– A MUD (Master Unit Die) system separates the mold into a shared standard frame and interchangeable component inserts.
– This modular tooling approach reduces initial capital costs by 50–70% by eliminating the need to purchase a custom mold base for every project.
– Quick change mold systems allow for insert swaps in as little as 5–10 minutes, significantly reducing downtime compared to standard tool changes.
– MUD inserts are ideal for prototyping, bridge tooling, and low-to-medium volume production runs but have size and cooling limitations.
What is the Definition of a MUD Mold System?
A MUD (Master Unit Die)1 mold is a standardized modular tooling system used in injection molding that separates the mold into two distinct functional units: a reusable "master frame" and interchangeable "inserts."
In traditional injection molding basics, a standard mold is a standalone unit comprising a structural base, cooling system, ejection system, and the cavity/core. Conversely, the MUD insert definition2 refers specifically to the removable steel blocks containing the part geometry (cavity and core) and local ejection plates. These inserts slide into the master frame, which remains bolted to the injection molding machine platens.
Originally popularized by DME (Detroit Mold Engineering), the term "MUD" has become the industry standard descriptor for this type of quick-change technology, similar to how "Kleenex" refers to tissues.
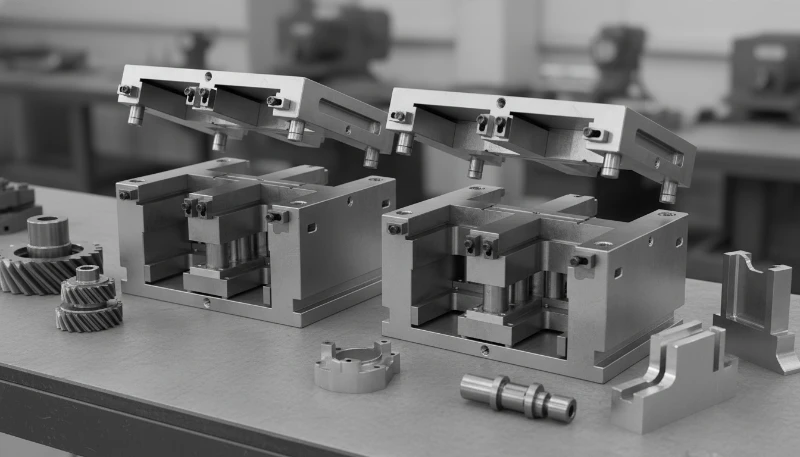

How is the MUD Architecture Structured?
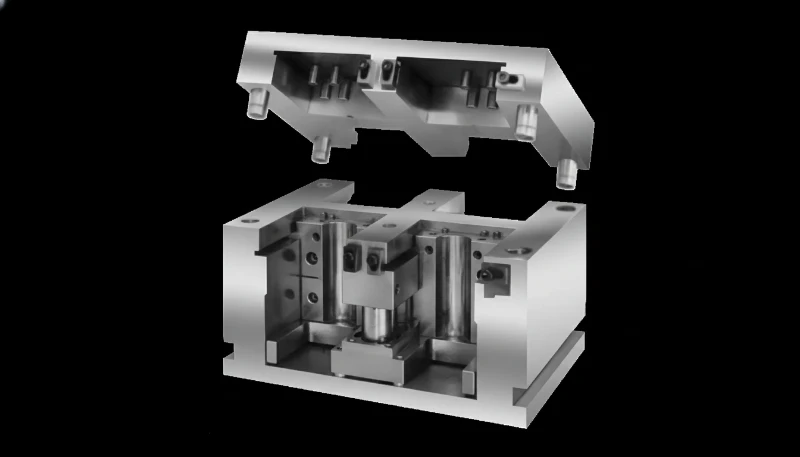
To understand what is a MUD mold, one must identify its structural hierarchy. The system relies on precise mating surfaces to ensure the insert withstands injection pressures ranging from 5,000 to 30,000 psi (34 to 207 MPa).
1. The Master Frame3 (Chassis)
The frame is the "skeleton" that remains in the machine. It provides the interface with the molding machine’s clamp and ejector system.
