– EV range anxiety and battery weight are the primary drivers for metal-to-plastic replacement.
– Glass-filled Polyamide (PA66-GF) and Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP) are replacing aluminum in structural components.
– Precision injection molding of fiber-reinforced materials requires specialized wear-resistant machinery and flow analysis.
– Structural integration (consolidating multiple metal parts into one plastic part) significantly reduces assembly costs.
What is the current state of automotive injection molding trends?
The automotive industry is currently undergoing a massive paradigm shift, transitioning from Internal Combustion Engines (ICE) to Electric Vehicles (EVs). This transition has elevated automotive injection molding trends toward aggressive lightweighting. Because EV battery packs are heavy—often exceeding 500 kg—manufacturers must reduce the weight of other components to maximize driving range and efficiency.
This demand has spurred the adoption of advanced thermoplastic composites. Materials such as Glass-Filled Nylon (Polyamide/PA) et Carbon-Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP)1 are being engineered to match the structural integrity of metals like aluminum and steel while offering a 30-50% reduction in weight. This process, often referred to as "metal-to-plastic conversion," utilizes moulage par injection à haute pression2 to create complex, consolidated geometries that were previously impossible with metal stamping.
Advanced fiber-reinforced thermoplastics can match the specific strength of die-cast aluminum in structural applications.Vrai
When engineered with high fiber content (30-60%) and correct fiber orientation, materials like PA66-GF50 offer strength-to-weight ratios comparable to metals.
Injection molding fiber-reinforced plastics requires the same standard tooling as unfilled commodity plastics.Faux
Glass and carbon fibers are highly abrasive; standard steel molds and screws will wear rapidly. Hardened steel molds and bimetallic screws are required.

