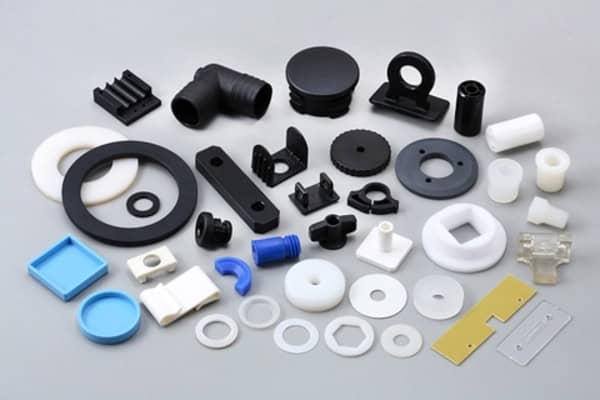
Low-volume injection molding provides an efficient and cost-effective solution for producing small quantities of parts, making it ideal for prototyping and limited production runs across industries.
Low-volume injection molding offers flexibility and cost savings by allowing the production of smaller part quantities without the high costs of traditional mass production. This process is widely used in medical devices, consumer electronics, and automotive industries for prototyping and short-run manufacturing. Key advantages include faster turnaround times, reduced waste, and lower tooling costs.
While low-volume injection molding presents clear benefits for limited production needs, understanding its specific tooling, material selection, and design considerations is essential for maximizing its value. Dive deeper to learn how to optimize your low-volume production strategy.
Low-volume injection molding is less cost-effective than mass production.False
Low-volume injection molding is actually more economical for small batch sizes due to lower tooling and setup costs.
Low-volume injection molding is best for prototyping and small production runs.True
This process is ideal for testing and limited runs, as it allows for faster, more flexible production without extensive tooling costs.
What is Low-Volume Injection Molding?
Low-volume injection molding involves producing fewer than 10,000 parts using standard injection molding machines. It is ideal for prototyping, testing, and small batch production. The process helps reduce tooling costs and time to market, making it a cost-effective solution for early-stage product development and limited production runs.
Injection molding is a process where you shoot melted stuff into a mold, where it cools and hardens into the part you want. You can use it with lots of different materials and it gives you really nice, high-quality finishes and parts that are the same every time. It’s always been thought of as the best way to make a lot of parts. But low-volume injection molding has also turned out to be really useful in a bunch of different industries.
Also called low-volume injection molding, it’s ideal for prototyping, creating custom parts, and small-batch production. It’s cost-effective, has shorter lead times, and offers design flexibility. It also gives businesses a path for scaling.
What are the Materials Used for Small Batch Injection Molding?
Common materials for small batch injection molding include thermoplastics such as ABS, polypropylene, and polycarbonate, as well as engineering plastics like nylon and PEEK. These materials offer durability, flexibility, and high performance. Selecting the right material depends on factors like part complexity, desired strength, and environmental conditions.
Low-volume injection molding is a versatile process that can handle a variety of materials, such as thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, and composites. The material you choose depends on what you need the part to do, how well it needs to perform, and how complicated the part is.
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics are the most commonly used materials for low-volume injection molding. They’re known for their excellent mechanical properties, durability, and ease of processing. Some common thermoplastics used in low-volume injection molding include polypropylene, polyethylene, ABS, and polycarbonate.
Thermosets
Thermosets are materials that cure through a chemical reaction to form hard, durable parts. They have high strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability, making them ideal for applications that require high-performance functionality. Examples of thermosets used in low-volume injection molding include epoxies, phenolics, and melamine.
Elastomers
Elastomers are materials that have rubber-like properties, such as being highly elastic, flexible, and resistant to deformation. They are commonly used by manufacturers in applications are used in low-volume injection molding are silicone, natural rubber, and nitrile rubber.that require seals, gaskets, and other flexible parts.
Composites
Manufacturers combine two or more materials to form composites to create stronger, more durable fabrics. They have excellent strength-to-weight ratios, impact resistance, and other desirable properties. Examples of composites used in low-volume injection molding include fiberglass, carbon fiber, and Kevlar.
What are the Design Considerations for Small Batch Plastic Parts?
