Injection molding is widely used for producing high-volume parts, but it comes with some challenges, including high initial setup costs and potential for defects.
Disadvantages of injection molding include high mold costs, long lead times, material waste, and limitations with complex geometries. The process is also not ideal for low-volume production.
While injection molding offers great efficiency in mass production, understanding its disadvantages is key to determining when it’s the right choice for your manufacturing needs.
Injection molding is always cost-effective for small production runs.False
Due to high tooling and setup costs, injection molding is generally not ideal for small production runs unless offset by high-volume production.
Injection molding has limited material options.False
Injection molding can use a wide variety of materials, including plastics, elastomers, and composites, offering flexibility in material choice for different products.
What is Injection Molding ?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into molds to create complex parts quickly and efficiently. It is ideal for high-volume production.
Injection molding is a process where melted plastic is injected into a mold cavity to form parts. It’s known for high efficiency, precision, and the ability to produce complex shapes with minimal waste. It’s used in industries like automotive, electronics, and medical.

Injection molding is when you take hot, melted stuff and shoot it into a mold. Then you let it cool and harden. Here’s how it works: You take little plastic pellets or powder and put them in the hopper of the injection molding machine. The machine heats them up and melts them into a liquid.
Then it squirts the liquid into a cold, closed mold through a nozzle at the end of the machine. The mold cools the liquid down and makes it hard. When you open the mold and take out the plastic, you’re done. That’s one cycle.
Injection molding is used for both small and large-scale production.True
Injection molding is versatile, suitable for both small-batch prototypes and large-scale, high-volume manufacturing.
Injection molding is only used for plastic parts.False
While commonly used for plastic, injection molding can also be used with other materials like metals, rubber, and glass-filled compounds.
What are the Steps in the Injection Molding Process?
The injection molding process involves several critical steps, each contributing to the creation of high-quality plastic parts efficiently and consistently.
The injection molding process includes clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection. It begins with melting plastic, injecting it into a mold, allowing it to cool, and then ejecting the finished part. These steps ensure precision, speed, and minimal waste in manufacturing.
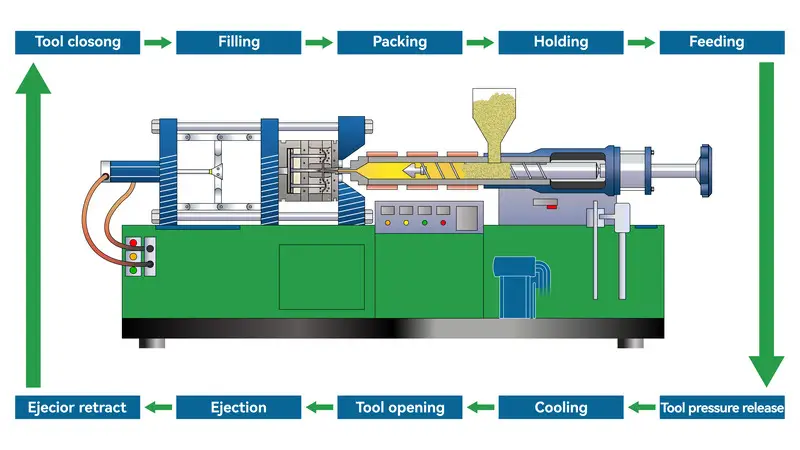
Filling Stage
Filling is the first step in the whole injection molding process. The time starts from the mold closing and the injection molding until the mold cavity is filled to about 95%. In theory, the shorter the filling time1, the higher the molding efficiency, but in practice, the molding time or injection speed2 is subject to many conditions.
Pressure Holding Stage
The pressure holding stage is there to keep the pressure on, pack the melt, make the plastic denser (densification), and compensate for the plastic’s shrinkage. The back pressure is high during the pressure holding stage because the mold cavity is already full of plastic.
During the pressure holding and packing stage, the screw of the injection molding machine can only move forward a little bit and slowly, and the plastic’s flow rate is also slow. This flow is called pressure holding flow. Since the plastic is cooled and solidified by the mold wall during the holding stage, and the melt viscosity increases quickly, the resistance in the mold cavity is very high.
In the later part of the holding stage, the plastic material reaches density keeps going up, and the plastic part starts to form. The holding stage should keep going until the gate is solid and sealed. At this point, the cavity pressure3during the holding stage is high.
Cooling Stage
The cooling system design is very important in injection molding molds. This is because only when the molded plastic products are cooled and solidified to be rigid enough can the plastic products be prevented from being deformed by external forces after demolding.

