Punti di forza
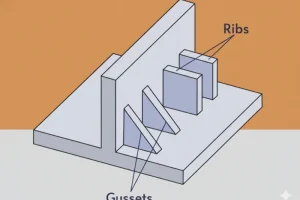
Ribs are structural features used to increase part stiffness without increasing overall wall thickness. However, improper rib design significantly impacts **Mold Flow** (causing hesitation or short shots) and **Cooling Efficiency** (creating thermal mass that leads to sink marks and extended cycle times). The optimal rib thickness is generally **40% to 60%** of the nominal wall thickness to balance structural integrity with manufacturability.
What Is the Definition of Rib Design in Injection Molding contexts?
Costole are thin, blade-like features protruding from the nominal wall of a part, designed to add bending stiffness and strength. In the context of Mold Flow, ribs act as flow channels that can either facilitate material distribution or cause "flow hesitation" depending on their geometry and placement. Regarding Raffreddamento, the intersection of a rib and a wall creates a localized thick section, often referred to as a "thermal hotspot," which dictates the required cooling time and influences the formation of cosmetic defects like sink marks.
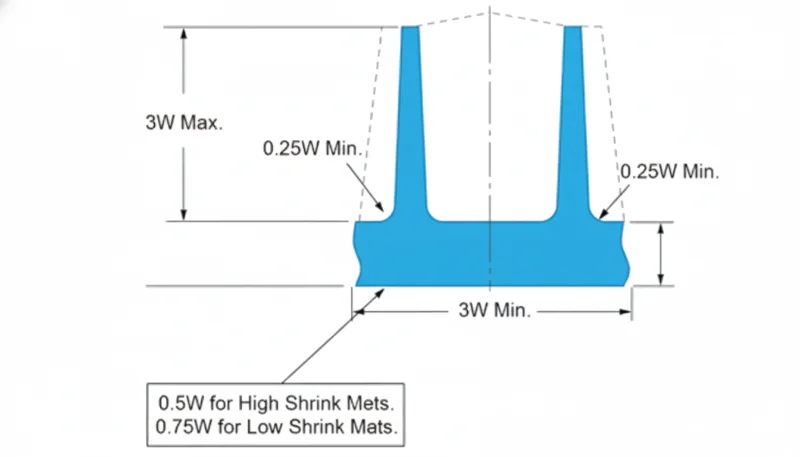
Ideally, rib thickness should be maintained between 40% and 60% of the adjacent nominal wall thickness to prevent cosmetic defects.Vero
