Introduction: As society develops and people’s living standards improve, people’s requirements for the quality of injection molds are getting higher and higher, and the number of injection molds produced by mold factories is also increasing.

Although we often use products processed by injection molds in our lives, many people do not have a deep understanding of injection molds. Today, Zetar Mold will introduce to you what injection molds are. Let’s follow the editor to take a look!
What is an Injection Mould?
injection moulding process is a manufacturing process that allows for mass production of parts. It works by injecting melted plastic into a mold.

It is often used as a mass production process to make thousands of identical products. Injection molding plastic materials include metals, glass, plastic resin , elastomers, and confectionery, but it is most commonly used with thermoplastic and thermoset polymers.
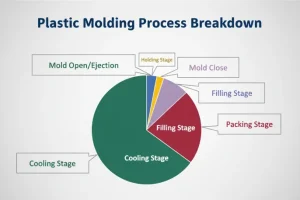
In rubber injection moulding, molten plastic flows through the mold cavity, is formed within the mold halves, and the finished product is removed from the mold using ejector pins.

Plastic injection molds are used in the plastic injection molding process . You can make custom molds using aluminum or steel to get good results. They usually have two parts-fixed molds and moving molds.
The fixed mold is mounted on the fixed plate of the molding machine, while the moving mold is mounted on the moving plate of the machine. During the injection molding process, both the fixed mold and the moving mold remain closed to create the injection system and cavity. After opening, these operators separate the molds to remove the product.

What are the Types of Injection Moulds?
Single Parting Surface Injection Mould
When you open the mold, you separate the moving and fixed molds to take out the plastic parts. This kind of mold is called a single parting surface mold, or a double plate mold. It’s a basic kind of injection mold. You can design it as a single cavity injection mold or a multi-cavity injection mold, depending on what you need. This kind of injection mold is used a lot.

Double-Parting Surface Injection Mold
The double-parting surface injection mold has two parting surfaces. Compared with the single-parting surface injection mold mentioned above, the double-parting surface injection mold has an additional intermediate plate that can be partially moved in the fixed mold part.

So the double parting surface injection mold can also be called a three-plate injection mold. Double parting surface injection molds are single cavity or multi-cavity injection molds commonly used for point gate feeding.
When you open the mold, the intermediate plate separates from the fixed mold plate at a fixed distance on the guide column of the fixed mold, which makes it easy to remove the solidified pouring system between the two mold plates.

The double parting surface injection mold has a more complicated structure, a higher manufacturing cost, and some difficulty in processing the parts. Therefore, it is generally not used for the molding of large plastic products.
Injection Mold with Movable Molding Parts in the Mold
Because of certain structures of plastic parts, the injection mold needs to have movable molding parts. For example: movable punch, movable die, movable insert, movable thread core or ring, etc. When demolding, it can be moved out of the mold together with the plastic part, and then separated from the plastic part.

Automatic Thread Removal Injection Mold
For plastic parts with threads that need to be automatically ejected, a rotating thread core or ring can be installed in the mold. Use the mold opening action or the rotating mechanism of the injection molding machine, or install a special transmission device to drive the thread core or thread ring to rotate, so as to eject the plastic part.
Runnerless Injection Mold
This mold uses runner heat insulation heating to keep the plastic between the nozzle and the injection molding machine cavity molten so that when the mold opens and the plastic part is taken out, there is no condensation in the pouring system.

Injection Mold with Demolding Mechanism on the Fixed Mold
In many injection molds, the demolding device is installed on the side of the movable mold, which is more convenient for the ejector device in the opening and closing system of the injection molding machine.

When you’re actually making stuff, sometimes you have to leave the plastic parts on the side of the mold that doesn’t move. You have to put something on the side of the mold that doesn’t move to get the plastic part out of the mold.
What are the Components of the Injection Mold Structure?
The plastic injection mold has a movable mold and a fixed mold. The movable mold is on the movable mold plate of the injection molding machine, and the fixed mold is on the fixed mold plate of the injection molding machine.

When you do injection molding, you close the movable mold and the fixed mold to make a gating system and a cavity. When you open the mold, you separate the movable mold and the fixed mold to take out the plastic product.
The structure of the mold may vary depending on the type and performance of the plastic, the shape and structure of the plastic product, and the type of injection molding machine, but the basic structure is the same. The mold consists of a gating system, a temperature control system, a molded part, and a structural part.

The gating system and the molded part are parts that are in direct contact with the plastic and change with the plastic and the product. They are the most complex and variable parts in the mold, requiring the highest processing finish and precision.
Gating System
The gate system is a set of channels that bring the plastic melt from the nozzle of the injection molding machine into the cavity. It usually consists of a main channel, a branch channel, a gate, and a cold slug well. It directly affects the quality of the molding and the production efficiency of the plastic parts.

