Introduction
Plastics are widely used in daily chemical packaging, medical equipment, automobiles and in daily products. This article gives a brief introduction to these plastic connection technologies. Unlike metal welding, there are many ways to connect plastics together.
Plastic Connection Types
Adhesive Connection:
Adhesive connection refers to the technology of connecting the surfaces of homogeneous or heterogeneous objects together with adhesive. Adhesive refers to the ability to make two or more plastic components through the adhesion and cohesion of the interface. Or a class of natural or synthetic, organic or inorganic substances that connect materials together, collectively called adhesives, also called adhesives, customarily referred to as glue. In short, adhesive is a substance that can bind adherends together through adhesion.
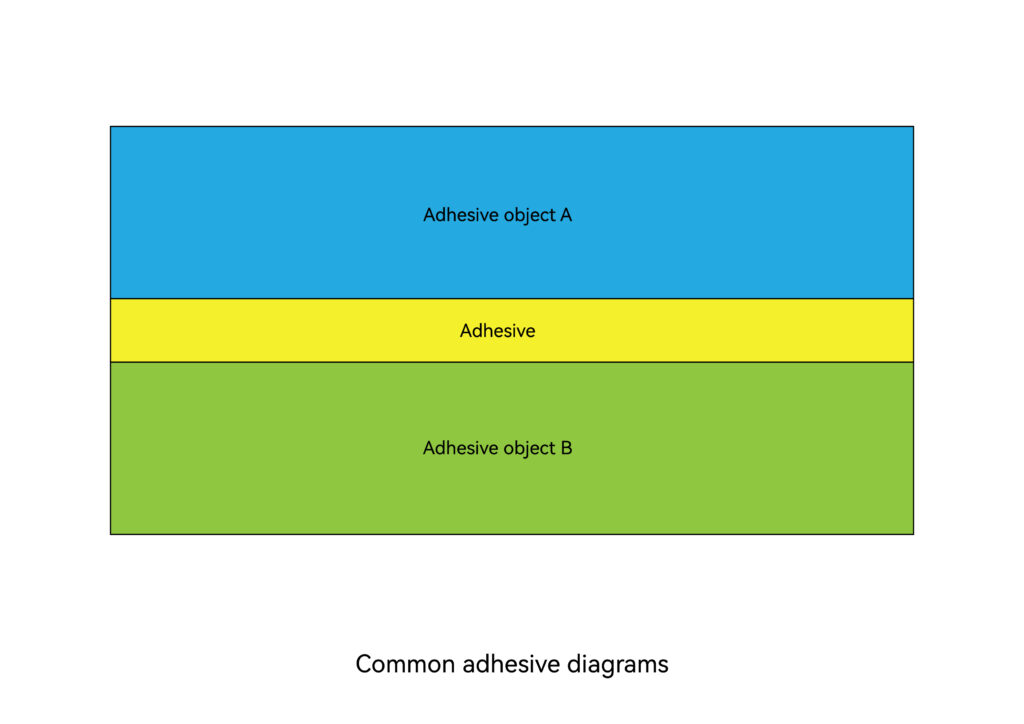
Solvent Connection:
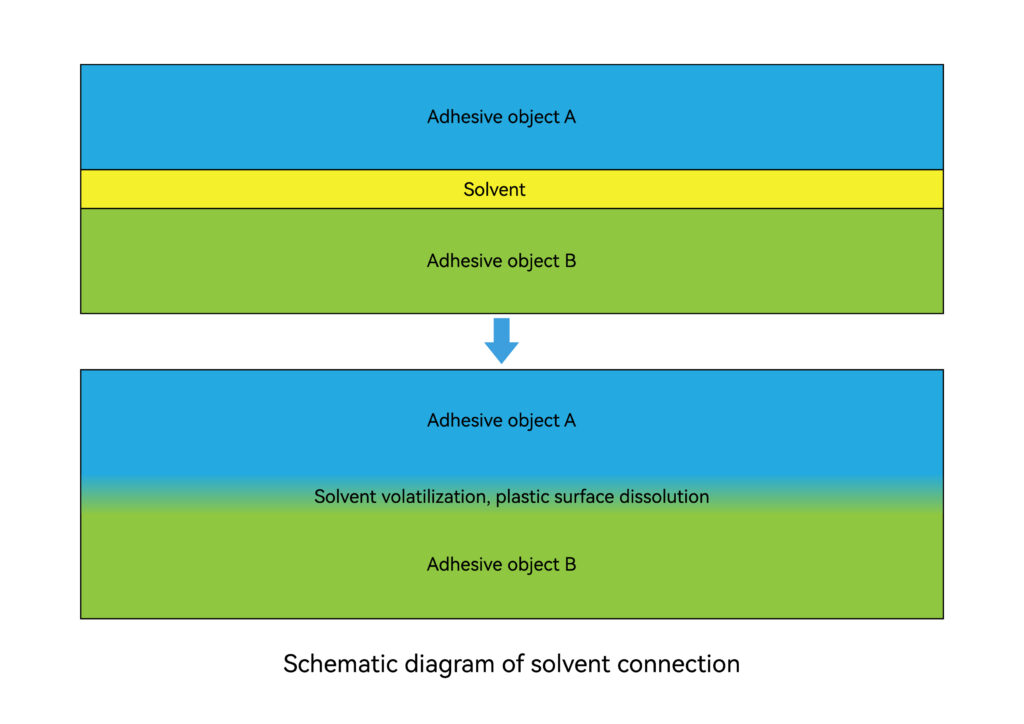
It means that the solvent dissolves the plastic surface to mix the materials between the plastic surfaces. When the solvent evaporates, a joint is formed. Plastics surface preparation involves ensuring all soils are removed. Poorly prepared plastic components will lead to solvent weld failures.
