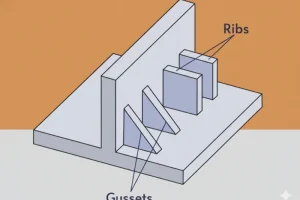
주요 내용
Effective rib design relies heavily on the shrinkage characteristics of the selected polymer. While ribs increase part stiffness and Moment of Inertia without significantly increasing cycle time, improper sizing relative to the nominal wall leads to cosmetic defects like sink marks. Generally, amorphous materials like Polycarbonate (PC) allow for thicker ribs (up to 60-70% of wall thickness), while semi-crystalline materials like Polypropylene (PP) require thinner ribs (40-50%) to prevent surface depressions.

What Are the Material Constraints for Rib Geometry?
In injection molding, a Rib is a reinforcing feature that projects from a nominal wall to add structural rigidity and stiffness. The primary challenge in rib design is managing the mass accumulation at the intersection of the rib and the base wall.
When molten plastic cools, it shrinks. If the intersection is too thick, the center remains molten longer than the skin. As this center cools and contracts, it pulls the solidified outer layers inward, causing a Sink Mark on the cosmetic surface (Class A surface). The severity of this shrinkage depends entirely on the material’s internal structure:
- Amorphous Polymers (e.g., Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Polycarbonate (PC)): Exhibit lower, isotropic shrinkage, allowing for slightly thicker ribs.
- Semi-Crystalline Polymers (e.g., Polyamide 66 (PA66), Polypropylene (PP)): Exhibit high, anisotropic shrinkage, requiring thinner ribs to avoid defects.
Ribs significantly increase part stiffness with minimal weight addition compared to increasing the entire wall thickness.True
Ribs increase the Moment of Inertia, providing strength where needed without the material cost and cooling time penalties of a generally thicker wall.
You can design ribs to be the same thickness as the nominal wall to maximize strength without side effects.False
Ribs equal to the wall thickness create a massive thermal hot spot at the intersection, guaranteeing sink marks and potentially creating vacuum voids.