Keeping ribs thinner than the main wall prevents excessive material accumulation at the intersection, significantly reducing the risk of sink marks and voids.
Making a rib the same thickness as the main wall is the best way to maximize part strength without side effects.Falso
Equal thickness creates a heavy mass at the intersection, leading to severe sink marks, internal voids, and significantly increased cooling times due to heat retention.
Key Parameters for Rib Design Optimization
The following parameters are critical for ensuring smooth filling patterns and uniform cooling.
| Parametro | Valore/intervallo consigliato | Impact on Mold Flow | Impact on Cooling |
|---|---|---|---|
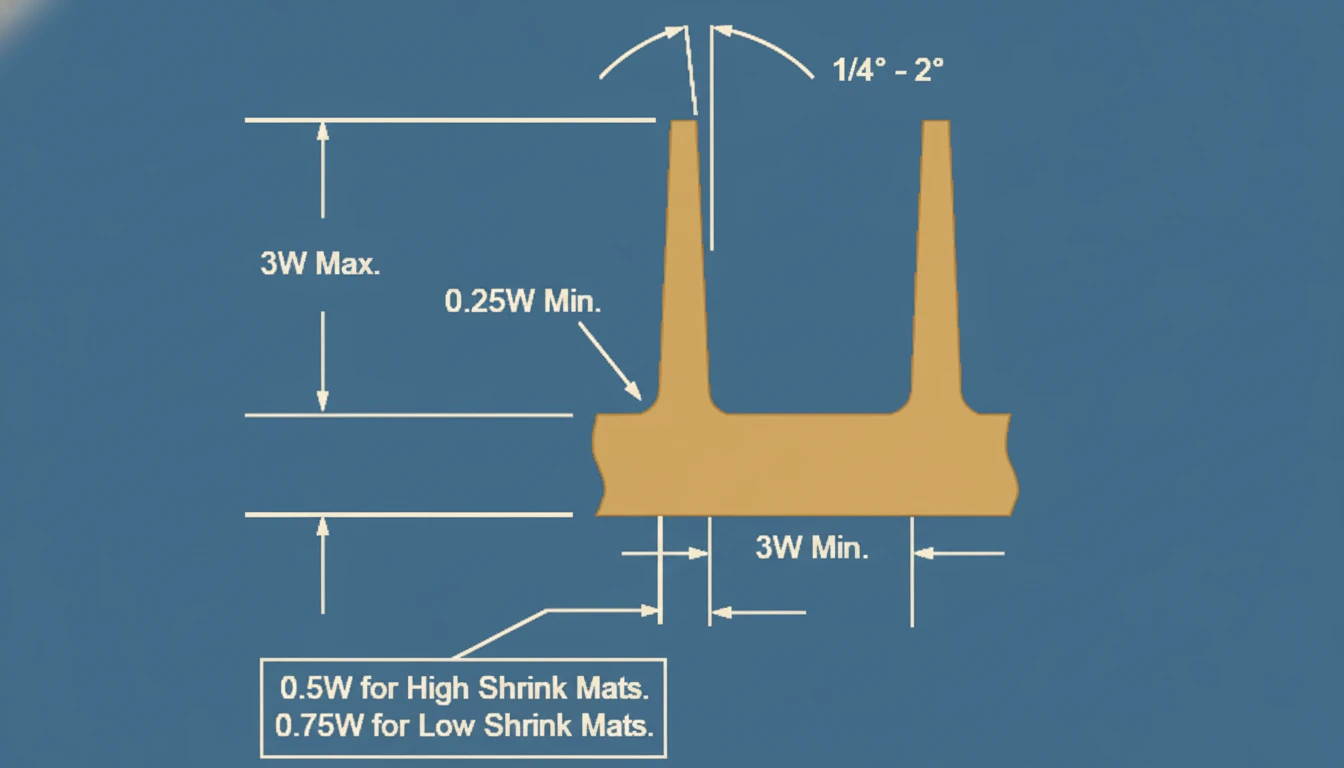
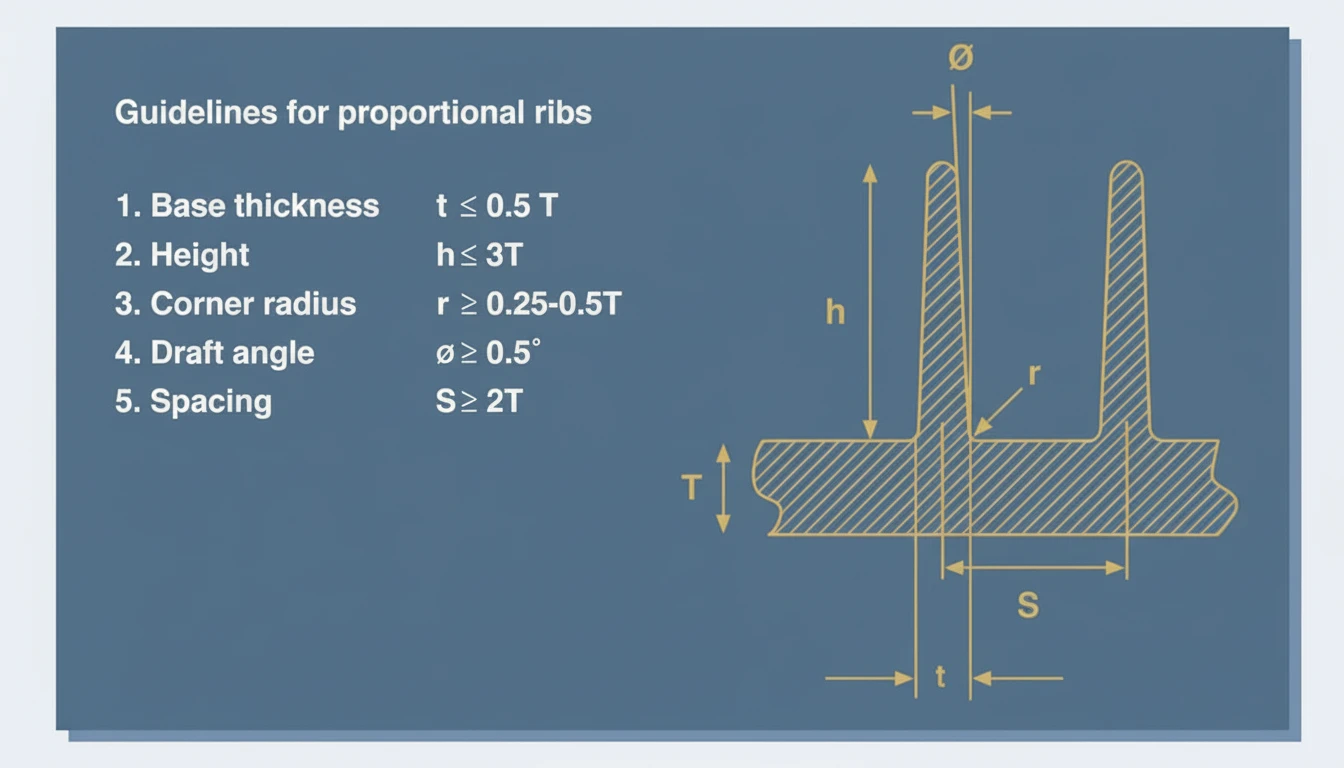
| Rib Thickness (t) | 40% – 60% of Nominal Wall (T) | Thin ribs may cause flow hesitation1; thick ribs improve flow but risk defects. | Thicker ribs increase local mass, requiring longer cooling to prevent sink marks. |
| Rib Height (H) | ≤ 3.0 × Nominal Wall (T) | Excessive height increases injection pressure requirements and may lead to gas traps (burning). | Deep ribs are difficult to cool; heat becomes trapped at the tip, causing warpage. |
| Angolo di sformo | 0.5° – 1.5° per side | Higher draft facilitates ejection but reduces the effective thickness at the tip, increasing flow resistance. | Minimal impact, though insufficient draft causes drag marks and ejection stress. |