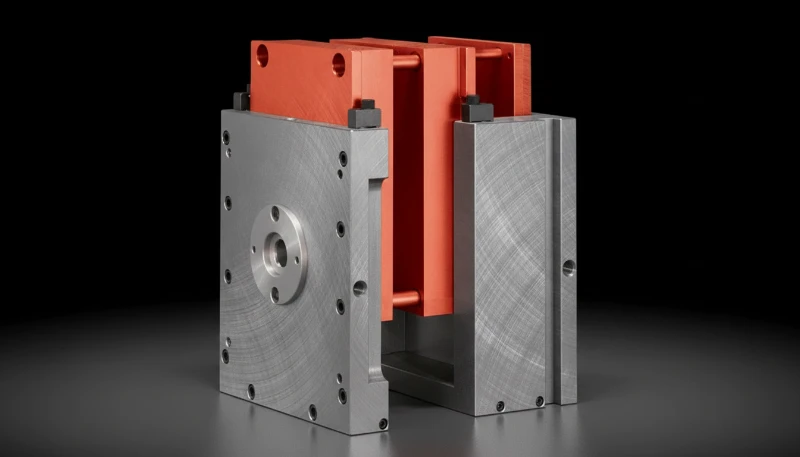
- U-Frame: Designed to hold a single insert.
- H-Frame: Designed to hold two inserts side-by-side (Double H-Frame) or four inserts (Quad Frame), allowing for simultaneous molding of different parts if materials and cycle times align.
2. The Companion Insert
The insert contains the "heart" of the mold:
- A-Plate: Contains the cavity (stationary side).
- B-Plate: Contains the core (moving side).
- Ejector Package: A localized set of ejector plates and pins integrated into the insert, which couples with the master frame’s ejection bar.
What are the Technical Parameters of MUD Systems?
The following table outlines standard industrial specifications for quick change mold systems4. Note that specific values may vary based on the manufacturer (e.g., DME, HASCO, STRACK).
| Parametr | Standard Specification Range | Uwagi |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Frame Material | Pre-hardened Steel (e.g., AISI 4140) | Designed for long-term durability and repeated sliding friction. |
| Insert Material Options | Aluminum (7075-T6), P20, H13, S7 | Material choice depends on volume (Alum for <5k, S7 for >500k). |
| Typical Changeover Time | 5 to 15 minutes | Requires "warm swap" procedures (leaving water connected to frame). |
| Insert Size Standard | 08/09 Series (approx. 8" x 9") to 18/20 Series | Larger frames exist but reduce the ergonomic advantage of hand-loading. |
| Tolerance Capabilities | +/- 0.002 in (0.05 mm) | Slightly looser than Class 101 tools due to frame-to-insert fitment. |
| Cooling Connections | Integrated or Direct Plumbed | Water lines can route through the frame (risk of leaks) or directly to inserts. |
MUD frames are universally compatible, meaning an insert built for a DME frame will fit a HASCO or proprietary frame without modification.Fałsz
MUD systems are proprietary standards. While functional concepts are identical, bolt patterns, slide geometries, and ejector coupling mechanisms differ between brands.
MUD inserts reduce raw material consumption because the molder reuses the heavy structural steel of the frame for multiple projects.Prawda
By reusing the mold base (which constitutes roughly 50-70% of a tool's total weight), the consumption of high-grade tool steel is significantly lowered.
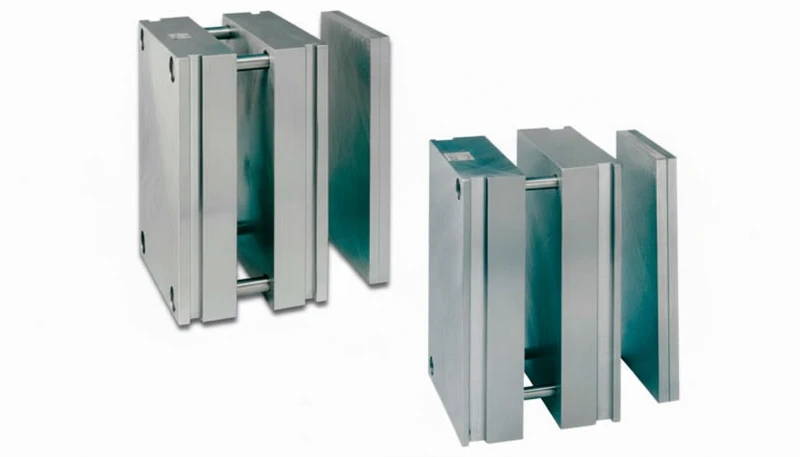

How Does the Quick Change Installation Process Work?
