Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering precision and versatility for producing complex parts with high efficiency.
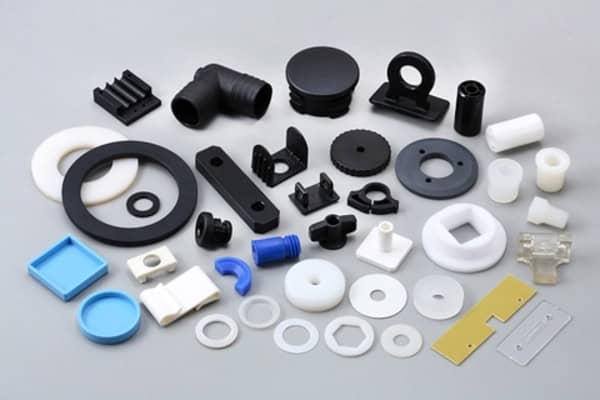
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into a mold to create parts with high accuracy and repeatability. It is widely used in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. Key benefits include high production speed, cost efficiency for large volumes, and the ability to produce intricate designs.
While this overview covers the basic advantages of injection molding, understanding its various components and process stages is vital for maximizing its efficiency and quality. Dive deeper into specific techniques to further optimize your production.
Injection molding is the most cost-effective process for high-volume production.True
Injection molding is ideal for mass production due to its ability to produce large quantities of consistent parts quickly and with minimal waste.
Injection molding can only be used with plastic materials.False
Although injection molding is primarily used for plastics, it can also be used with metals and other materials in specific applications like metal injection molding (MIM).
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a versatile process where molten material is injected into a mold to create precise parts. It is efficient, cost-effective, and can produce high volumes of complex shapes. Key benefits include reduced material waste, faster production times, and the ability to use a wide range of materials.
Injection molding is the process of injecting molten plastic or metal into a mold under high pressure. It’s used to mass produce complex parts with consistent quality and precision. The molds you choose or create are important because they affect the final product. They also determine how well the details of your complex parts are captured. Each injection molding project needs a unique mold based on size and shape.
How Does the Injection Molding Process Work?
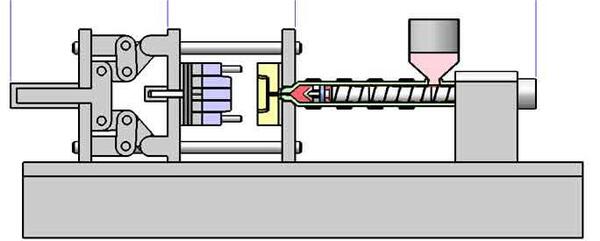
The injection molding process involves melting plastic material and injecting it into a mold cavity under pressure. After cooling, the part is ejected from the mold. It\’s efficient, cost-effective, and commonly used in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer products. Key advantages include high production rates, precision, and the ability to create complex shapes.
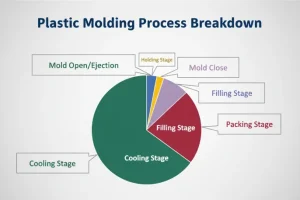
Plastic injection molding is a process that involves a series of steps, each of which is important in creating high-quality plastic parts. Let’s take a closer look at each step:
Clamping
First, we clamp the mold. This is when we close the mold to keep the plastic from leaking out when it gets hot. We use a clamping device to push the mold halves together and make sure they’re sealed tight. This is the first step in the process and it’s important because it keeps everything stable when we inject the plastic and let it cool.