Since the cooling time4accounts for about 70% to 80% of the entire molding cycle, a well-designed cooling system can greatly shorten the molding time, improve injection molding productivity, and reduce costs. Improperly designed cooling systems will prolong the molding time and increase costs; uneven cooling lines will further cause warping and deformation of plastic products.
Demolding Stage
Demolding is the last link in an injection molding cycle. Although the product has been cold-formed, demolding still has a very important impact on the quality of the product. Improper demolding methods may cause uneven force on the product during demolding and product deformation during ejection.
There are two main ways to demold: ejector and stripper. When designing a mold, choose the appropriate demolding method based on the structural characteristics of the product to ensure product quality.
Injection molding is a quick and cost-effective production method.True
Injection molding allows for high-speed production and efficient use of materials, making it a cost-effective method for mass-producing parts.
Injection molding only works with certain types of plastic.False
Injection molding can work with a variety of thermoplastic and thermosetting materials, not just a limited selection of plastics.
What are the Disadvantages of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process, but it has its downsides, including high initial costs and limitations with complex geometries or materials.
Disadvantages of injection molding include high setup costs, the need for expensive molds, and limited flexibility with material choices. It’s less effective for small production runs due to expensive mold-making and setup.

High Initial Mold Cost
One of the big downsides of injection molding is the high cost of making the mold. Designing and making molds that fit a specific part shape can be really expensive, especially for complex or fancy designs. This upfront cost can be a deal breaker for companies with smaller production or limited budgets.
The upfront cost is high because you have to design it, test it, and tool it. You have to design it and prototype it (possibly through CNC or 3D printing), then you have to design the prototype mould tool to mass-produce replicas of the part. Finally, only after extensive testing in these two stages can you finally injection mold the part.
Low Efficiency
The speed of plastic injection molding depends on the size of the injection machine and the process conditions. The bigger the injection machine, the faster the production.
But even with a big injection machine, it takes tens of seconds to inject one shot. So, the production speed of plastic injection molding is relatively slow compared to other manufacturing processes, which affects the production efficiency of industrial products.
The Injection Molding Process is Irreversible
While injection molding can shape multiple plastic materials into any form, it’s a one-way street. Once the molding is done, the shape is set. If you need to change or modify the design, you have to make a new mold, which costs time and money.

High Scrap Rate
The scrap rate in the production process of plastic injection molding is also relatively high. This is because the changes in temperature and pressure during the injection molding process can cause defects such as warpage, flash, and voids. Once these problems exist, the injection mold needs to be remade or the bad part needs to be thrown away, increasing the waste of money and time.
Size Limitations
Injection molding has size limits, especially for big parts. The size of the injection molding machine and the size of the cavity will limit the biggest part you can make. If you want to make a big part, you might need special equipment or multiple mold cavities, which will make it more expensive and complicated.
Design Limitations
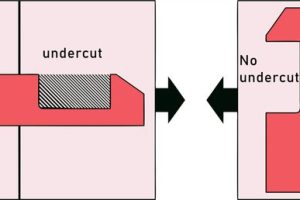
Designing plastic parts. When designing plastic parts, you need to keep in mind that they will be made using injection molding. This means you need to follow some basic rules, such as: try to avoid undercuts and sharp edges. Use uniform wall thickness to prevent defects like sink marks 5 that happen when the cooling process isn’t consistent. Use draft angles6 to make it easier to remove the part from the mold.
Remember, tools are usually made of steel or aluminum, so it’s hard to make design changes. If you need to add plastic to a part, you can make the tool cavity bigger by cutting away the steel or aluminum. But to take plastic away, you have to make the tool cavity smaller by adding aluminum or metal. This is really hard and in a lot of cases means you have to throw the tool (or part of it) away and start over.
Also, the weight and size of the part will determine the tool size and press size you need. The bigger the part, the harder and more expensive it is.
Injection molding is a versatile process for making all kinds of shapes and details. But there are limits to what you can do. Some shapes, like sharp corners, thin walls, or deep holes, can make it hard to fill the mold, cool the part, or get it out of the mold.
When you design a part for injection molding, you have to think about things like draft angles, wall thickness, and other stuff to make sure the mold works and the part is good. Sometimes you have to add extra stuff to the mold or do extra things to the part to make it work. That makes it harder and more expensive to make the part.
High Upfront Costs
Plastic injection molds are complicated. Only experienced engineers know how to design and build them, which means labor costs are high. Plus, there are many steps to making a mold that will produce millions of identical parts over time. A simple single-cavity mold starts at $2,000-3,000. A high-production multi-cavity mold made of hardened tool steel can cost $100,000 or more.
Long Lead Time
A good plastic injection mold will last forever. So, it takes a lot of planning and testing to get it right. The design, prototyping, testing, and machining phases can take months. Compared to other types of plastic fabrication, plastic injection molding takes a long time to make.
If you want a mold that can make multiple plastic parts in one shot, it may take even longer. For this type of mold7, the mold maker can design, build, and test a single-cavity tool before even trying to make a multi-cavity tool. Of course, the multi-cavity tool must also go through the design, prototyping, building, and testing phases.
But once you’ve done the planning and machining, a plastic injection mold can make millions of parts over its lifetime. The scale of plastic part production often outweighs the upfront costs and lost time.
Unbendable Materials
Unlike CNC machining, which makes physical parts from computer design files that can be changed at any time by software engineers, it’s hard to make big changes to a plastic mold after machining because it’s usually made of steel.
There are two ways to change a plastic mold. One way is to make the mold cavity bigger by cutting away parts of the metal mold. This adds plastic to the part. It is harder to take plastic away from the part. Sometimes you can weld metal into the cavity, but sometimes you can’t and you need a new cavity or a whole new mold. This means you have to go back to the design stage.