| Base Radius (R) | 25% – 50% of Nominal Wall (T) | Generous radii reduce flow shear stress and pressure loss. | Large radii increase the inscribed circle diameter at the base, creating hotspots. |
| Spacing (Pitch) | ≥ 2.0 × Nominal Wall (T) | Tight spacing can create "race-tracking" where flow accelerates in thick sections around ribs. | Crowded ribs create heat pockets that the mold steel cannot dissipate effectively. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Rib Structures?
| Vantaggi | Svantaggi |
|---|---|
| High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Increases stiffness significantly without the material cost of a solid thick wall. | Sink Marks: The intersection of the rib and wall is a primary location for surface depressions. |
| Riduzione del tempo di ciclo: Compared to a solid wall of equivalent stiffness, ribbed designs cool faster. | Flow Hesitation: If the rib is too thin, the melt front may bypass it, causing the material to freeze before filling the rib. |
| Resistenza alla curvatura: Strategic rib placement can disrupt residual stress patterns and reduce part distortion. | Venting Challenges: Deep ribs create dead ends for gas, requiring active venting to prevent the "Diesel effect" (burn marks). |
| Risparmio di materiale: Reduces polymer consumption compared to increasing global wall thickness. | Tooling Complexity: Requires EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) for deep ribs, increasing mold cost. |
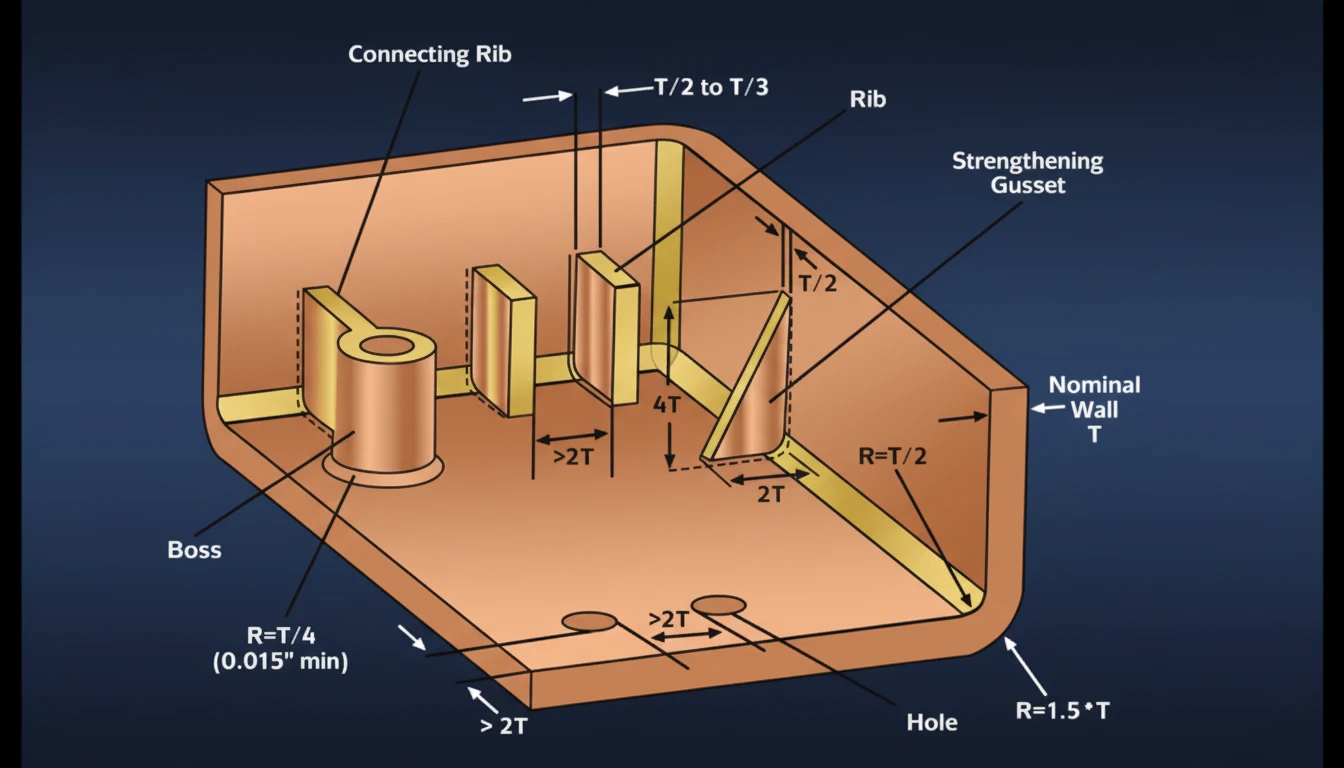
Where Are Rib Designs Most Commonly Applied?
- Automotive Structural Components: Door panels, bumpers, and instrument panels utilizing Polypropylene (PP) or Polyamide (PA).
- Alloggiamenti per elettronica di consumo: Laptop shells and phone cases made from Polycarbonate/Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (PC/ABS).
- Power Tool Casings: Glass-fiber reinforced handles requiring high rigidity.
- Battery Enclosures: Structural grids to prevent warping under thermal load.
- Appliance Internals: Gears and brackets in washing machines and refrigerators.
Adding a radius at the base of a rib reduces stress concentrations and aids material flow.Vero
Fillets reduce the notch effect, improving impact strength, and smoothen the flow path for the molten plastic, reducing shear stress.
Ribs cool faster than the nominal wall because they are thinner, so they require no special cooling considerations.Falso
While the rib blade cools fast, the rib 'base' (intersection) holds heat longer than the surrounding wall. Without proper core cooling, this hotspot causes cycle delays and sink marks.