The runner system refers to the flow channel part before the plastic enters the cavity from the nozzle, including the main channel, cold slug well, runner, gate, etc. The molded parts refer to the various parts that make up the shape of the product, including the moving mold, fixed mold and cavity, core, ejector rod, vent, etc.
Main Channel
The main channel is the channel that connects the nozzle of the injection molding machine to the runner or cavity in the mold. The top of the gate is concave to engage with the nozzle. The inlet diameter of the gate should be slightly larger than the diameter of the nozzle to avoid overflow and prevent the two from being blocked due to inaccurate connection.

The diameter of the feed port depends on the size of the product and is generally 4-8mm. The diameter of the gate should expand inward at an angle of 3° to 5° to facilitate the release of runner debris.
Cold Material Hole
The cold slug well is a pocket at the end of the main runner that captures the cold slug formed between two shots at the end of the nozzle, preventing the runner or gate from being blocked. If cold material gets into the pocket, the part will have internal stress.

The diameter of the cold slug well is about 8-10mm and the depth is 6mm. To facilitate ejection, the bottom is usually supported by the ejector pin. The top of the ejector pin should be designed with a serrated hook or groove so that the gate can be pulled out smoothly during ejection.
Divider
The runner is the channel that connects the main channel to each cavity in a multi-cavity mold. In order to make the melt fill each cavity at the same speed, the runner layout on the mold should be symmetrical and equidistant. The shape and size of the runner section have an impact on the flow of the plastic melt, the demolding of the product, and the difficulty of mold manufacturing.

If the flow of equal amounts of material is considered, the runner with a circular cross-section has the smallest resistance. However, due to the small specific surface area of the cylindrical runner, it is not conducive to the redundant cooling of the runner, and the runner must be opened on both halves of the mold, which is labor-intensive and easy to center.
Typically, trapezoidal or semicircular runners are used, and one half of the mold has a push rod. The runner surface must be polished to reduce flow resistance and provide faster filling speed. The size of the runner depends on the type of plastic, as well as the size and thickness of the product.

For most thermoplastics, the cross-sectional width of the runner is mostly no more than 8m. Under the premise of meeting the needs, the cross-sectional area should be minimized as much as possible to avoid adding debris to the diversion pipe and prolonging the cooling time.
Gate
The gate is a channel that connects the main channel (or branch channel) and the cavity. The cross-sectional area of the channel can be equal to that of the main channel, but it is usually reduced, so the gate is the part with the smallest cross-sectional area in the entire runner system. The shape and size of the gate have a great influence on the quality of the product.

The function of the gate is:
Control the flow rate.
Keep the melt in this area from solidifying too soon during the injection molding process and causing backflow.
By shearing the melt strongly to increase the temperature, the apparent viscosity is reduced and the fluidity is improved.

It’s convenient to separate the product from the runner system. The design of the shape, size and position of the gate depends on the properties of the plastic, as well as the size and structure of the product. Generally, the cross-sectional shape of the gate is rectangular or circular, with a small cross-sectional area and a short length.

This is not only based on the above effect, but also because small gates are easier to enlarge, while large gates are difficult to reduce. The gate position should generally be selected at the thickest part of the product without affecting the appearance. The size design of the gate should take into account the properties of the plastic melt.

Thermostat System
To meet the requirements of the injection process for mold temperature, you need a temperature control system to adjust the temperature of the mold. For thermoplastic injection molds, the cooling system is mainly used to cool the mold.

The common way to cool the mold is to open a cooling water channel in the mold and use circulating cooling water to take away the heat of the mold. In addition to heating the mold, you can use hot water or steam in the cooling water channel, and you can install electric heating elements inside and around the mold.
Molding Part
The molded part is made up of a core and a mold. The core makes the inside of the thing, and the mold makes the outside shape of the thing. When the mold is closed, the core and the cavity make the mold’s cavity.

Depending on the process and the manufacturing requirements, sometimes the core and the mold are made up of several blocks, sometimes they are made as one piece, and sometimes a plug is used for parts that are easy to break and hard to make.
Exhaust Hole
The exhaust port is a groove-shaped air outlet opened in the mold. It is used to discharge the original gas and the gas brought in by the melt. When the melt is injected into the cavity, the air originally stored in the cavity and the gas brought in by the melt must be discharged out of the mold through the exhaust port at the end of the material flow.

Otherwise, the product will have pores, poor connection, unsatisfactory filling of the mold, and even the accumulated air will burn the product due to the high temperature caused by compression.
Typically, the vent can be located either at the end of the melt flow in the cavity or at the parting surface of the mold. The latter is a shallow groove on one side of the mold with a depth of 0.03-0.2mm and a width of 1.5-6mm.

During the injection process, no large amount of molten plastic material will seep out of the vent, because the molten material will cool and solidify there and block the channel. The opening position of the vent should not face the operator to prevent the molten material from accidentally spraying out and causing injury.
Also, the clearance between the ejector pin and the ejector hole, the clearance between the ejector block and the stripper plate, and the clearance between the cores can also be used for venting.