Injection
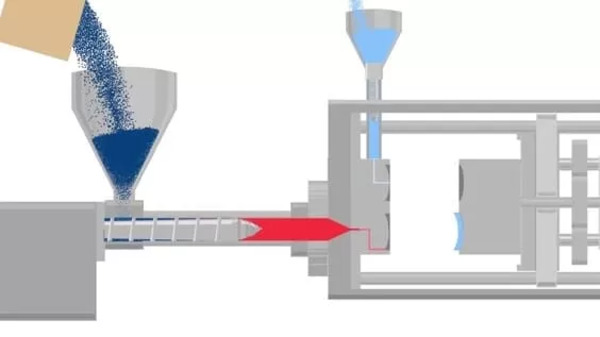
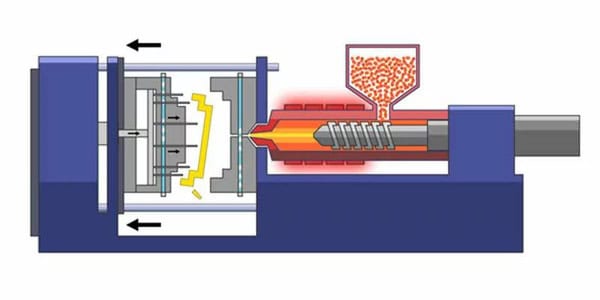
The injection phase starts with the injection of molten plastic into the mold cavity under high pressure. Molten plastic is plastic that has been melted to its melting point. This step requires precise control of injection speed1, pressure, and temperature to make sure the material completely and evenly fills the cavity.
Usually, a screw inside an injection molding machine pushes the melted material forward into the mold under controlled conditions. When you put pressure on the injection, the melted plastic goes through the runner system and into the mold cavity, where it takes on the shape of the part you want.
Dwelling
After the hot plastic is shot into the mold, there’s a little pause called the holding phase.In this phase, the material just sits there in the metal mold, letting it settle and build up evenly. You have to let it sit there long enough to make sure it spreads out and fills in all the little nooks and crannies of the part. This is what helps keep the part from having any holes or gaps and makes it solid and even all the way through.
Heat Sink
After the packing phase, the mold goes into a cooling phase where the molten plastic inside the mold cavity hardens. Cooling can be done in a number of ways, like running a coolant through channels in the mold or letting the mold cool down on its own in the air.
Cooling is super important to get the part properties you want, make sure the part is the right size, and stop the part from getting all bent out of shape. We control how fast the part cools down and how even the cooling is to make sure the part doesn’t get all stressed out inside and to make sure the part cools down the same way all over.
Mold Opening
Once the plastic hardens, the mold opens and the two halves separate to show the part.Mold opening is usually done with a hydraulic or mechanical system that applies force to the mold\’s clamping mechanism to release and open it. Precision and consistency are important during this phase to make sure the part is ejected smoothly without damage. Proper mold opening also helps prevent any deformation or distortion when the part is released from the cavity.
Ejection (Part Removal)
Once the mold is opened, the final plastic part is kicked out of the mold cavity, which is the last step of the injection molding process. The kicked out part can be taken out by the operator or automatically by using ejector pins or ejector plates that are built into the mold design.
When you’re taking parts off, be careful not to mess them up. You can also cut off any extra stuff, called flash2, to make the part look and fit right.
What Materials are Used for Injection Molding?
Common materials used in injection molding include thermoplastics like ABS, polycarbonate, and polypropylene, as well as thermosets like epoxy and phenolic. These materials are selected based on factors like strength, durability, and heat resistance. Thermoplastics are particularly popular for their ease of processing and recyclability, while thermosets are favored for their superior heat resistance and electrical insulation properties.
The choice of material isn’t random; it’s a strategic decision based on what you’re making. Whether it’s the clarity of polycarbonate in an optical part or the wear resistance of nylon in a mechanical part, each material plays a critical role in the success of the injection molding process.
Polypropylene (PP)
PP, or polypropylene, is a versatile thermoplastic3 that has a lot of uses in the injection molding industry. It’s lightweight, can handle chemicals well, and is really good at resisting fatigue. That’s why it’s a popular choice for making things like packaging, containers, and car parts.
ABS
ABS, or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, is a super strong, impact-resistant, and dimensionally stable plastic. It’s also easy to mold and color, which is why it’s a popular choice for making things like consumer goods, automotive parts, and electronic housings.
