People often associate die casting molds and injection molds together, but the difference between the two is still very big.
The basic difference between injection mold and die casting mold is that the material is different, one is plastic or metal and the other is alloy.
So the die-casting mold has to bear much greater pressure and high temperature than the plastic mold, the structure of the mold needs to be strengthened, the way of feeding, flow channel, cooling design is different.
The Metal Injection Molding process is a net shape process that forms and sinters metal powder to create high strength components. This is followed by a sintering process where the part is put into an oven at a temperature close to the melting temperature of the metal allowing the fine metal powder to sinter together, leaving a strong net-shape component.

Injection molding vs Die casting
Although both need to use mold molding to do products, the working principle is not much different, the raw material is different, the material costs are different, the natural use of the mold is also different.
When it comes to mold manufacturing, several different methods are commonly used. Plastic injection molding and die casting are two of the most popular manufacturing methods, but what are the differences between them?
In this blog post, we will discuss the major differences between die casting and injection molding, as well as their advantages and disadvantages.

What is die casting?
Die casting is a metal casting process characterized by the use of a mold cavity to apply high pressure to the molten metal.
The mold is usually machined from a stronger alloy, a process somewhat similar to plastic injection molding.
Most die castings are non ferrous metal parts, such as zinc, copper, aluminum, magnesium, lead, tin, and lead-tin alloys and their alloys.
Depending on the type of aluminum die-casting, either a cold chamber dies casting machine or a hot chamber die casting machine is used.
Because of the high cost of casting equipment and molds, the die casting process is generally only used to manufacture large quantities of products in bulk.
Die casting is particularly suitable for manufacturing large quantities of small to medium-sized castings and is, therefore, one of the most widely used of the various casting processes.
Compared to other casting techniques, die casting has a flatter surface and higher dimensional consistency.
Based on the traditional die casting process, several improved processes have been created, including the non-porous die casting process, which reduces casting defects and eliminates porosity.
The direct injection process, mainly used for processing zinc, reduces waste and increases the yield.
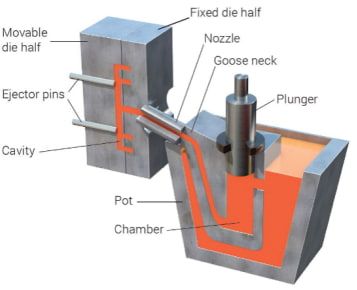
Die Casting Process
The traditional die casting process consists of four main steps, these four steps include
(1) Mold preparation
(2) Filing
(3) Injection
(4) Sand drop
They are the basis for various modified versions of the die casting process.

During the preparation process, the mold cavity is sprayed with lubricant, which helps control the melting temperature of the mold and also helps to release the casting from the mold.
The mold is then closed and the molten metal is injected into the mold at high pressure, which ranges from about 10 to 175 MPa. Dies must withstand high pressure and melted-metal temperatures which may wear them out quickly.
Once the molten metal is filled, the pressure is maintained until the casting is solidified.
The pusher then pushes out all the castings, and since there may be more than one cavity in a mold, more than one casting may be produced per casting process.
The sand drop process then requires the separation of residues, including mold builders, runners, gates, and flying edges.
This manufacturing process is usually accomplished by extruding the casting through a special dressing die.

Die-casting vs Injection molding molds are different
(1) Pressure
The major difference between die casting and injection molding is that the extreme pressure of die-casting mold is high, so the requirements for the mold template are higher and should be relatively thick to prevent deformation.
(2) The Gate
The gate of die-casting mold is different from that of injection mold, so it should be made for the high pressure of shunt cone to break down the material flow.
(3) Harden Treatment
Die casting mold kernel does not need to harden and quench, because the temperature inside the die cavity is relatively high during die casting, which is equivalent to a quenching, while the injection mold needs quenching treatment.
(4) Cavity Treatment
Die casting mold general cavity to nitriding treatment, to prevent the alloy sticky film cavity.External Surface Treatment
General die-casting mold corrosion is relatively large, the external surface will generally do the blue treatment.

(5) External Surface Treatment
General die-casting mold corrosion is relatively large, the external surface will generally do the blue treatment.
(6) Exhaust system
Injection mold generally relies on the ejector pin, parting type can exhaust, the die-casting mold must open exhaust groove and slag collection package.
(7) Face Type Fit Requirements
The die-casting mold with higher requirements for the face type, should be alloy fluidity than plastic much better, high temperature and high-pressure flow material from the face type fly out of the two will be very dangerous.
(8) Active Distribution Part Fit Clearance
Die-casting mold and injection mold, compared with the die-casting mold, die-casting mold with the active distribution complex parts of the gap to be larger, because the high temperature of the die-casting process will cause thermal expansion if the gap is too small will cause the mold stuck.

Die-casting vs Injection molding materials are different
Injection molding is the process of injecting polymer materials into a plastic mold through an injection molding machine to cool the mold.
The molding is simply a process of heating the plastic material from a solid-state to a soft fluid and then pushing the heated and softened plastic into the mold by rotating the screw to cool the plastic molds. The plastic injection molding processing temperature is lower. The speed is a little slower.
Custom Injection molding is the main manufacturing method of thermoplastic molding. Thermoplastics are made of thermoplastic resins that can be repeatedly heated to soften and cooled to cure, a physical process that is reversible.
Die-casting molding is generally made of zinc or aluminum alloy and magnesium as raw materials and produces metal die-cast parts sheet metal molding is also made of sheet metal.
Die casting molding is the metal material through the die casting machine into the die casting mold cooling molding, molding requirements from the solid-state heating into a liquid state, and then into the mold cooling molding.
The inlet hot chamber and cold chamber are larger than the metal injection molding inlet. The process temperature is high, the speed is fast.

Die-casting vs Injection molding mold temperature control is different
For Custom injection molding, the mold temperature is basically below 180℃, and the temperature control requirement can be satisfied by using the water transportation type mold temperature controller.
In die-casting, the temperature of casting liquid can reach more than 600 degrees, and the temperature of mold can be as high as 300 degrees.
In the die-casting process, the mold temperature manufacturing needs to be maintained below 300 degrees.
It is necessary to configure a special high-temperature mold temperature machine for die casting, using heat-conducting oil as the heat-conducting medium and indirect cooling through a cooler.