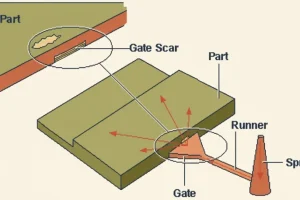
- Polyethylene1 (PE) injection molding requires melt temperatures of 180–280°C depending on grade, with HDPE at 220–260°C and LDPE at 180–240°C.
- PE has high shrinkage (1.5–3.0%) compared to amorphous plastics, requiring mold compensation factors of 1.015–1.030 in cavity dimensions.
- HDPE injection molding produces rigid containers, caps, and structural parts; LDPE produces flexible, impact-resistant components with superior low-temperature performance.
- PE requires minimal pre-drying (moisture content rarely exceeds 0.02%), saving processing time compared to hygroscopic resins like nylon or PC.
- PE injection molded parts are fully recyclable and widely accepted in recycling stream PE2 (HDPE) and PE4 (LDPE), supporting sustainability goals.
What Is PE Injection Molding and Which Grade Should You Use?
PE injection molding is the process of melting polyethylene resin and injecting it into a steel or aluminum mold cavity at pressures of 50–130 MPa to produce parts ranging from thin-walled caps and closures to thick-walled industrial containers and mechanical components. Polyethylene is the world’s most widely produced plastic, available in multiple density-based grades: LDPE (0.910–0.940 g/cm³), LLDPE (0.915–0.940 g/cm³), MDPE (0.926–0.940 g/cm³), HDPE (0.941–0.960 g/cm³), and UHMWPE (0.930–0.935 g/cm³, injection-molded only in specialized low-pressure processes).
Grade selection drives everything downstream. HDPE offers higher stiffness (flexural modulus: 700–1,400 MPa), better chemical resistance, and higher service temperature (70–120°C HDT) — making it the preferred choice for food-contact containers, industrial crates, pipe fittings, and caps. LDPE provides superior flexibility (flexural modulus: 200–400 MPa), exceptional toughness at low temperatures (-70°C ductile failure), and compliance with FDA regulations for food packaging. For injection molding, HDPE dominates the market due to its better flow properties and broader processing window compared to LDPE.
What Are the Key Processing Parameters for PE Injection Molding?
Melt temperature is the most critical processing parameter for PE injection molding. HDPE should be processed at 220–260°C barrel temperature, with the nozzle set 10–15°C above the front zone. LDPE processes at 180–240°C. Exceeding 300°C causes PE thermal degradation: oxidation and chain scission produce volatile compounds including aldehydes and ketones that discolor the material and generate gas bubbles. Processing below minimum temperature causes viscosity to increase dramatically, requiring higher injection pressures that stress the mold.
Injection pressure for PE typically ranges from 50–130 MPa depending on part complexity and wall thickness. PE’s relatively low viscosity (compared to PC or ABS) means it fills thin walls efficiently at moderate pressures. Holding pressure should be 30–60% of injection pressure, applied for a time sufficient to seal the gate — typically 3–8 seconds for standard gates. Back pressure during plasticizing is set low (3–10 MPa) to avoid shear heating that degrades PE’s molecular weight.
| Parameter | LDPE | HDPE | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melt temperature | 180–240°C | 220–260°C | Nozzle 10–15°C above front zone |
| Mold temperature | 20–50°C | 30–70°C | Higher = better crystallinity4, lower shrinkage variation |
| Injection pressure | 50–100 MPa | 70–130 MPa | Adjust for wall thickness |
| Holding pressure | 30–50% of injection | 40–60% of injection | Until gate freeze |
| Cooling time | 15–40 s | 20–60 s | Longer for thicker walls |
| Shrinkage | 1.5–2.5% | 1.5–3.0% | Higher mold temp → lower shrinkage variation |
| Pre-drying required | No (≤0.02% moisture) | No (≤0.02% moisture) | Not hygroscopic |
| Back pressure | 3–8 MPa | 5–10 MPa | Low to prevent degradation |
Mold temperature significantly affects PE part quality and shrinkage. Higher mold temperatures (50–70°C for HDPE) promote higher crystallinity, reducing the variation in shrinkage between runs and improving dimensional stability. Lower mold temperatures (20–30°C) speed cooling and reduce cycle time but increase crystallinity variation, leading to less predictable dimensions. In our factory, we use water-cooled molds for PE tooling with independent temperature zones on core and cavity to balance crystallization on both surfaces.

How Does PE Shrinkage Affect Mold Design?
PE’s high shrinkage rate3 (1.5–3.0%) is the most demanding aspect of mold design for polyethylene parts. All mold cavity dimensions must be enlarged by the expected shrinkage factor — a 100 mm nominal part dimension requires a 101.5–103.0 mm cavity dimension. The challenge is that PE shrinkage varies with wall thickness, mold temperature, injection speed, and cooling rate, making it difficult to predict accurately for complex geometries.