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is a lightweight plastic that’s known for being flexible and cheap. It has different types like HDPE and LDPE and can be used in a bunch of different industries from packaging and containers to agricultural products and toys.
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is clear, hard and cheap. PS is often used in throwaway stuff like packaging, food containers and throwaway cutlery, and is liked for its easy molding and cheapness.
Nylon (PA 6)
Nylon, especially nylon 6 or PA 6, is known for being strong, tough, and wear resistant. It’s great for making mechanical parts and is used a lot in things like gears, bearings, and other parts that need to be made fast, last a long time, and be made just right.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate, or PC, is known for being clear, tough, and able to handle high temperatures. That’s why it’s used to make things like eyeglass lenses, parts for electronics, and clear parts that need to last a long time in all kinds of industries.
Acetal/Polyoxymethylene Resin(POM)
POM, also known as acetal or Delrin, is a super strong engineering plastic that doesn’t change shape. It’s perfect for making gears, bushings, and other parts that need to be just right. It’s also slippery and doesn’t wear out, and it can handle chemicals.
What are the Advantages of Injection Molding?
Injection molding offers several key advantages, including fast production times, high precision, and the ability to create complex geometries. It reduces material waste and allows for the use of multiple materials in a single process. Key benefits include cost-effectiveness for large runs, design flexibility, and minimal post-production work.
Injection Molding Offers Complex Part Designs
Injection molding is great for making complex parts, keeping things consistent, and making a million parts that are all the same. To make a lot of parts and make them good, you need to think about a few things.
Designing parts to take advantage of high-volume molding high-volume molding efficiencies is key. With the right design, you can make high-quality parts without sacrificing complexity.
Injection Molding Can Increase Production Efficiency And Speed
There are a lot of good reasons why this is the most common and effective form of molding. First, the injection molding process is faster than other methods, and the high production output makes it more efficient.
The speed depends on the complexity and size of the mold, but there are only about 15-120 seconds between each molding cycle. With shorter cycles between cycles, more injection molded parts can be produced in a given production time.
Injection Molding is Stronger
Over the years, plastics have gotten a lot stronger and more durable. Modern lightweight thermoplastics can handle the toughest environments just as well as metal parts, and sometimes even better.
Plus, there are over 25,000 engineering materials to choose from for complex injection molding applications. You can also make high-performance plastic blends and hybrids to meet specific part requirements and properties, like high tensile strength.
Injection Molding is Flexible in Color and Materials
Plastic injection molding is a flexible process. It’s flexible in the properties of the plastic used. It’s flexible in the ability for the OEM to customize color choices to meet specific project requirements. The benefit of plastic injection molding is the freedom of design choices it offers to OEMs, especially when compared to metals. You can use many materials.
The molding process can achieve the desired color by adjusting the plastic, additives, and biocompatibility to produce transparent parts or a variety of colors. However, when a product often requires multiple colors, this can be achieved through overmolding.
Injection Molding Reduces Waste
Plastic injection molding doesn’t produce much waste compared to other manufacturing processes. The only waste plastic comes from the gates and runners. But any leftover or scrapped plastic can be ground up and recycled for future use.
Low Labor Costs for Injection Molding
Injection molding operations have low labor costs compared to other types of molding processes. The ability to produce high-quality parts at high production rates helps to reduce manufacturing costs through its efficiency and effectiveness.
Molding equipment often comes with auto-gating, automated process tools to keep operations streamlined and mass production conducted with minimal supervision.
Injection Molding Offers a Variety of Surfaces
Most injection molded parts have a smooth surface finish that is close to the desired final appearance. However, a smooth appearance is not suitable for all applications.
Depending on the physical and chemical properties of the plastic material used, the plastic injection molding manufacturing process creates a surface finish that does not require secondary operations. The process provides flexibility in surface treatments, from matte surfaces and unique textures to engraving.