Design considerations for small batch plastic parts include material selection, part geometry, and production methods that minimize waste. A key challenge is optimizing mold design to ensure quick setup times and minimal tooling costs while maintaining high-quality results. Common considerations also include the impact of part size and complexity on cycle times and cost.
When you’re designing something, you need to think about how it’s going to be made. Here are some things to keep in mind:
Choosing the Right Material for Your Molded Part
When it comes to low-volume injection molding, choosing the right material is a big deal. There are a bunch of different commercial-grade plastic materials to choose from.
What material you choose depends on what you’re going to use your low-volume plastic part for and where you’re going to use it.
Finishing the Surface Finish of the Part
One of the most common mistakes in plastic injection molding is selecting a better surface finish than necessary. This can seriously affect the function of the product. For example, a very smooth surface finish requires hand polishing of the mold cavity surface. Polishing can be done with diamond polishes up to 2 Ra.
This practice significantly increases mold manufacturing costs and lead times. A more cost-effective surface finish is a milled surface that may show some tool marks. Two other available options involve using 600 grit stone or a sandblasted textured finish. The surface finish selected must be compatible with the function of the part.
Scale Wall Thickness in Both Directions
Wall thickness is super important for fast injection molding. You don’t want walls that are too thick for the plastic family you’re using. If you do, those walls might sink, deform, or have other molding defects. A good rule of thumb is to always use wall thicknesses between 0.04 and 0.14 inches throughout the part.
Multi-Cavity Molds May be a Good Choice
If you want to mold multiple identical parts at once, multi-cavity molds are your friend. They’re great for making two or more designs with minor iterations at the same time. This lets you test different product designs quickly. They’re also a good choice when you need more than just a sample. Plus, they can help you lower your unit costs.
How Does Low-Volume Injection Molding Production Run?
Low-volume injection molding allows manufacturers to produce high-quality plastic parts with fewer molds and reduced setup costs. This process is ideal for runs ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand units. It is often used for prototype development, limited edition products, and market testing. The key benefits include faster time to market and lower upfront costs compared to traditional high-volume production.
Optimized Design for Manufacturability
Design for manufacturability (DFM) covers every aspect of the injection molding process, from part design, mold design, material selection to processing. You don’t have to wait until production to find out if there are design problems. With optimized DFM, our engineers will make sure your parts can be molded and injection molded, and save you as much manufacturing cost as possible.
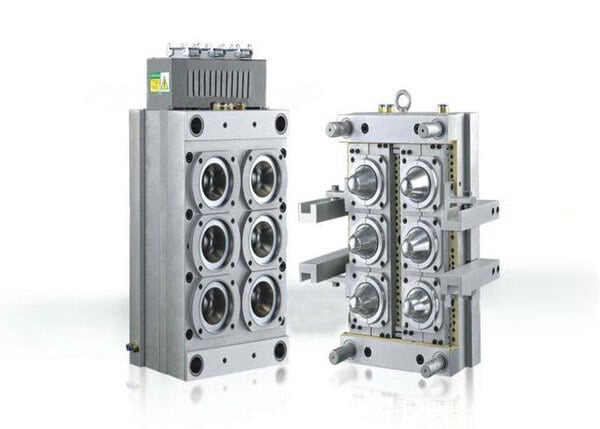
Choosing the Right Mold Material
Choosing the right mold material involves considering factors such as usage, quantity, budget, as well as design complexity, mold structure, etc. Not sure which one to choose? We will help you weigh each of these advantages to find the best solution for your product needs.
We can make rapid molds using aluminum 7075, P20 and NAK80 semi-hardened steels, and H13 fully hardened steel. We also offer standard SPI polishing, EDM textures, and a range of etched textures, including the Mold-Tech® MT series and VDI® 3400 series.
Cost-Effective Mold Manufacturing Process
To meet the needs of fast production and cost reduction, we usually use the MUD mold quick change system method to save mold opening time and reduce costs. More importantly, the engineering change only involves the MUD mold core part, not the entire standard mold base. You can also arrange several similar parts in a set of molds to save more money. In addition, manual or semi-automatic inserts are also often used in fast mold processing.
Zetar Mold\’s mold engineers will start the design review process with you. We believe that a good solution means full communication while ensuring that you have access to available resource options.
