding. ↩