What are the Disadvantages of Injection Molding?
Injection molding disadvantages include high upfront tool costs, limited design flexibility, and long setup times. It\’s also unsuitable for small production runs due to the initial investment in molds. Additionally, complex designs may lead to challenges with material flow and cooling. Key concerns include potential warping, sink marks, and high energy consumption in some cases.
High Initial Mold Cost
One of the big downsides of injection molding is the high cost of making molds. Designing and manufacturing molds that fit specific part geometries can be very expensive, especially for complex or intricate designs. This initial investment can be a deal breaker for companies with smaller production runs or limited budgets.
Takes Longer to Get Started
Injection molding usually takes longer to set up and start than some rapid prototyping methods like 3D printing. You have to design and make molds, run mold trials, and dial in process parameters before you can start making parts in volume. So the time from concept to finished part can be longer than with faster prototyping methods.
Size Limitations
Injection molding can be limited in size, especially for big parts. The size of the injection molding machine and the size of the cavity can limit the biggest part you can make. If you want to make really big parts, you might need special equipment or multiple mold cavities, which makes it more expensive and complicated.
Design Limitations
Injection molding is super versatile for making all kinds of shapes and details, but there are still some things you gotta think about when you’re designing your part. Some shapes, like sharp corners, thin walls, or deep holes, can make it harder to fill the mold, cool the part, or get it out of the mold.
When you’re designing an injection molded part, you gotta think about things like draft angles, wall thickness, and other stuff to make sure your part can be made and will be good quality. Sometimes you might need to add extra stuff to the mold or do extra things to the part to make it work, and that can make it more expensive.
What are Some Common Defects in Injection Molding?
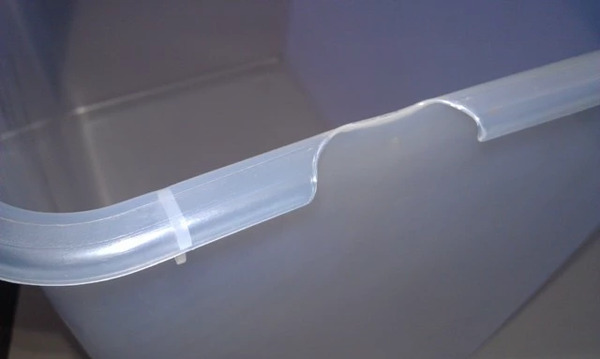
Common injection molding defects include warping, short shots, sink marks, and flash. Warping occurs when the material cools unevenly, while short shots result from insufficient plastic flow. Sink marks are depressions caused by uneven cooling, and flash refers to excess material leaking from mold cavities. Understanding these defects helps in troubleshooting and improving molding quality.
Injection molding is a process that requires precision at every stage. However, even with the utmost care, defects can occur that can affect the quality and functionality of the final product. Understanding and addressing these defects is critical to achieving consistently high-quality results. Here are common defects in injection molding.
Injection molding is a process that needs to be done just right. But even if you do everything right, sometimes things go wrong. And when they do, it can mess up your parts. So, you need to know what can go wrong and how to fix it. That way, you can make good parts every time.
Warpage
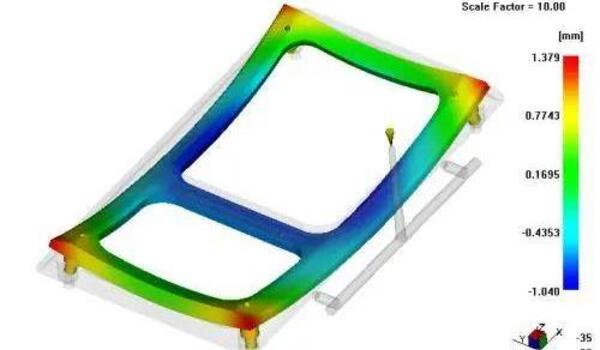
Warpage in injection molding is when your part twists or bends unexpectedly because the inside of the part shrinks unevenly as it cools. This happens when the mold cools unevenly or inconsistently, which puts stress on the material.