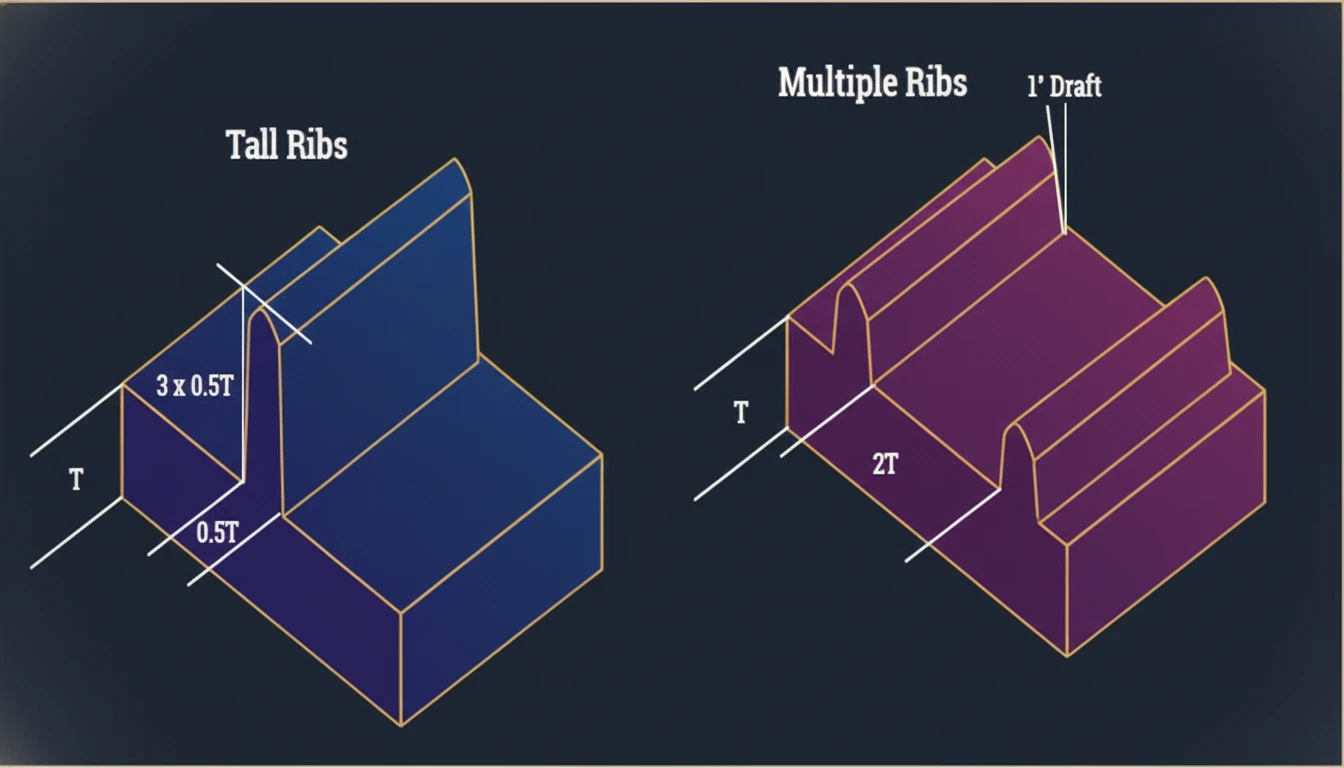
How Should Engineers Optimize Rib Design for Flow and Cooling?
To ensure ribs function structurally without compromising the molding process, engineers should follow this stepwise approach:
-
Establish Nominal Wall Thickness (T):
Determine the base wall thickness based on the material’s flow length ratio. -
Calculate Rib Thickness (t):
Apply the formula: t = 0.5 × T (for high-gloss resins like PC/ABS) or up to t = 0.7 × T (for low-shrinkage or textured materials). Avoid exceeding 70% to prevent segni di lavandino2. -
Determine Draft and Height:
Apply a minimum of 0.5° draft. Calculate the resulting thickness at the rib tip. Ensure the tip thickness is not less than 0.75mm to avoid venting issues and short shots. Limit height to 3 × T. -
Address Cooling at the Intersection:
If ribs are deep or clustered, incorporate mold cooling channels (baffles or bubblers) directly into the core steel opposite the ribs to extract heat from the base. -
Simulate Flow and Warp:
Use Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) software (e.g., Moldflow) to check for "Flow Hesitation." This phenomenon occurs when plastic races through the thick wall and hesitates to enter the thin rib. -
Check for Trapped Gas:
Ensure the mold design allows for venting at the end of the rib. Trapped air will superheat under pressure, causing material degradation.
Flow hesitation occurs when the melt front advances in the variable thickness areas, preferring the path of least resistance.Vero
The polymer melt prefers thick sections (low resistance) over thin ribs (high resistance). If the melt slows too much in the rib, it may freeze off before filling.
Increasing injection speed is the only solution to fix short shots in deep ribs.Falso
While speed helps, excessive speed causes jetting, gas burns, and flash. The correct solution involves optimizing rib thickness, gating location, and venting.