Size Limitations
If you need to make a big plastic part, injection molding has its limits. There are injection molding machines big enough to make a boat hull, but the molding scenarios I’m talking about here are for smaller parts, three pounds or less. If you need a bigger part, the lead time and cost can go up exponentially.
High Costs
Injection molding is a high-precision manufacturing technology that requires a lot of money to ensure the quality and stability of the product. The production of injection molding requires a lot of equipment, processes, and human resources, resulting in high production costs. In addition, the need to use high-quality raw materials and additives in the injection molding process further increases costs.
Small batch parts can be expensive. The tooling is complex and you have to clean out the machine before you can make the next part. So, it takes a long time to set up. That’s why injection molds have traditionally been considered too expensive for small batch parts.
High Equipment Requirements
Injection molding needs a lot of equipment, like injection molding machines, molds, automatic transportation equipment, and related auxiliary equipment. These equipment need strict maintenance and management, and once a failure happens, the repair cost is relatively high. Besides, injection molding also needs high-precision temperature control systems and pressure control systems, so the equipment needs to be very stable and reliable.
Long Production Cycle
Compared to some rapid prototyping methods like 3D printing, injection molding usually takes longer to set up and get started. This includes designing and making molds, running mold trials, and dialing in process parameters before you can start making parts at scale. So the time from concept to finished parts can be longer than faster prototyping methods.
The production cycle of injection molding is relatively long, generally taking several days to several weeks. This is mainly because injection molding requires multiple links such as mold making, mold trial, and batch production, and each link takes a long time. This also makes the injection molding producle not conducive to the processing of urgction cyent orders.
Finished Product Defects
Injection molding technology has been developed and applied, but there are still some defects in finished products. For example, bubbles, shrinkage holes, and unreal sections may occur, which will seriously affect the quality and appearance of the product.
Environmental Pollution
When you’re making stuff with injection molding, you might make some bad stuff too, like chemical resistant plastics , plastic waste , waste gas and wastewater, which can mess up the world. Plus, injection molding takes a lot of energy and materials and there is a lot of unused or waste plastic, which is also bad for the world.
Injection molding has high initial costs.True
The cost of mold creation and machine setup can be significant, making it more suitable for large-scale production runs.
Injection molding is always the most cost-effective option.False
For small batches or highly complex designs, injection molding may not be the most cost-effective choice due to the upfront mold costs and design limitations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plastic injection molding is a common manufacturing process, although injection molding sometimes has low labour costs and low cost,it also has some obvious disadvantages.
These disadvantages include low efficiency, high initial cost, irreversible injection molding process, and high scrap rate. While using this process, companies need to be aware of these problems in order to better solve them and improve production efficiency and economic benefits.
-
Learn about How to Calculate the Filling Time of an Injection Molding Machine? Injection molding machine fill time is one of the most crucial factors in injection molding. ↩
-
Learn about Injection Speed : The injection speed essentially determines the degree of molecular orientation and, thus, affects the adhesion, orientation, and shrinkage . ↩
-
Learn about Cavity pressure : In injection molding, cavity pressure is a key indicator of the quality of the molded part that is produced. ↩
-
Learn about The importance of cooling time in injection molding : Cooling time will directly affect the molding cycle and output of plastic products. ↩
-
Learn about Injection Molding Defects: Sink Marks : Sink marks are one of the most common injection molding defects that usually occur as depressions in the thicker sections of the plastic part. ↩
-
Learn about Draft Angle Guidelines for Injection Molding : Draft is a taper applied to the faces of the part that prevent them from being parallel to the motion of the mold opening. ↩
-
Learn about The Eight Types of Injection Molds : In mold types commonly encountered, we find the two-color mold, overmolding, and family mold. ↩