What are the key properties of EV lightweighting materials?
To understand why engineers are selecting specific polymers, we must compare their mechanical properties against traditional automotive metals. The table below highlights the performance gap and overlap between EV lightweighting3 materials and metals.
Table 1: Comparative Properties of Structural Materials
| Matériau | Densité (g/cm³) | Résistance à la traction (MPa) | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (6061-T6) | 2.70 | 310 | 69.0 | Chassis, Body Panels |
| Polyamide 66 + 30% Glass Fiber (PA66-GF30) | 1.37 | 160 – 190 | 9.0 – 10.0 | Intake Manifolds, Brackets |
| Polyamide 66 + 50% Glass Fiber (PA66-GF50) | 1.56 | 230 – 250 | 16.0 – 17.0 | Structural Mounts, Pedals |
| Carbon Fiber Reinforced PEEK (CF-PEEK) | 1.40 | 280 – 300 | 20.0 – 25.0 | High-Voltage Connectors |
| Polycarbonate/ABS (PC/ABS) | 1.15 | 55 – 65 | 2.4 | Interior Trim (Non-structural) |
Note: Values are typical ranges based on ISO 527 (Tensile) and ISO 178 (Flexural) standards. Actual performance depends on fiber orientation derived from the molding process.
How does the fiber reinforced injection molding process work?
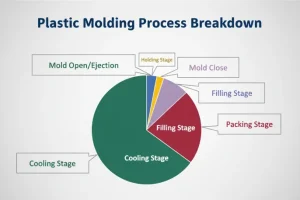
Fiber reinforced injection molding differs significantly from standard molding due to the inclusion of rigid fibers (glass or carbon) within the polymer matrix. The process involves specific steps to ensure structural integrity.
- Préparation du matériel : Pellets containing short or long fibers are dried strictly according to manufacturer specs (e.g., PA66 requires moisture content <0.2%).
- Plastification : The material is melted. A specialized screw design with low compression ratios is often used to prevent fiber breakage (reducing fiber length reduces impact strength).
- Injection and Orientation: As the plastic flows into the mold cavity, the fibers align in the direction of the flow.
- Critical Note: Strength is high in the direction of flow but lower in the transverse direction (anisotropy).
- Packing and Cooling: High holding pressure is applied to compensate for volumetric shrinkage, which is generally lower in fiber-filled materials than unfilled plastics.
- Ejection : The part is ejected. Fiber-filled parts set up faster, potentially allowing for shorter cycle times.
What are the pros and cons of using glass filled nylon in automotive applications?
Glass filled nylon automotive components are the industry standard for under-the-hood and structural parts. However, they present specific manufacturing challenges.
| Fonctionnalité | Avantages | Inconvénients |
|---|---|---|
| Réduction du poids | Up to 50% lighter than steel; 30% lighter than aluminum. | - |
| Part Consolidation | Complex geometries (snaps, bosses, ribs) molded in one shot, eliminating fasteners. | High mold complexity and upfront tooling costs. |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands high temperatures (approx. 200°C for PA66-GF) suitable for e-motor surroundings. | Hygroscopic nature (absorbs moisture), affecting dimensional stability over time. |
| Résistance mécanique | High stiffness and tensile strength comparable to die-cast alloys. | Anisotropy: Parts are weaker perpendicular to flow; prone to warpage. |
| Manufacturing | High-volume production with low cycle times. | Abrasion : Glass fibers wear down screws, barrels, and mold gates rapidly. |
How can manufacturers optimize plastic car components for structural use?
To successfully implement plastic car components in structural applications, engineers must adhere to strict design and processing guidelines.
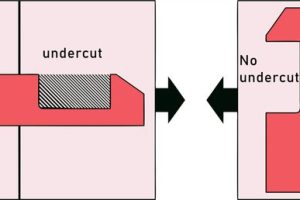
- Conduct Mold Flow Analysis: Before cutting steel, simulation software must be used to predict fiber orientation. Weld lines (where flow fronts meet) represent structural weak points and must be moved to non-critical areas.
- Manage Wall Thickness: Unlike metal casting, plastic parts require uniform wall thickness to prevent sink marks and internal voids. Ribbing should be used to add stiffness rather than increasing general wall thickness.
- Wear Protection: Use bimetallic barrels and tungsten-carbide coated screws. Molds should be made from hardened tool steels (H13 or greater) or coated with PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) treatments to resist the "sandpaper effect" of glass fibers.
- Gate Placement: Gates should be positioned to ensure fibers align with the primary stress vectors of the part in service.
Fiber orientation is the single most critical factor in the structural performance of reinforced injection molded parts.Vrai
Because fibers align with flow, a part can be twice as strong in the flow direction compared to the cross-flow direction. Ignoring this leads to part failure.
Using higher glass content (e.g., 60%) always guarantees a better automotive part.Faux
While stiffness increases, higher glass content reduces surface finish quality, increases brittleness, and significantly increases processing difficulty and machine wear.
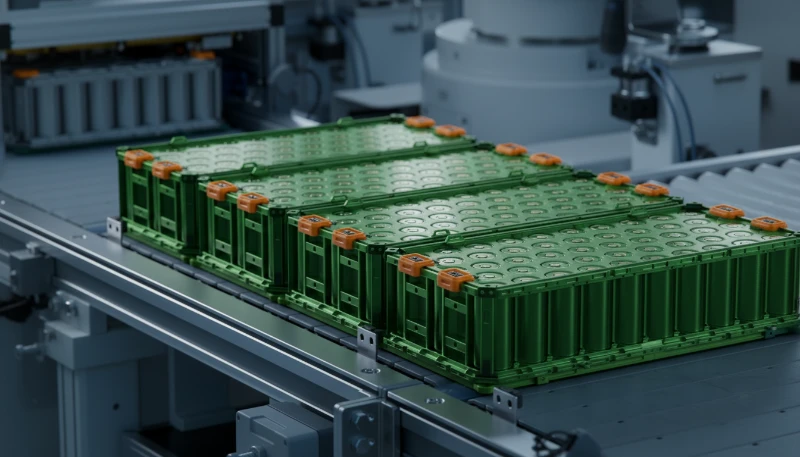

