Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves the use of molds to make plastic products.
The molten plastic flows into the plastic injection molds, where it is cooled and takes the shape of the mold. This process is used to create everything from toys to car parts.
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at how injection molding works and discuss some of its benefits.

Principle of injection molding
The principle of injection molding is that the plastic in the form of pellets or powder is fed into the barrel from the hopper of the plastic injection molding machine, heated and melted to a flowing state in the barrel, and then injected into the closed mold cavity at a lower temperature through the nozzle at the front of the barrel at a faster speed under the impetus of the plunger or screw.
After cooling and curing, the injection unit is obtained. When the accumulation of molten material at the front of the barrel causes a certain pressure on the screw (called the backpressure of the screw), the screw backs up in rotation until it makes contact with the adjusted stroke switch, and the pre-molding and storage of plastic with one injection volume of the mold (i.e., the storage of molten plastic at the front of the barrel) ends.
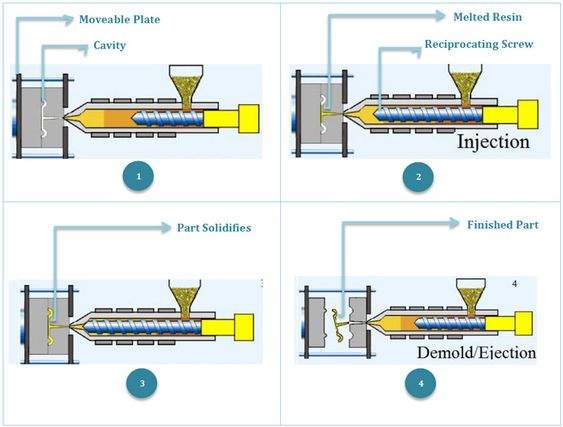
Then the hydraulic injection cylinder starts to work, and the screw connected to the piston of the hydraulic cylinder injects the molten material at a certain speed and pressure into the closed mold cavity at a lower temperature through the nozzle at the front of the barrel, holding the pressure for a certain time, and the molten plastic cools and cures to maintain the shape and size given by the mold cavity.
The mold is opened by the opening and closing mechanism, and the injection-molded plastic parts are removed by the pushing mechanism.
Injection Molding Process Conditions
The most important factors in the injection molding manufacturing process conditions are temperature, pressure, and time.
(1) Temperature
The temperature to be controlled in the injection molding process is mainly barrel temperature, nozzle temperature, and mold temperature.
Barrel temperature
The choice of barrel temperature is related to the variety and characteristics of plastic materials. If the barrel temperature is too low, the plasticization will not be sufficient; if the barrel temperature is too high, the plastic may be overheated and decomposed.
The temperature distribution of the material is generally based on the principle of high front and low back, i.e., the temperature at the back end of the barrel is low and the temperature at the front end near the nozzle is high to prevent degradation of the plastic due to sheer friction heat.
For the screw injection machine to prevent the shear friction heat between the screw and melt, melt and melt, melt and barrel and plastic degradation, the temperature of the front part of the barrel can be slightly lower than the middle part.
To determine whether the barrel temperature is appropriate, the air injection method can be used to observe or directly observe the quality of plastic parts.

When injecting into the air, if the material flow is uniform, smooth, no bubble, uniform color, it means that the material temperature is appropriate; if the material flow is rough, there is silver or discoloration, it means that the material temperature is not appropriate.
Nozzle temperature
Nozzle temperature is generally slightly lower than the maximum temperature of the barrel, to prevent the temperature from being too high to melt in the nozzle salivation phenomenon.
Mold temperature
Mold temperature has a great influence on the flow of the melt, cooling rate, and the performance of the molded part.
The temperature of the mold depends on the crystallinity of the plastic, the size of the molded part, and the performance of the molded part. Structure and performance requirements and other process conditions (such as melt temperature, injection speed, and injection pressure).

(2) Pressure
The pressure in the injection molding process includes plasticizing pressure and injection pressure, which directly affect the plasticization of plastic and the quality of plastic parts.
Plasticizing pressure, called backpressure, refers to the pressure on the melt at the head of the screw when the screw is rotating and backing off when a screw injection machine is used.
The plasticizing pressure increases, the temperature of the melt and its uniformity increases, the mixing of the color material is uniform, and the gas in the melt is discharged. However, the plasticizing rate decreases, and the molding cycle is prolonged.
In general operation, under the premise of ensuring the quality of plastic parts, the plasticizing pressure should be as low as possible, generally about 6MPa, usually rarely more than 20MPa. Injection pressure is the pressure exerted by the plunger or screw head on the plastic melt.
Size: The size of injection pressure depends on the plastic species, injection machine type, mold structure, the wall thickness of plastic parts, and other process conditions.
Function: To overcome the flow resistance of the melt in the process of filling the injection mold when injecting, so that the melt has a certain filling rate; to compact the melt and prevent backflow when holding the pressure.
In general: injection pressure for high viscosity plastics > low viscosity plastics; high injection pressure for thin-walled, large-area, complex-shaped plastic parts; simple mold structure, larger gate size, lower injection pressure.
Plunger injection machine injection pressure > screw injection machine; barrel temperature, mold temperature is high, the injection pressure is lower.
(3) Time
The time required to complete an injection molding process is called the molding cycle. It includes mold filling time, holding time, in-mold cooling time, other times, etc. Other times include mold opening, mold release, mold release agent application, insert placement and mold closing, etc.