To prevent warpage, make sure the walls of your mold are the same thickness all the way around and give your part enough time to cool down slowly. Materials that have a semi-crystalline structure are especially prone to warping.
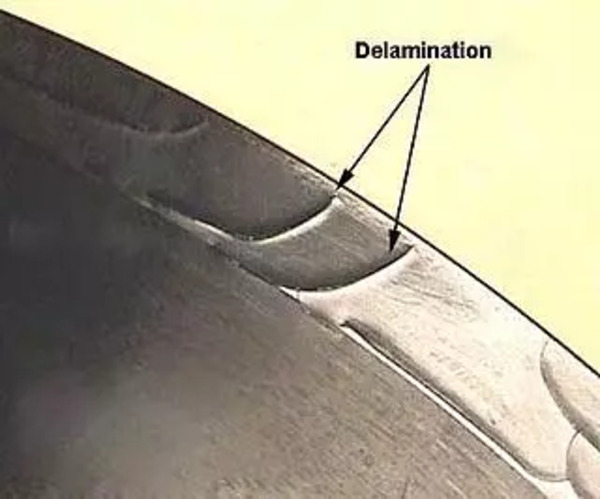
Surface delamination
Surface delamination is when the surface of a part separates into thin layers, similar to a peelable coating. This problem is caused by contaminants in the material or using too much mold release agents.
Delamination is bad because it makes the part look bad and it’s not as strong. You can stop it by making sure the mold is the right temperature, not using too much mold release, and drying the plastic before you use it.
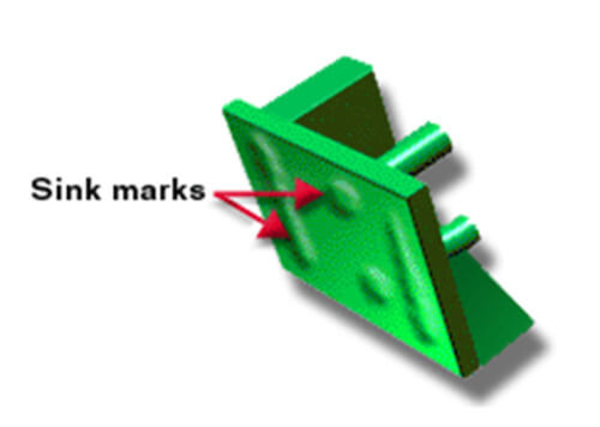
Sink Marks
Sink marks are those little dents or depressions you sometimes see on the surface of a molded part. They’re caused by uneven cooling or by the material not filling the mold completely. In this article, we’ll explain what sink marks are, what causes them, and how to fix them so you can have a smooth, perfect surface.
Weave or Weld Lines
Meld lines or weld lines are where two streams of molten resin meet on their way through the mold. These lines often form around holes in a geometric shape. As the plastic flows around the hole, the intersection of the two streams creates a visible line.
Weld lines are bad. They make parts weak. You can get weld lines if the resin is too cold or if you inject too slow or if you don’t have enough pressure. You can get rid of weld lines by changing the mold. You can take out the things that make the weld lines.
Drag Marks
Drag marks, also known as streaks or scratches, can ruin the look of an otherwise perfect part. We’ll take a closer look at what causes drag marks, from mold temperature to injection speed, and talk about practical ways to get rid of this defect and make molded parts and products look better.
Flow Lines
Flow lines are complex patterns that are often discolorations, streaks, or variations on the surface of a part. These marks are a visual representation of the molten plastic as it moves through the injection mold. As the plastic moves at different speeds, it solidifies at different rates, creating these lines.
If you see flow lines, you might have a problem with injection speed or pressure. You can minimize this defect by making sure the wall thickness is consistent and the gate is in the right place.