Where are advanced composites applied in EVs?
The application of reinforced plastics has moved beyond cosmetic covers to critical systems.
- Battery Manifolds & Cooling Lines: Hydrolysis-resistant PA66-GF30 is used for thermal management systems circulating glycol coolants.
- High-Voltage Connectors: Flame-retardant (orange colored) PBT or PA66 is used for busbars and connectors requiring high dielectric strength.
- Front End Modules (FEM): Large structural carriers holding headlights, radiators, and latches, molded from Polypropylene (PP-LGF) or PA6.
- Brake Pedals: Replaced metal pedals with PA66-GF50 utilizing internal ribbing structures to handle emergency braking loads without failure.
- Motor Housings: Reducing noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) compared to metal housings.
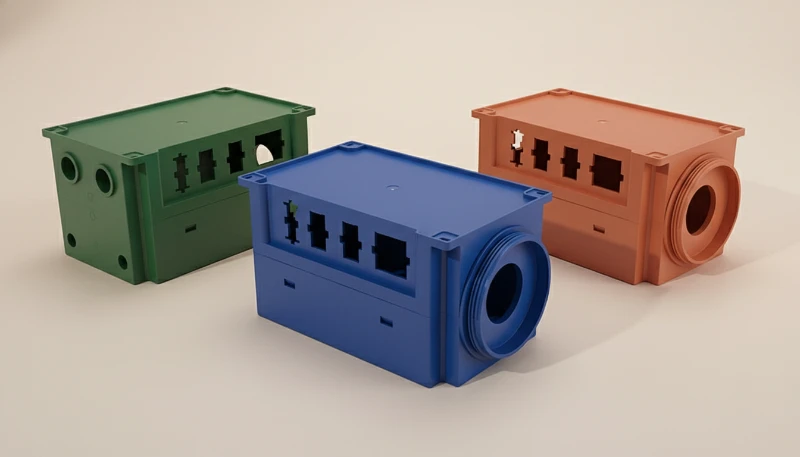

What are the recommended processing parameters?
Pour glass filled nylon automotive4 parts (specifically PA66-GF30), strict adherence to processing windows is required to maintain property retention.
- Séchage : 4 hours at 80°C (Dehumidified dryer). Moisture > 0.2% causes hydrolysis (polymer chain degradation).
- Température de fusion : 280°C – 300°C. Do not exceed 310°C to avoid thermal degradation.
- Température du moule : 80°C – 100°C. Higher mold temps ensure a resin-rich surface, hiding fibers and improving surface finish.
- Vitesse d'injection : Moderate to High. Fast speeds help fill thin walls before freezing but increase shear heat and fiber breakage.
- Back Pressure: Low (5-10 bar). High back pressure breaks fibers during plasticization.

Foire aux questions (FAQ)
1. Why is "automotive injection molding trends5" shifting towards composites?
The shift is driven by government regulations on emissions (for ICE) and the need for range extension in Electric Vehicles (EVs). Composites offer the highest strength-to-weight ratio, essential for offsetting heavy battery packs.
2. What is the difference between Short Glass Fiber and Long Glass Fiber (LGF) molding?
Short fibers (typically <1mm) are standard in pellets. Long fibers (>10mm) are used in special pultrusion pellets (LFRT). LGF offers significantly higher impact strength and creep resistance, making it ideal for large structural parts like door modules.
3. How do you prevent warpage in fiber reinforced injection molding?
Warpage is caused by differential shrinkage (anisotropy) where fibers shrink less than the plastic matrix. Solutions include using mold flow analysis to optimize gating, using conformable cooling in the mold, and designing symmetrical parts with uniform wall thickness.
4. Can EV lightweighting materials be recycled?
Thermoplastics like PA66-GF and PP-LGF can be mechanically recycled (re-melted), although fiber length degrades with each heat history, reducing properties. Thermoset composites (like standard carbon fiber epoxy) are much harder to recycle.
5. Is Carbon Fiber Injection Molding6 cost-effective for mass-market cars?
Generally, Carbon Fiber (CF) is reserved for high-end or performance vehicles due to material cost. However, "Pitch-based" carbon fibers mixed with nylon are appearing in mass-market EV components where specific conductivity or extreme stiffness is required in small parts.

Conclusion
The transition to electric mobility has fundamentally altered the landscape of manufacturing. Automotive lightweighting is no longer a luxury but a necessity for EV viability. By mastering the fiber reinforced injection molding process—understanding the nuances of anisotropy, tool wear, and material selection—manufacturers can produce plastic car components that meet the rigorous safety and performance standards of the automotive industry. The future lies in the intelligent combination of polymer science and precision mold engineering.
-
Discover how CFRP is revolutionizing electric vehicle design and performance with its lightweight and strong properties. ↩
-
Find out how high-pressure injection molding enhances the production of complex automotive parts. ↩
-
Discover the significance of EV lightweighting in enhancing vehicle efficiency and performance. ↩
-
Discover the benefits of using glass filled nylon in automotive parts and its impact on weight reduction. ↩
-
Explore the latest trends in automotive injection molding to understand how they are shaping the future of vehicle manufacturing. ↩
-
Understand the cost-effectiveness of Carbon Fiber Injection Molding for mass-market vehicles and its applications. ↩