Injection Molding Process
Mainly includes preparation before molding, injection process and post-treatment of plastic parts, etc.
(1) Pre-forming preparation
The main preparations before the injection molding cycle are inspection of the appearance and process performance of raw materials, preheating and drying; cleaning or replacement of the barrel of the injection machine.
For mold release difficulties, a reasonable choice of release agent; preheating of the insert, some molds also need to preheat.
Material appearance inspection and process performance measurement: including plastic color, particle size and uniformity, fluidity (melt index, viscosity) thermal stability, and shrinkage inspection.
Plastic preheating and drying: remove excess moisture and volatile thees from the material to prevent defects or degradation on the surface of the injection molded parts, which affects the appearance and internal quality of the plastic parts.
Material drying methods: small batch production, using oven drying; large batch production, using boiling drying or vacuum drying.
Barrel cleaning: when changing products, changing raw materials and colors are required to clean the barrel.
Preheating of the insert: reduce the temperature difference between the material and the insert, reduce the shrinkage stress of the plastic around the insert, and ensure the quality of the plastic parts.
The choice of release agent: commonly used release agents include zinc stearate, liquid paraffin, and silicone oil.

(2) Injection process
The injection process is the main stage of plastic transformation into plastic parts. It includes several stages such as adding material, plasticizing, injecting, holding pressure, cooling and shaping, and demolding.
Feeding: Adding granular or powdered plastic to the hopper of the plastic injection molding machines.
Plasticizing: The plastic material in the screw is heated by the heating device of the injection molding machine to melt and become a plastic melt with good plasticity.
Injection: The plasticized plastic melt is pushed by the plunger or screw of the injection machine, and passes through the nozzle and the pouring system of the mold at a certain pressure and speed to enter and fill the mold cavity.
Pressure-holding and shrinkage replenishment: After the melt fills the cavity, the melt still keeps the pressure for replenishment under the push of the plunger or screw of the injection machine, so that the melt in the barrel continues to enter the cavity to replenish the shrinkage needs of the plastic in the cavity, and it can prevent the melt from backflowing.
Cooling after gate freezing: After some time make the molten plastic in the cavity solidify into a solid, to ensure that the plastic part has enough rigidity to not warp or deform when the mold is released.
Demoulding: The molded part is cooled to a certain temperature, and the molded part is pushed out of the mold by the push-out mechanism.
(3) Post-treatment of the molded part
Post-treatment can eliminate the internal stress of the plastic part, and improve the performance of the plastic part and the stability of the size.

The post-treatment of plastic injection parts manufacturing includes annealing and wetting treatment.
Annealing treatment is to make the plastic parts in a fixed temperature heating liquid medium (such as hot water, hot mineral oil, liquid paraffin, etc.) or hot air circulation oven for some time, and then slowly cool. Its purpose is to eliminate the internal stress of the plastic parts and stabilize the size.
a) Temperature: 10°~15° above the use temperature or 10°~20° below the heat deflection temperature.
b) Time: related to the plastic variety and thickness of the plastic part can generally be calculated by about half an hour per millimeter.
c) Effect: To eliminate the internal stress of the plastic part, stabilize the size of the plastic part, improve the crystallinity and stabilize the crystalline structure, to improve its elastic modulus and hardness.
Humidity adjustment treatment: a post-treatment method to put the plastic parts which have just been remolded into the heating medium (such as boiling water, potassium acetate solution) to accelerate the moisture absorption equilibrium speed. (Mainly used for plastics with strong hygroscopicity and easy oxidation, such as PA)
a) Temperature: 100~121℃ (the upper limit is taken when the heat deformation temperature is high, and the lower limit is taken vice versa).
b) Time: insulation time is related to the thickness of plastic parts, usually taking 2~9h.
c) Purpose: to eliminate residual stress; to make the products reach moisture absorption equilibrium as soon as possible to prevent dimensional changes during use.

Process Parameters of Injection Molding
Humidification treatment is a treatment method in which the freshly demolded plastic parts are placed in hot water to isolate the air, prevent oxidation of the plastic parts, and accelerate the achievement of moisture absorption equilibrium. The purpose is to stabilize the color and size of the molded part and improve its performance.
Injection process
It generally includes the following steps: adding material, plasticizing, mold filling, holding pressure, pouring, cooling and demolding.
- Adding material
The pellets are added to the hopper of the injection molding machine. - Plasticizing
The added plastic is added in the hopper to make it change from solid particles to molten states and have good plasticity, this process is called plasticization. - Mold filling
The plasticized melt is pushed by the plunger or screw to the front of the barrel, then through the nozzle and mold pouring system into and fill the cavity, this stage is called mold filling. - Holding pressure
When the melt in the mold cools and shrinks, the plunger or screw forces the melt in the barrel to continuously replenish the mold, thus forming a plastic part with complete shape and dense texture, this stage is called pressure-holding. - Backflow
At the end of the holding pressure, the plunger or screw recedes and the pressure in the cavity is lifted.
At this time, the pressure of the melt in the cavity will be higher than that in front of the gate, if the gate is not yet frozen, the melt in the cavity will flow back to the casting system through the gate, this process is called backflow.
This process is called backflow. Backflow causes shrinkage, deformation, and loose texture of the molded part. If the gate is already frozen at the end of holding pressure, there will be no backflow.
- Cooling
The cooling process of the plastic part in the mold is the whole process from when the plastic melt at the gate is completely frozen to when the plastic part will be pushed out of the mold cavity. This will then cool down to form a solid product. Finally, ejectors push the cooled product out of the machine as a finished part. The injection moulding manufacturing process is complete.

The cooling process starts when the plastic is injected into the cavity, and it includes the period from the completion of mold filling and pressure-holding to the time before demolding.
- Demolding
The mold is opened when the part cools to a certain temperature, and the part is pushed out of the mold under the action of the push-out mechanism.
The key parameters that determine the quality of the product are temperature, time, pressure, speed, and position.