Key Material Parameters for Rib Sizing
The following table outlines recommended design parameters based on polymer family. These values adhere to general industry standards such as those found in DFM guidelines1 and ISO 294-4 shrinkage standards.
| 매개변수 | Amorphous Materials (e.g., PC, ABS, PMMA) | Semi-Crystalline Materials (e.g., PP, PE, PA6) | Glass-Filled Materials (e.g., PA66-GF30) | 참고 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rib Thickness [t(rib)] | 50% – 70% of Wall [t(wall] | 40% – 50% of Wall [t(wall)] | 55% – 75% of Wall [t(wall)] | Measured at the base of the rib. |
| 수축률 | Low (0.2% – 0.8%) | High (1.0% – 3.0%) | Very Low (Anisotropic) | Higher shrinkage requires thinner ribs. |
| 구배 각도 | 0.5° – 1.0° per side | 1.0° – 1.5° per side | 0.5° – 1.0° per side | Required for ejection; affects top thickness. |
| Base Radius (R) | 25% – 50% of t(wall) | 25% – 40% of t(wall) | 25% – 50% of t(wall) | Reduces stress concentration; too large causes sink. |
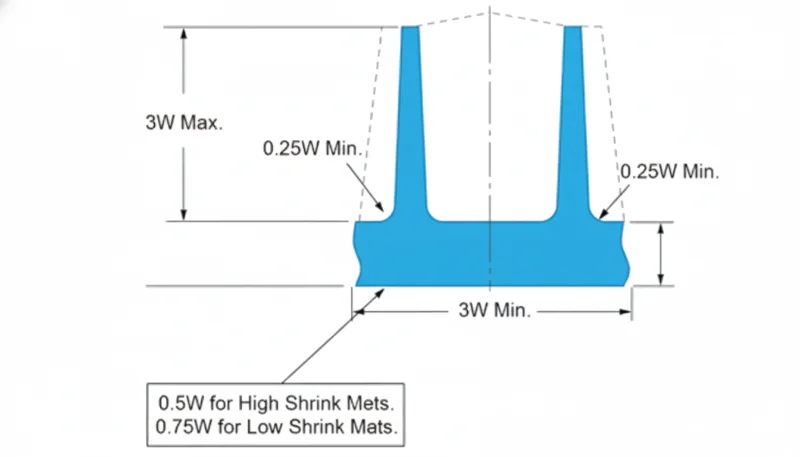
| Rib Height ($H$) | ≤ 3.0 × t(wall) | ≤ 2.5 × t(wall) | ≤ 3.0 × t(wall) | Deep ribs may require venting solutions. |
참고: Glass fibers orient in the direction of flow, significantly reducing shrinkage in that direction. This allows Glass-Filled (GF) materials to tolerate slightly thicker ribs without visible sink marks compared to their unfilled counterparts.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Ribbed Structures?
| 기능 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Integrity | Increases stiffness-to-weight ratio; prevents part warping under load. | Improper design creates stress concentrators leading to failure. |
| 주기 시간 | Faster cooling than a thick solid wall (material savings). | Deep ribs can trap heat, requiring complex 금형 냉각2 (e.g., beryllium copper inserts). |
| Material Usage | Reduces raw material consumption compared to solid sections. | Increases flow length; may require higher injection pressure. |
| 표면 마감 | N/A | High risk of sink marks or "read-through" on the cosmetic side. |
| 성형 프로세스 | Aids in melt flow distribution (can act as flow leaders). | Can cause flow hesitation or gas traps if ribs are too thin/deep. |
Glass-filled materials allow for rib thickness up to 75% of the nominal wall in some applications.True
The structural reinforcement of the glass fibers resists volumetric shrinkage, reducing the severity of sink marks even with thicker rib intersections.
Ribs should be placed without radiused corners to ensure maximum material flow velocity.False
Sharp corners at rib bases create high stress concentrations leading to part failure; a radius is essential for stress distribution and material flow.
What Are the Common Application Scenarios?
- 자동차 인테리어: Dashboard substrates using Polypropylene (PP) + Talc requiring thin ribs (40% ratio) to prevent visual defects on the textured side.
- 소비자 가전: Laptop housings made of Polycarbonate/Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (PC/ABS) utilizing ribs for boss support and EMI shielding stiffness.
- 구조 브래킷: Glass-filled Polyamide (PA66-GF) parts under high load, utilizing cross-ribbing patterns for maximum torsional rigidity.
- Crates and Pallets: High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) designs using deep, drafted ribs to support heavy loads while minimizing part weight.
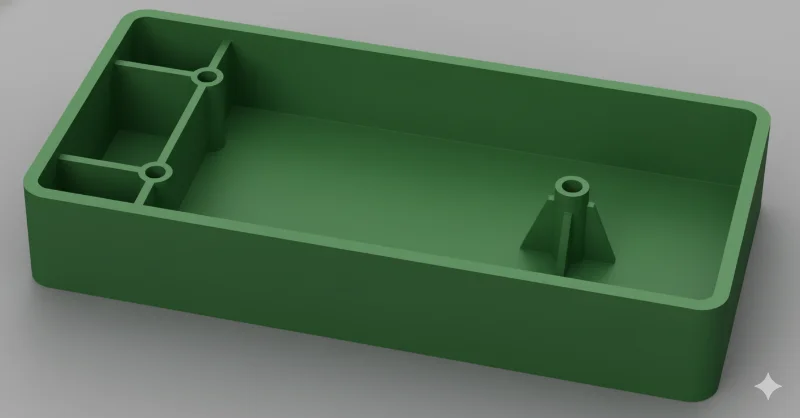
How Should You Execute the Rib Design Process?
To optimize for both mechanical performance and Aesthetics3, follow this stepwise workflow:
- Define Mechanical Requirements: Determine the required stiffness and load-bearing capacity.
- 소재를 선택합니다: Choose the polymer based on environmental and mechanical needs. Note its shrinkage class (Amorphous vs. Semi-crystalline).
- Calculate Nominal Wall [t(wall)]: Establish the main body thickness.
- Determine Rib Thickness [t(rib)]:
- Multiply t(wall) by 0.5 (for crystalline) or 0.6 (for amorphous).
- 예시: For a 3.0mm PP wall, max rib base = 1.5mm.
- Apply Draft Angle: Add 0.5° to 1.5° draft per side to facilitate ejection. Ensure the tip of the rib does not become too thin (minimum 0.75mm is recommended for filling).
- Add Base Radii: Apply a radius of 0.25 × t(wall) at the base. Do not exceed 0.5 × t(wall) to avoid creating a thick mass.
- Space the Ribs: Ensure spacing between ribs is at least 2 × t(wall) (preferably 3 ×) to ensure adequate cooling channel placement and steel strength in the mold.
- Mold Flow Simulation: Run a Moldflow analysis4 to predict volumetric shrinkage and check for air traps at the rib tips.
FAQ: Rib Design and Materials
Q1: Can I use ribs to hide flow lines?
A: While ribs can disrupt flow and move knit lines, they are more likely to cause cosmetic issues like sink marks or flow hesitation (shadows) if not designed with the correct wall thickness ratio.
Q2: Why do glass-filled materials wear the mold faster in rib areas?
A: Glass fibers are abrasive. In narrow rib cavities, high shear rates occur during injection, causing accelerated erosion of the mold steel. Hardened tool steel (e.g., H13) or coatings are recommended.
Q3: What is the minimum thickness for a rib to fill properly?
A: Generally, the tip of the rib should not be less than 0.75mm to 1.0mm. If it is thinner, the injection pressure required to fill it may spike, or the material may freeze off before filling (short shot).
Q4: How does "coring out" relate to rib design?
A: Coring out involves removing thick sections of material to maintain uniform wall thickness. Ribs are then added back into the cored-out area to restore the strength lost by removing the bulk material.
Q5: Can gas-assist injection molding help with thick ribs?
A: Yes. Gas-Assist Injection Molding (GAIM) allows for hollow ribs. Nitrogen gas is injected into the melt stream, coring out the rib from the inside. This allows for much thicker ribs without sink marks, as the gas pressure packs the plastic against the mold walls.

요약
Rib design is a balance between structural engineering and rheology. The material choice dictates the geometric limits: Amorphous materials (PC, ABS) offer more leniency, allowing rib-to-wall ratios up to 70%, while Semi-crystalline materials (PP, PE) demand strict adherence to 40-50% ratios to prevent sink marks. Always verify designs using FEA5 for stress and Moldflow for processability.
-
Comprehensive design guides covering wall thickness, ribs, bosses, and draft angles for manufacturability. ↩
-
Detailed overview of cooling channel configurations, including baffles and bubblers often used to cool deep rib structures. ↩
-
Explanation of SPI and VDI surface finish standards and how underlying geometry like ribs can impact the final visual quality. ↩
-
Industry-standard simulation software used to predict filling patterns, shrinkage, warpage, and potential defects before steel is cut. ↩
-
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) helps engineers predict how a part reacts to real-world forces, vibration, and heat, confirming if the rib pattern provides adequate stiffness. ↩