Structural Part
Structural parts are the different parts that make up the mold structure. They include things like guide molds, demolding, core pulling, and parting. For example, the front and rear clamping plates, front and rear buckle templates, bearing plates, bearing columns, guide columns, stripping plates, stripping rods, return rods, and so on.

Guide parts: To make sure the movable mold and the fixed mold line up right when the mold closes, you need guide components in the mold. In injection molds, you usually use four sets of guide pins and guide bushings to make the guide components. Sometimes, you also need matching taper pins on the movable mold and the fixed mold to help with positioning.

Start mechanism:When the mold is opened, you need something to push or pull the plastic part and the water that has condensed in the runner out of the mold. You push the stationary platen and the push plate together to hold the push rod. The return rod is usually held in the push rod. When the moving half and the stationary half of the mold are closed, the return rod pushes the push plate back.
Side core pulling mechanism:Some plastic products with side concave or side holes need to be side-parted before being pushed out. The side core pulling can be pulled out before they can be demolded smoothly. At this time, a side core pulling mechanism needs to be set in the mold.

Standard Template
To reduce the heavy workload of mold design and manufacturing, most injection molds use standard mold bases.
What Materials are Suitable for Injection Molds?
Tool Steel
Tool steel is one of the most commonly used materials for injection molds. It has excellent mechanical properties and wear resistance. Common tool steels include P20 steel, 718 steel, NAK80 steel, and others. These tool steels have high hardness, strength, and wear resistance. They are suitable for producing large quantities of plastic products.
.jpg 600w, https://zetarmold.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/工具钢(Tool-Steel)-300x165.jpg 300w)
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a material that doesn’t rust easily. It can resist acid and alkali and can withstand high temperatures. Common stainless steel materials include S136 and 420. Stainless steel molds don’t rust easily and have a smooth surface. They are good for making plastic products that need to look nice.

Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloy is a light material with good thermal conductivity. Commonly used aluminum alloys include 7075, 6061, etc. Aluminum alloy molds have low density and good thermal conductivity, and are suitable for the production of large, thin-walled plastic products.
Copper Alloy
Copper alloy has good thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. Common copper alloys include H13, H11, etc. Copper alloy molds have high thermal conductivity and wear resistance, and are suitable for the production of plastic products with high requirements for product dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
.jpg 600w, https://zetarmold.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/铜合金(Copper-Alloy)-300x202.jpg 300w)
High-Temperature Alloy
High-temperature alloy is a material that can keep working good in high temperature. Common high-temperature alloys include Inconel, Hastelloy, etc. High-temperature alloy molds have high heat resistance and corrosion resistance, and are suitable for the production of high-temperature plastics or plastic products with special process requirements.
.jpg 600w, https://zetarmold.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/高温合金(High-Temperature-Alloy)-300x191.jpg 300w)
What are the Applications of Injection Molds?
Home Appliance Industry
In the home appliance industry, injection molds are used a lot. For example, large home appliances like TVs, mobile phones, refrigerators, washing machines, and small home appliances like electric shavers and hair dryers all need injection molds to make them.

Injection molds can help manufacturers make a lot of plastic shells of different sizes and shapes to make sure the products look good and are the right size.
Automobile Industry
In the car making industry, injection molds are also a big deal for making car parts. For example, car dashboards, door panels, buffers, sunroof frames, steering wheel covers, bumpers, and other parts all need to be made with injection molds. Using injection molds can make production faster, save money, and make sure the parts are the right size and look good. It can also help make cars safer.

Daily Necessities Industry
In the daily necessities industry, injection molds are also widely used. For example, household daily necessities such as plastic cups, plastic bowls, plastic chopsticks, and plastic trash cans, as well as personal items such as cosmetics and toothbrushes, all need to be produced using injection molds.

The use of injection molds can greatly improve production efficiency and product quality, while also helping to reduce production costs and protect the environment.
Medical Device Industry
In the medical device industry, injection molds are also very important. For example, syringes, infusion sets, blood measuring instruments, artificial organs, etc., all need to be produced using injection molds.

Injection molds can help manufacturers produce medical devices of various materials and shapes, ensure product accuracy and quality, improve production efficiency, and better serve the development of the medical industry.
Other Industries
Injection molds are used in many industries, not just the ones mentioned above. They’re used in toy manufacturing, electronics, construction materials, aerospace, and more. Injection molds are used in a wide range of applications and are a big part of the plastic product manufacturing industry.

Summary
Molds are the core tools in the production of plastic products. They are divided into many types, including single parting surface, double parting surface, etc. The structure of the mold is complex, involving multiple components such as pouring system, temperature regulation, and molding part.

Molds are widely used in industries such as home appliances, automobiles, daily necessities, and medical devices. With the development of technology, the design and manufacturing of molds are constantly optimized to improve production efficiency and product quality.