Injection Molding Machine
Once you’ve finished designing the mold and selecting the material, it’s time to set up the injection molding machine. The machine has three parts: the injection unit, the clamping unit, and the control system. The injection unit heats and melts the plastic material, while the clamping unit holds the mold in place during production. The control system controls the temperature, pressure, and other parameters during production.
Injection Molding Process
The injection molding process is divided into four sub-steps, which I will explain below:
Clamping
This involves using a clamping system that creates a clamping force that holds the mold in place, closing the gap between the mold halves. The clamping force should be equal to the injection force to prevent destructive movement, and should be lower in 3D printed injection molds that are protected by a metal frame.
Injection
It depends on the machine, but you transfer the molten plastic to an injection barrel and then inject it into the mold.
Heat Sink
Once the molten stuff is shot into the plastic injection mold, the molten plastic cools and hardens. The cooling/hardening time depends on the mold type, because heat transfer in plastics is slower than in metals, so it takes longer to cool. In this case, cooling can be improved by using compressed air or interchangeable chimneys.
Ejection
You can get small plastic parts out of the mold by hand or by using ejector pins. If you use ejector pins, the clamping plates move back and the mold halves open. Then the ejector pins push the final part out.
Quality Control and Post-Processing
Quality control is all about checking the small batch plastic parts for any defects and making sure they meet quality standards. Then, we trim the molded parts and use secondary surface finishing operations.
What are the Main Applications of Batch Injection Molding?
Batch injection molding is commonly applied in automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods industries. It allows for the production of multiple parts at once, reducing cycle times and improving cost-efficiency. Key benefits include scalability, high precision, and reduced material waste.
Low-volume injection molding is a cost-effective manufacturing solution for small and medium-sized businesses. The main applications of this manufacturing solution include:
Rapid Prototyping
It’s the perfect way to prototype plastic parts. It has advantages like fast and cheap production, easier testing and verifying designs before making mass production tools, and easier improvements.
Low-Volume Injection Molding
It’s also great for making small amounts of parts, which is a cheap way to do it, especially if you don’t have a lot of money to make a lot of parts. It’s cheaper than traditional injection molding and it’s good for small amounts of parts, so you can change your mind and make something else.
On-Demand Injection Molding
As the name implies, on-demand manufacturing allows businesses to make parts as they need them. This means they don’t have to keep a lot of inventory on hand, which saves on storage costs. It also makes it easier to respond to changes in demand, which is why low-volume plastic injection molding is a good fit for businesses in unpredictable industries.
What are the Main Advantages of Low-Volume Injection Molding?
Low-volume injection molding allows for the production of limited quantities of parts at a fraction of the cost of traditional molding methods. It is commonly used for prototyping, small production runs, and custom products. Key benefits include faster time to market, reduced upfront costs, and flexibility in design changes.
Injection molding is one of the main processes for rapid manufacturing. It is a fast-developing model that can speed up production time to market. However, traditional processes are not as fast as you would like. In some ways, the needs of the plastics market contradict the nature of production. The complexity of mold design may further increase the time required to manufacture a part. However, low-volume injection molding helps to effectively solve these problems. Here are some of its advantages.
Use of Softer Aluminum Tools
Low-volume injection molding doesn’t need the hardened steel molds that traditional molding methods require. Instead, it uses softer aluminum materials to make the molds. Aluminum is a much softer material than steel. So, it’s easier and faster to work with.
Plus, aluminum tools can be heat treated more easily because you don’t have to do an extra annealing step. You usually have to anneal steel tools to reduce any internal stresses and fully toughen the metal. Plus, aluminum molds can handle most of the surface treatments that you usually use for steel.
Quality Part Manufacturing
Low-volume injection molding is a practical manufacturing technology for producing many types of products. It produces highly durable and functional parts, despite the use of softer mold materials. Aluminum has better heat transfer rates than steel.
Better electrical conductivity makes the positioning of cooling lines less important. This allows for more mold components. Therefore, low-volume injection molding ensures better design flexibility, bridging the gap between prototyping and high-volume production.
People often think that you can save money when you buy things. That’s not always true. It’s true for household items, but not for building items. When you make things, the cost per unit is mostly about the materials you use to make it. Sometimes, high-volume injection molding companies have minimum order requirements. They do this to help pay for the big investment they made to make the thing.