Short Shots
A short shot is when the resin doesn’t fill the mold all the way, so you end up with a part that’s not complete and you can’t use it. Things like flow restrictions in the mold, small gates, gates that are blocked, trapped air, and not enough injection pressure can all cause short shots.
Understanding these issues is critical to optimize the injection molding process and ensure complete, consistent part production.
What are the Main Applications of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is used in automotive, consumer goods, medical devices, and electronics industries to produce complex, high-volume parts. It offers benefits like cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and fast production speeds. Key applications include automotive components, medical instruments, packaging, and household items.
Injection molding is the best way to make plastic parts. It’s used to make things like phone cases, bottles, car parts, combs, and almost everything else made of plastic. Injection molding is great for making a lot of parts because you can make many parts at once with a mold that has many parts in it.
Some of the good things about injection molding are that it makes parts that are very accurate, you can make the same part over and over again, you can use lots of different materials, it doesn’t take a lot of people to make the parts, you don’t waste a lot of plastic, and you don’t have to do much to the part after it’s made. Some of the bad things about injection molding are that it costs a lot of money to make the mold and there are some things you can’t do with it.
Automotive Industry
Plastic injection molding is used a lot in the car industry to make inside and outside parts like dashboards, panels, and bumpers. It makes parts that are strong and last a long time.
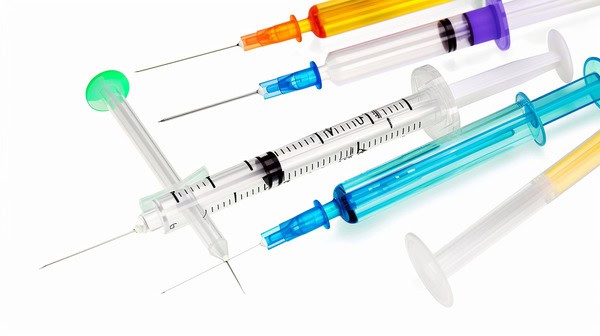
Medical Industry
The medical industry uses plastic injection molding a lot to make medical devices and equipment, like syringes, IV components, and diagnostic tools. It’s a way to make sterile, precise, consistent products that meet strict safety and regulatory requirements.
Consumer Products Industry
The consumer products industry uses plastic injection molding to make all sorts of things, like toys, kitchen stuff, and electronics. It’s a way to make really good-looking products that are the right size and shape and work the way they’re supposed to.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry uses plastic injection molding to make lightweight and durable parts, like interior panels and air ducts. This process lets you make complex shapes that are strong but don’t weigh much, which is important for aerospace stuff.
Construction Industry
The construction industry uses plastic injection molding to make building components like insulation, piping, and electrical fittings. This process makes durable and cost-effective products with exact dimensions and functional characteristics.
Plastic injection molding is a super versatile and reliable manufacturing process that finds application across a wide range of industries. Its ability to produce high-quality, consistent, and super specific products with minimal waste makes it a preferred manufacturing method for many companies.
Conclusion
Plastic injection molding is a super popular way to make stuff. It’s a manufacturing process that’s been around for a long time and has a lot of benefits. It’s super efficient, cheap, and versatile. It’s also really good at making stuff without wasting a lot of material.
You have to think about a few things when you’re doing it, like what kind of plastic to use, how to make the mold, how many things you want to make, what to do after you make them, and how to make sure they’re good. But if you do it right, you can make all kinds of things with injection molding. You can make car parts, medical stuff, things for people to buy, airplane parts, and even buildings.
If you want to know more about Injection Molding, you can visit https://zetarmold.com/ for more information.
-
Learn about Why is injection speed important : Injection speed is a critical factor when creating a plastic product. ↩
-
Learn about What Causes & How To Avoid Flash In Injection Molding Process: Injection molding flash is a defect that occurs when molten plastic flows out of the mold during injection and solidifies. ↩
-
Learn about Thermoplastic : A thermoplastic is any plastic polymer material that moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. ↩