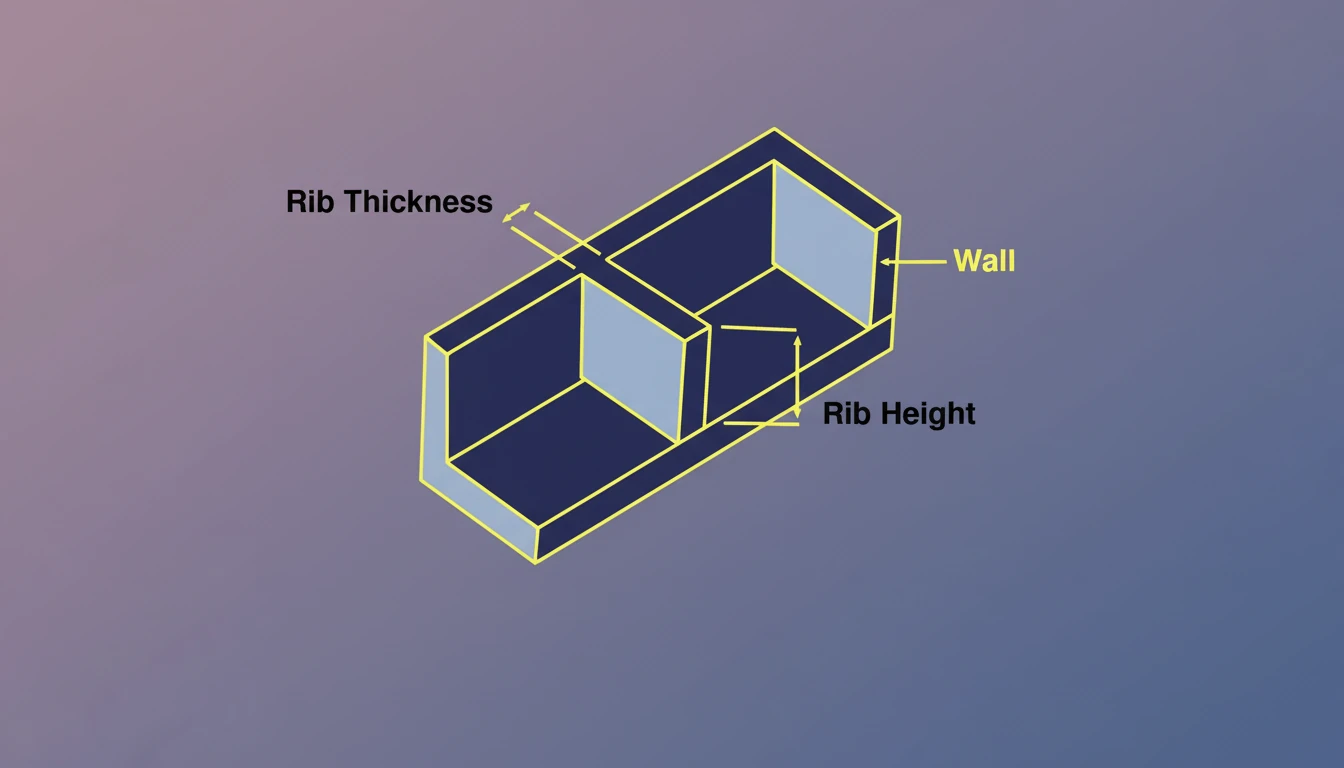
Domande frequenti (FAQ)
Q1: Why do ribs often cause sink marks on the visible surface (A-side)?
A1: Sink marks occur because the intersection of the rib and the wall contains a larger volume of material. As this mass cools, it shrinks inward. If the outer skin is not rigid enough, it pulls the surface down. This is mitigated by maintaining the rib thickness ratio below 60% of the wall thickness.
Q2: What is "Flow Hesitation" in ribbed parts?
A2: Flow hesitation happens when the plastic melt flows past a rib entrance without filling it immediately. The material enters the path of least resistance (the thicker wall). As the flow front advances, the material at the rib entrance cools and increases in viscosity, potentially freezing off and causing a "short shot" in the rib.
Q3: How does material selection affect rib design parameters?
A3: Amorphous materials like Polycarbonate (PC) are more prone to stress cracking and require generous radii at the rib base. Semi-crystalline materials like Polipropilene (PP)3 have higher shrinkage rates, making them more susceptible to sink marks, requiring tighter thickness controls (often <50%).
Q4: Can ribs replace solid wall thickness entirely?
A4: In many cases, yes. Replacing a thick wall with a thinner wall reinforced by ribs (coring out) is a standard practice to reduce weight, material cost, and cycle time while maintaining similar structural rigidity.
Q5: What is the "inscribed circle" method regarding ribs?
A5: It is a design check where a circle is drawn at the intersection of the rib and wall. The diameter of this circle represents the thermal mass. The goal is to minimize this diameter relative to the wall thickness to ensure uniform cooling.