Mold steel selection for PE tooling considers the abrasive nature of glass-fiber-filled PE grades and the moderate pressures involved. P20 pre-hardened steel (30–36 HRC) is standard for HDPE molds up to 1 million cycles. H13 tool steel (48–52 HRC after heat treatment) is preferred for glass-fiber-filled PE or abrasive mineral-filled grades that accelerate cavity wear. Aluminum molds (7075-T6) are feasible for LDPE prototyping runs of up to 50,000 parts due to PE’s relatively low processing pressure.
“HDPE injection molding requires shrinkage compensation of 1.5–3.0%, significantly higher than amorphous plastics like ABS (0.4–0.8%).”True
HDPE is a semi-crystalline polymer that undergoes significant volume reduction as polymer chains organize into crystalline structures during cooling. This crystallization shrinkage (1.5–3.0%) is 3–7× greater than the shrinkage of amorphous plastics. The high shrinkage requires careful mold cavity enlargement and can create significant warpage in large flat parts if cooling is not uniform. Mold designers must account for directional shrinkage differences: parallel to flow typically 1.5–2.5%, transverse to flow 1.8–3.0%.
“PE resin requires extensive drying before injection molding, similar to nylon or polycarbonate.”False
Polyethylene is non-hygroscopic: it does not absorb moisture from the atmosphere and arrives at the processing stage with moisture content well below the critical 0.02% threshold that causes splay and silver streaking. Unlike nylon (must be dried at 80°C for 4–8 hours) or polycarbonate (120°C for 4–6 hours), PE can be molded directly from the bag without any pre-drying step. This saves process time and energy, and eliminates the risk of over-dried material that can occur with desiccant hopper dryers.
What Are the Primary Applications of PE Injection Molding?
HDPE injection molding dominates packaging applications: bottle caps, closures, containers, crates, and pallets. The combination of chemical resistance, FDA food-contact compliance, excellent impact strength at room temperature, and low cost makes HDPE the material of choice for high-volume packaging. In our factory, HDPE caps account for over 30% of our annual injection molding volume, with typical cycle times of 6–18 seconds for 28 mm diameter closures on 32-cavity molds.
LDPE injection molding serves flexible component applications including flexible lids, soft-touch grips, squeeze bulbs, and low-temperature gaskets. Its outstanding flexibility (elongation at break 300–800%), transparency in thin sections, and chemical resistance make it useful for laboratory and medical supply components. LDPE’s extremely low moisture permeability (0.08 g·mm/m²·day at 38°C) qualifies it for moisture-barrier packaging applications.
Industrial applications of PE injection molding include pipe fittings (HDPE meets DIN 16963 / ISO 4427 standards), agricultural tanks, material handling bins, and marine components. Ultraviolet stabilization with carbon black (2–3% loading) or HALS (hindered amine light stabilizers) extends outdoor service life to 20+ years. Our engineering team regularly specifies UV-stabilized HDPE grades for injection molded outdoor product components where polyethylene’s natural outdoor durability exceeds that of ABS or polypropylene.
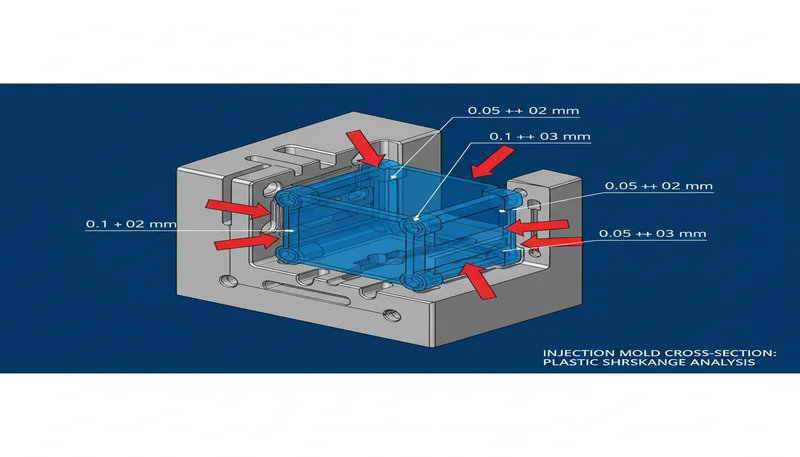
How Do You Troubleshoot Common PE Injection Molding Problems?
Warpage is the most common quality issue in PE injection molding due to the high shrinkage and semi-crystalline structure. Asymmetric cooling — when core and cavity mold temperatures differ by more than 10°C — produces differential crystallization rates that warp large flat parts. The remedy is balanced cooling circuits on both core and cavity, with independent temperature control zones verified by thermocouple measurement. For persistent warpage in thin-walled HDPE parts, transitioning to glass-fiber-reinforced HDPE (20–30% GF) reduces linear shrinkage to 0.5–1.0%, dramatically improving flatness.
Sink marks in HDPE parts over ribs and bosses are addressed by reducing boss diameter, hollowing thick sections, and ensuring rib thickness does not exceed 60% of the nominal wall. HDPE’s high shrinkage makes it more susceptible to sinking than amorphous plastics of the same wall thickness. Increased holding pressure time — maintaining pack pressure until the gate fully freezes — reduces sink severity but cannot eliminate it when the root cause is excessive wall thickness ratio.