On the other hand, low-volume injection molding usually has much lower overhead. They can make the thing without a minimum order. This is great if you want to make a few plastic things. You also won’t get things from old inventory. All of this saves you money.
Shorter Lead Time
Besides being cheaper, the manufacturing technology also makes plastic parts better. It works with a system that makes quotes faster. The software also checks the part design to make sure it’s right and fast.
Also, aluminum is soft, so it’s easier and faster to make molds. You don’t have to harden it to make it last longer. So, the molds can get to the factory faster and you can start making stuff. In a lot of cases, this makes the time to market a lot faster, which is good for small and big product teams.
Flexibility in Design
Large-scale injection molding means making a few parts in a short time. So, if you want to change the design, it’s not a big deal. That way, you can make the product perfect before you sell it.
Good plastic injection molding helps you make stuff better. It lets you try new things in different industries before you make a lot of parts.
If you want to make a lot of parts, small-scale plastic manufacturing is how you start. It helps you make a few parts before you make a lot. That way, you can make a good part without spending a lot of money. It also helps you make the part and the process better.
High-Quality Part Production
Even with softer mold materials, small-scale injection molds can produce more durable and fully functional products. You can make a lot of things with this production method. Plus, aluminum transfers heat to steel much faster than steel does. This increased conduction power means you don’t have to be as precise with the placement of coolant lines. You can grow more mold this way. So, the small-scale injection molding system gives you more design flexibility. It bridges the gap between mass production and prototyping.
Design Modularity
The goal of small-scale injection molding is to make fewer parts in less time. So, if a company wants to make small changes or modifications to the design, it’s not a big deal. You can use this process to iteratively improve products before you deliver them to customers.
Exceptional plastic injection molding gives you instant feedback, which improves the manufacturability of a product. It lets you test new concepts in a range of areas before you have to do expensive large-scale manufacturing.
Scale Overpass
If you want to mass-produce your products someday, you should start small-scale plastic manufacturing. It helps you go from prototyping to mass-production. Now you can make prototypes that can be made in large quantities. It also makes the process and the final product better.
What are Some Examples of Small Batch Injection Molding Applications?
Small batch injection molding is ideal for industries such as automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer goods. It is commonly used to produce prototypes, limited-edition products, and customized components. Key benefits include reduced tooling costs, faster turnaround times, and the ability to fine-tune designs without committing to large production runs.
Low-volume injection molding is used in many industries, such as automotive, medical, aerospace, and consumer goods. Some examples of low-volume injection molding applications include:
Automotive Industry
Low-volume injection molding is used in the automotive industry to produce small batches of customized parts like dashboard components, interior trims, and door handles. Porsche is a German luxury car manufacturer known for its high-performance sports cars and racing cars. Like any other luxury brand, Porsche uses low-volume production techniques to make its rarest and most exclusive cars.
Medical Devices
In the medical industry, low-volume injection molding is used to make small batches of custom parts. These parts include surgical instruments, drug delivery devices, and prosthetics.
Aerospace Industry
Low-volume injection molding is used in the aerospace industry to produce small batches of customized parts, such as air ducts, interior trims, and control panels.
Consumer Goods
Low-volume injection molding is used in the consumer goods industry to produce small batches of customized parts, such as smartphone cases, game controllers, and kitchen appliances. Louis Vuitton is a luxury fashion brand that was founded in 1854. It offers designer bags, shoes, clothes, accessories, and more. The company uses low-volume production techniques to keep things exclusive and luxurious.
Conclusion
So, in conclusion, low-volume molding is a great solution for companies that need to make small batches of custom parts. Whether it’s for prototypes, testing, or small batch production, low-volume molding has a lot of advantages over other manufacturing methods. It can make high-quality parts quickly and efficiently. It’s going to be a big part of the manufacturing industry in the next few years.
Zeta Mold is the best low-volume injection molding partner you can find. We use our experience, expertise, and great facilities to get your plastic parts from production to market in a short amount of time. Our quick quote system uses the latest technology to give you a quote in seconds.
We’re proud of how fast we can turn around small batch plastic injection moldingMaterials used in small batch injection molding services without sacrificing quality. If you choose Zetar Mold, you’ll get high-quality prototypes, short lead times, and affordable prices. Upload your design files and let us give you the best service you can get.