Injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that has become the preferred method for producing a wide range of plastic parts and components. However, with the availability of several other processes, it is important to understand the relative advantages and disadvantages of injection molding. Plastic is a major industrial material and therefore plays a critical role in the industrial production of the modern world. There are many different plastic molding processes that can be named, but injection molding is the most widely used process. When it comes to manufacturing processes, injection molding has several unique characteristics that set it apart from the others.
In this blog post, we will go through the details of injection molding and its advantages over several other common manufacturing processes for molding such as blow molding, extrusion, compression molding, thermoforming, and 3D printing.
Understanding Injection Molding
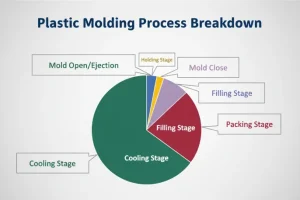
The process of injecting the melted material into the mold cavity, where it cools and hardens to make the desired shape, is called the injection molding. In most cases, it is carried out with thermoplastics, but you can also use metals and other materials. The process of the process is initiated by loading the raw material into a barrel, heating it until it melts, and then injecting the melted material into a mold at high pressure.
The foremost advantage of injection molding is that it can create complex, intricate shapes with high precision. Through the use of molds we are able to create any geometry that can be dreamt of. Injection molding has a lot of design freedom which you can choose from, such as intricate textures, undercuts, and complex geometries.

Advantages of Injection Molding
Cost Efficiency
Injection molding is inexpensive, particularly for high-volume production runs. Of course, the tooling costs at the beginning are higher than other methods like 3D printing or CNC machining, but as the volume goes up, the cost per unit goes down like a wild goose chase. Besides, injection molding is a swift, automatic, and automated process, which in turn, helps you to cut down the labor costs, thus, making it the cheaper option for mass production.

High Production Rates
Injection molding is a process that can make parts in a really short time, thus you can produce a lot of parts in a short period of time. Thus, it’s the best for the industries where the deadlines are close and the orders are high. Injection molding is far superior to methods like 3D printing, which is so time-consuming when you’re making a lot of parts.
Design Flexibility
The main advantage of the process is the design flexibility that it offers. You can create a mold of any shape, size, and feature, which means you can make complicated parts with ease. Injection molding enables you to make your design into reality by giving you the chance to create various details, use different wall thicknesses and have different textures.

Consistency and Quality
Injection molding is a suitable technology for the mass production in terms of consistency and quality. Every molded piece is almost identical to the neighbor one, hence the uniformity is established in the whole process and the reliability is guaranteed. The accuracy to such a high level is very important for the sectors that are focused on the quality of their products, such as the automotive and medical device industry.
Material Variety
The process of injection molding deals with many kinds of materials and thus they can range from different thermoplastics. Thus, manufacturers can choose the material which is most suitable for their application requirements which can be strength, durability, chemical resistance or aesthetic appeal. Injection molding is one of the plastic processes that have a solid-state feature and offers a wide range of materials from commodity resins to engineering-grade polymers.

Reduced Post-Processing
Different from other manufacturing methods that demand a lot of finishing to attain the nice surface finish, injection molded parts usually need very little secondary operations. This not only eliminates the time and effort, but also cuts down the chances of the defects that are possible to occur during the other processing stages. With injection molding, the parts are made to be of high quality immediately after the molding process is over, thereby increasing the production efficiency and lowering the costs at the same time.

Comparing Injection Molding to Other Processes
Injection Molding vs. Blow Molding
These two methods of injection molding and blow molding are the main techniques for shaping plastic materials, each of which has its distinct features and uses.

1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a process of injecting liquid material, such as thermoplastic resins, into a mold cavity under high pressure. The material cools and hardens and takes the shape of the mold cavity. This method makes complex shapes, intricate details, and high-quality surfaces.

2. Blow Molding
Blow molding is the process of making hollow parts and containers, as opposed to solid parts. First, a parison (a hollow tube of molten plastic) is extruded, then clamped into a mold. Air is blown into the parison, expanding it to the shape of the mold cavity. After cooling, the part is removed from the mold.

3. Comparison
Complexity of Parts: Injection molding is great for making parts with complex shapes and features, while blow molding is better for making hollow shapes and containers.
Production Volume: Injection molding is the way to go for high-volume production runs because it’s more efficient with fast cycle times, while blow molding might be cheaper for big, hollow parts.
Material Selection: Injection molding can work with lots of different materials, including engineering-grade resins, while blow molding only works with some thermoplastics.
Tooling Costs: Injection molding usually has higher upfront tooling costs, but it can deliver low per-unit costs for large production runs. Blow molding usually has cheaper tooling for certain shapes, but it has higher material costs.
Injection Molding vs. Extrusion
Injection molding and extrusion are the two most popular processes in the plastic manufacturing industry. Both processes are widely used and have their own advantages and applications.

1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used process in the manufacturing industry for creating complex parts with high tolerance. It involves injecting hot liquid into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies to form the final desired shape. Injection molding is suitable for small to medium batch production and offers high precision and repeatability.