“Glass-fiber reinforcement at 20–30% reduces PE injection molding shrinkage from 1.5–3.0% to 0.5–1.0%, significantly improving part flatness.”True
Glass fibers act as a dimensional reinforcement skeleton that resists the volumetric contraction of the PE matrix during crystallization. The fibers, which have near-zero thermal expansion, constrain shrinkage in their alignment direction (parallel to flow). With 30% GF loading, HDPE shrinkage drops to 0.4–0.7% parallel to flow and 0.6–1.2% transverse to flow, enabling flat parts with tight dimensional tolerances that unfilled HDPE cannot achieve.
“PE injection molded parts cannot be painted or bonded because the material has too low surface energy.”False
Untreated PE surfaces have low surface energy (31–34 mN/m), which resists adhesion of conventional paints and adhesives. However, surface treatment methods including flame treatment, corona discharge, and plasma treatment reliably raise PE surface energy to 42–58 mN/m, enabling excellent adhesion with standard adhesives and paints. Surface-treated HDPE containers are routinely screen-printed, hot-stamped, and label-glued in high-volume production. Chemical adhesion promoters (chlorinated polyolefin primers) also achieve strong bonding on PE without surface treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between HDPE and LDPE in injection molding?
HDPE (high-density polyethylene, 0.941–0.960 g/cm³) is stiffer, stronger, and more heat-resistant than LDPE (low-density polyethylene, 0.910–0.940 g/cm³), making it better suited for rigid containers, caps, and structural components. LDPE is softer, more flexible, and more impact-resistant at low temperatures down to -70°C, making it preferred for flexible grips, squeeze bulbs, and cold-environment parts. HDPE has better chemical resistance and higher service temperature (70–120°C HDT vs 40–65°C for LDPE). HDPE also has a higher melt temperature requirement (220–260°C vs 180–240°C for LDPE) and greater shrinkage variability, demanding more precise mold temperature control.
Why does PE injection molded parts warp so much?
PE warpage is caused by its semi-crystalline nature and high shrinkage rate. As PE cools in the mold, polymer chains form crystalline regions that occupy less volume than the amorphous melt — this is the crystallization shrinkage (1.5–3.0%). If cooling is non-uniform across the part, different areas complete crystallization at different rates, creating differential shrinkage that warps the part. Asymmetric wall thickness, poor cooling system design, and mold temperature imbalance all amplify warpage. The solution is balanced cooling with core and cavity temperatures within 5°C of each other, uniform wall thickness, and multiple gates to reduce flow-direction anisotropy.
Can PE injection molded parts be recycled?
PE is one of the most widely recycled plastics globally. HDPE is recycling code #2 and LDPE is code #4, both of which are accepted in most municipal recycling programs. Recycled PE maintains approximately 70–90% of virgin mechanical properties for most applications, making it suitable for non-food-contact molded products. In our factory, we use up to 25% post-consumer recycled HDPE in non-critical applications, reducing material costs and improving the sustainability profile of our customers’ products. Pure PE scrap from runners and rejected parts is 100% regrindable and reprocessable.
What injection molding machine tonnage is required for PE parts?
Required clamp tonnage for PE injection molding is calculated using projected part area multiplied by 2–4 tonnes per cm² of cavity pressure. PE’s moderate viscosity and low processing pressure (50–130 MPa) mean it requires less clamp force than materials like PC or PA. A typical 100 cm² projected area HDPE part requires 200–400 tonnes of clamp force. In practice, our factory standard is to size the press at 20–30% above minimum calculated requirement to ensure mold protection and flash prevention across the full processing window for each PE grade.
What surface finishes can be achieved on PE injection molded parts?
PE injection molded surface finish depends primarily on mold cavity surface treatment. High-gloss finishes (SPI A1–A2, Ra 0.025–0.05 µm) are achievable with polished steel cavities, though PE’s semi-crystalline nature can create a slightly waxy appearance on mirror surfaces. Textured surfaces (SPI C1–D2) mask minor surface defects and are widely used for industrial parts. Matte finishes are produced with EDM (electrical discharge machining) texture on cavity steel. PE does not accept electroplating or in-mold decoration as readily as ABS, but is compatible with hot stamping and pad printing after surface treatment.
-
polyethylene: Polyethylene (PE) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polymer composed of repeating ethylene units (-CH2-CH2-)n, produced by addition polymerization and classified by density into LDPE, LLDPE, MDPE, HDPE, and UHMWPE grades. ↩
-
melt flow index: Melt flow index (MFI) is a measure of the ease of flow of a melted polymer, defined as the mass of polymer extruded through a standard die in 10 minutes under a specified temperature and load, measured in grams per 10 minutes (g/10 min). ↩
-
shrinkage rate: Shrinkage rate refers to the percentage decrease in a molded part’s dimensions compared to the mold cavity dimensions after the part cools to room temperature, measured as a percentage of the nominal cavity dimension. ↩
-
crystallinity: Crystallinity is a measure of the degree of structural order in a polymer material, defined as the fraction of polymer chains aligned in regular crystalline lattice structures versus amorphous disordered regions, expressed as a percentage. ↩