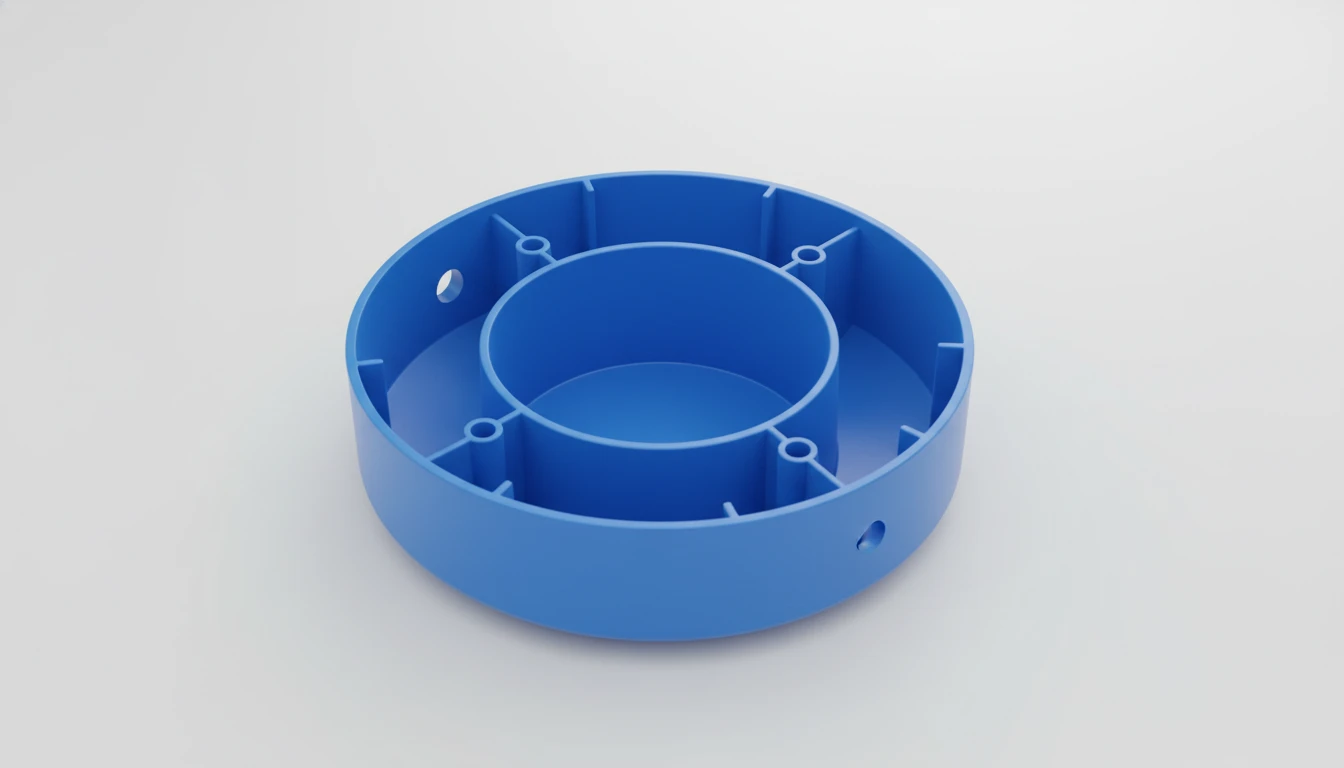

Sintesi
The impact of rib design on injection molding creates a tension between structural requirements and processing limitations. While ribs effectively increase part stiffness, they introduce complexities in Mold Flow, such as hesitation and gas traps, and challenges in Raffreddamento, specifically regarding thermal hotspots and sink marks. Adhering to the industry standard of keeping rib thickness between 40-60% of the nominal wall, applying adequate draft, and utilizing simulation software are essential steps to ensure a defect-free manufacturing process.
-
Aorbit Design Principles: Provides fundamental guidelines on flow resistance and hesitation effects caused by variations in wall thickness. ↩
-
ZetarMold Design Guide: Offers academic and practical benchmarks for rib geometry to minimize cosmetic defects like sink marks. ↩
-
ScienceDirect Polypropylene Overview: Details the crystallization behavior of PP, explaining why high-shrinkage materials require stricter rib design controls. ↩