The efficiency of a quick change mold system lies in its installation procedure. Unlike standard molds that require an overhead crane for every changeover, MUD inserts are often light enough to be changed by hand or with a small lift assist.
- Machine Stop: The injection molding cycle is stopped, and the clamp is opened to the service position.
- Clamp Loosening: The technician loosens the mechanical clamps (often typically 2–4 bolts or a toggle system) holding the insert into the H-Frame or U-Frame.
- Ejector Decoupling: The ejector system is disconnected (unless using a spring-loaded return system native to the insert).
- Removal: The existing insert is slid out of the frame laterally.
- Insertion: The new MUD insert is slid into the frame. Guide rails ensure proper alignment.
- Lock and Load: Clamps are tightened, and the machine is ready to heat up the new tool.
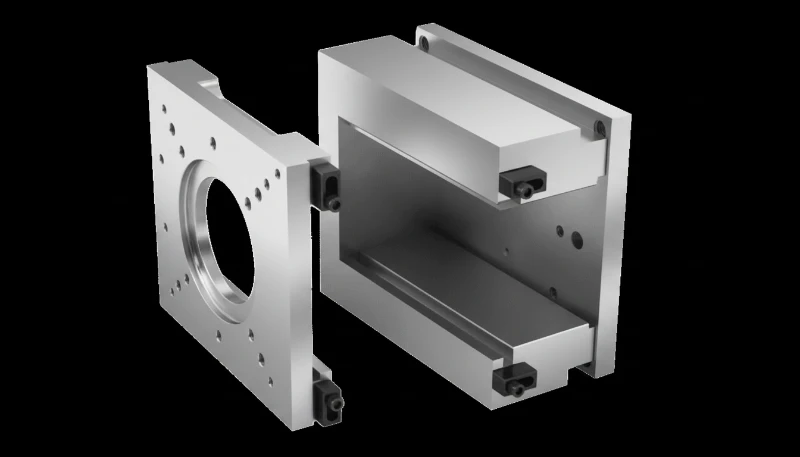
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Modular Tooling?
A balanced view of modular tooling reveals that while cost-effective, it is not a universal solution for all molding projects.
| Advantages (Pros) | Disadvantages (Cons) |
|---|---|
| Lower Tooling Cost: Clients only pay for the cavity/core fabrication, saving 40–60%. | Restricted Geometry: Limited space for complex slides, lifters, or hydraulic core pulls. |
| Prędkość: Production can begin weeks earlier as there is no need to order and machine a standard mold base. | Ograniczenia rozmiaru: Not suitable for large automotive parts or housings exceeding the frame dimensions. |
| Inventory Efficiency: Storing 10 inserts takes up the space of 1 standard mold base. | Cooling Constraints: Cooling channels are limited by the insert size, potentially extending cycle times. |
| Elastyczność: Ideal for "family molds" where different versions of a product are run on the same machine. | Ownership Ambiguity: The molder usually owns the Frame; the client owns the Insert. Transferring tooling requires the new molder to have a compatible frame. |

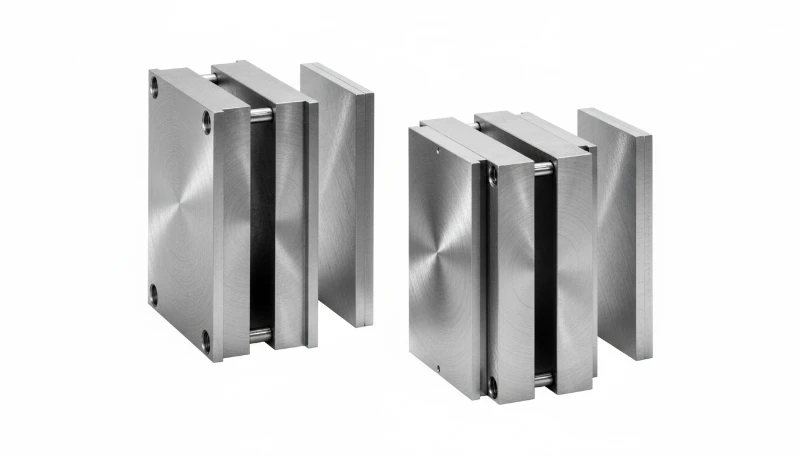
Where is MUD Tooling Most Effectively Applied?