2. Extrusion
Extrusion is the process of pushing molten plastic through a die to shape continuous forms with a consistent cross-section. The main purpose of extrusion is to produce pipes, tubing, profiles, and sheet materials. Extrusion is a method that allows for the production of large quantities of material at a high speed and is also a cost-effective way to produce long, continuous lengths of material.

3. Comparison
Product Complexity: The injection molding process can deliver parts with more design complexity and intricate details, so it’s good for parts with lots of features and undercuts. Extrusion is better for shapes that have a continuous outline and the same cross-section all the way through.
Material Usage: Injection molding is more efficient with materials and makes less waste compared to extrusion, where you might have to trim or cut the material to the right length.
Production Speed: Extrusion is generally faster than injection molding for making long continuous lengths, but it’s not as good as injection molding for making individual parts.
Tooling Costs: Injection molding usually means the tooling costs more because the molds are more complicated, while extrusion tooling is easier and cheaper for some shapes.
Injection Molding vs. Compression Molding
Injection molding and compression molding are two methods used to shape thermosetting and thermoplastic materials, each with its own advantages and applications.

1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a popular method for making precise plastic parts that have consistent quality every time. It involves injecting hot material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. Injection molding is great for mass production with high-volume production runs and offers excellent dimensional accuracy.

2. Compression Molding
Compression molding involves placing a pre-measured amount of material into a heated mold cavity and compressing the material under high pressure until it takes on the shape of the mold. This method is commonly used for producing thermosetting plastics, composites, and rubber materials. Compression molding is the ideal technique for producing large, intricate parts with uniform wall thickness.

3. Comparison
Production Volume: Injection molding is better for making a lot of parts because it’s faster and the machines can run without a lot of people. Compression molding is good for making a few parts or really big parts. It’s good for making a few parts or really big parts.
Material Selection: Injection molding can use more kinds of plastic like thermoplastics and engineering-grade resins. Compression molding is mostly used for thermosetting plastics and composites.
Tooling Costs: Injection molding costs more to get started because you have to make molds and get everything set up. Compression molding can be good for some things, but it can take longer and be less efficient if you’re making a lot of parts.
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming
Injection molding and thermoforming are both ways to shape plastic, but they’re different in how they’re done and what they’re used for.

1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a versatile way to make complex parts that are consistently high quality. You inject a liquid material into a cavity in a mold. The material cools and hardens, taking the shape of the part you want to make. Injection molding works with lots of different materials and makes parts with a good finish and tight tolerances.

2. Thermoforming
Thermoforming is when you heat a sheet of thermoplastic until it’s soft, and then you press it over a mold to make the shape you want. You use this method to make lots of big, shallow parts, like trays, packaging, and car parts. Thermoforming is fast and cheap, but it has limits on how complex the parts can be and what materials you can use.

3. Comparison
Part Complexity: Injection molding allows for more complex designs and intricate details, making it ideal for parts with varying features and undercuts. Thermoforming is best suited for large, flat or shallow parts with simple shapes.
Material Selection: Injection molding offers more material options and can use engineering-grade resins, while thermoforming is limited to thermoplastic materials.
Production Volume: Injection molding is ideal for high-volume production runs due to its faster cycle time and automated processes. Thermoforming may be better suited for low to medium volume production or the creation of large parts.
Injection Molding vs. 3D Printing
There are two ways to make plastic parts: injection molding and 3D printing (also called additive manufacturing). Each has its own strengths and best uses.

1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a very efficient way to make plastic parts with high precision and repeatable results in high volumes. You pour liquid plastic into a mold, let it cool and solidify, and then open the mold to get the part. Injection molding works well for many materials and has fast cycle times and low costs per part for high-volume production.

2. 3D Printing
Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing builds parts layer by layer from digital designs. It’s great for quick prototyping and customization, meaning you can make complex shapes and even parts that don’t need tooling. 3D printing is good for low to medium volumes, custom parts, and fast design changes.

3. Comparison
Production Speed: Injection molding is faster and cheaper for high-volume production. 3D printing is slower and more expensive per unit, but is still a fast way to prototype and design.
Part Complexity: Injection molding can make more intricate designs and more complex details, so it’s the best method for parts with lots of features and undercuts. 3D printing is best for making complex shapes and personalized parts without extra tooling.
Material Selection: Injection molding uses thermoplastics that are melted and shaped into the form of the part. Injection molded parts can be any temperature or density you want. Injection molding has more material options, including engineering-grade resins and specialty polymers. 3D printing has limited material options.
Conclusion
There are many different ways to make plastic products, and one of the most popular is injection molding. Injection molding is widely used because it has a lot of advantages. But before you decide to use it, you should learn more about it. That’s why it’s so important to weigh the pros and cons of injection molding and then make a decision based on your own situation.

So, in conclusion, even though injection molding is the most popular process for making lots of plastic parts, all the other processes have their own advantages and uses. It’s important to know the good and bad things about these processes so you can pick the right way to make your parts. Whatever you do, you have to pick the right way to make your parts based on how many you’re going to make, how hard they are to make, what kind of stuff you’re going to make them out of, and how much it’s going to cost you to make them. You want to pick the way that’s going to make you the most parts for the least money and make you the most money.