To maximize Return on Investment (ROI), MUD inserts should be deployed in specific scenarios:
- Prototyping & Pilot Runs: When you need 50–1,000 real injection-molded parts (not 3D printed) for functional testing.
- Bridge Tooling: Production of parts to meet immediate market demand while a high-cavitation Class 101 production mold is being built.
- Low-Volume / High-Mix Production: Medical devices or specialized electronics where annual volumes are under 50,000 units.
- Marketing Samples: Creating multiple texture or logo variations of the same part geometry to test consumer preference.
MUD inserts are restricted to prototyping and cannot be used for production runs exceeding 10,000 cycles.Fałsz
If machined from hardened steel like H13 or S7, a MUD insert can easily withstand hundreds of thousands of cycles, provided the frame is maintained.
Using a MUD system allows for 'blind' tooling quotes, where the exact machine size does not need to be known immediately.Prawda
Because MUD frames are standardized to specific machine tonnage ranges, quoting an insert often requires less immediate compatibility checking than a full custom base.

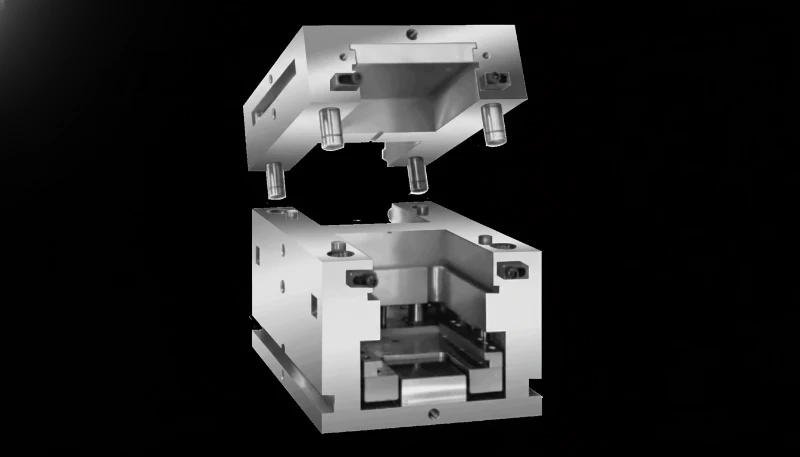
Frequently Asked Questions About MUD Inserts
1. What does "MUD" actually stand for?
MUD stands for Master Unit Die. It is the trademarked name from DME that has become the generic industry term for frame-and-insert modular tooling systems.
2. Can I run high-temperature materials in a MUD mold?
Yes, but with caution. Materials like PEEK or PPS require high mold temperatures (>150°C). You must ensure the MUD frame is equipped with appropriate insulation plates to prevent heat transfer to the machine platens, and that thermal expansion does not seize the insert in the frame.
3. Are MUD inserts cheaper than standard molds?
Yes. Typically, a MUD insert costs 30% to 60% less than a complete standalone mold because you are not purchasing the mold base, leader pins, bushings, or clamp plates—only the cavity and core steel.
4. Can I use a MUD insert for a 3-plate mold design?
It is difficult and rare. MUD systems are primarily designed for 2-plate open/close actuation. While some complex custom frames exist, standard MUD applications are best suited for conventional 2-plate molding.
5. How does water cooling work on a MUD insert?
There are two methods:
- Through the Frame: Water lines connect to the frame and seal against the back of the insert (requires O-rings).
- Direct Plumbed: Water hoses connect directly to the insert itself. This is safer against leaks but slightly slows down the changeover process.

Podsumowanie
A MUD insert is a cornerstone of modern, agile manufacturing. By decoupling the molding geometry from the structural frame, this quick change mold system offers a compelling balance of speed and economy. While it may not replace dedicated tooling for high-volume, complex automotive parts, it remains the industry standard for prototyping, bridge tooling, and cost-conscious low-volume production. Understanding what is a MUD mold empowers buyers and engineers to select the right tooling strategy, minimizing risk and maximizing budget efficiency.
-
Explore this link to understand the foundational concept of MUD systems and their significance in modern manufacturing. ↩
-
Understanding the definition of MUD inserts is crucial for anyone involved in injection molding and tooling. ↩
-
Explore the importance of the Master Frame in MUD systems and how it interacts with inserts during production. ↩
-
Discover how quick change mold systems can minimize downtime and enhance productivity in manufacturing processes. ↩