Solvent welding is a process where a solvent is used to soften non-crystalline thermoplastic materials. The connection is completed when the solvent is completely consumed or evaporated. The connection is achieved through the dissolution of the plastic being welded.
When the joint contains a certain amount of parent material components, the strength is higher. The solvent should fill the gaps in the connection area. This method cannot be used for PE, PP, fluoroplastics, etc.
The strength of the joint can reach the strength of the parent material. The required welding equipment is simple, the operation is very simple, and the cost is low.
The welding speed is slow, it takes a long time to evaporate, some solvents are toxic and harmful to the human body, so protection should be taken into account.
The main tools used include: injection needles, testing tools, dipping containers, etc.; clamping tools, drying devices; solvent recovery devices, etc.
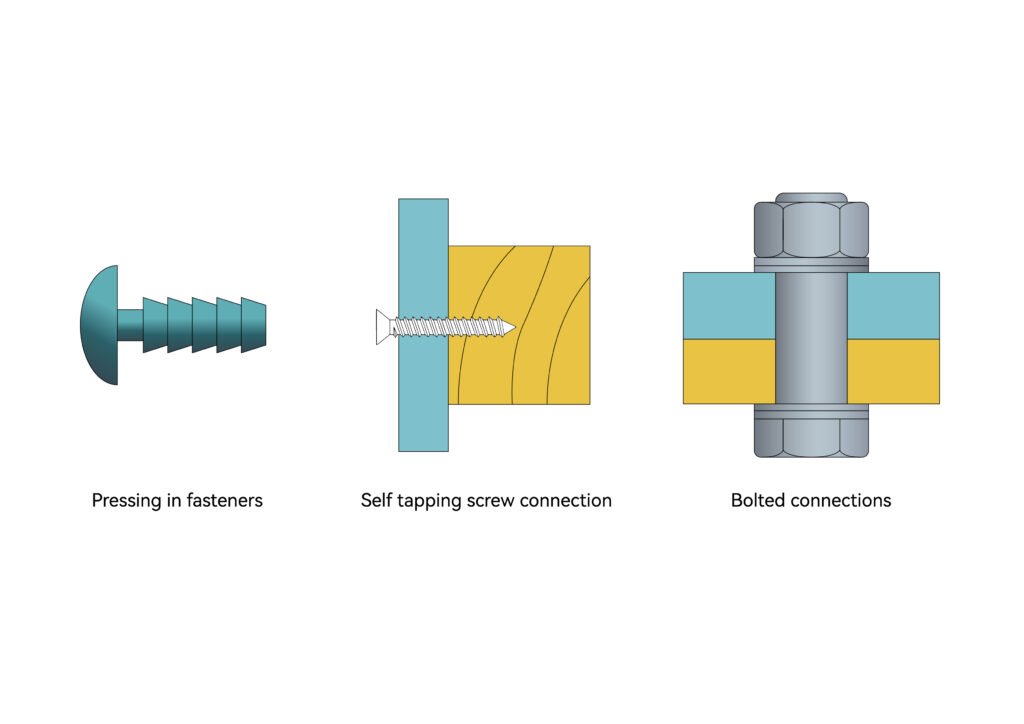
Fastener Connection
Fastener connection refers to the application of fasteners to connect plastic parts, including press-in fasteners, self-tapping screws and bolt connections. Press-in fasteners, as they are commonly referred to, connect plastic parts by forming an interference fit between a certain protrusion on the stem and the plastic cavity. Self-tapping screws use self-tapping threads to connect without tapping threaded holes.
Hinge Connection
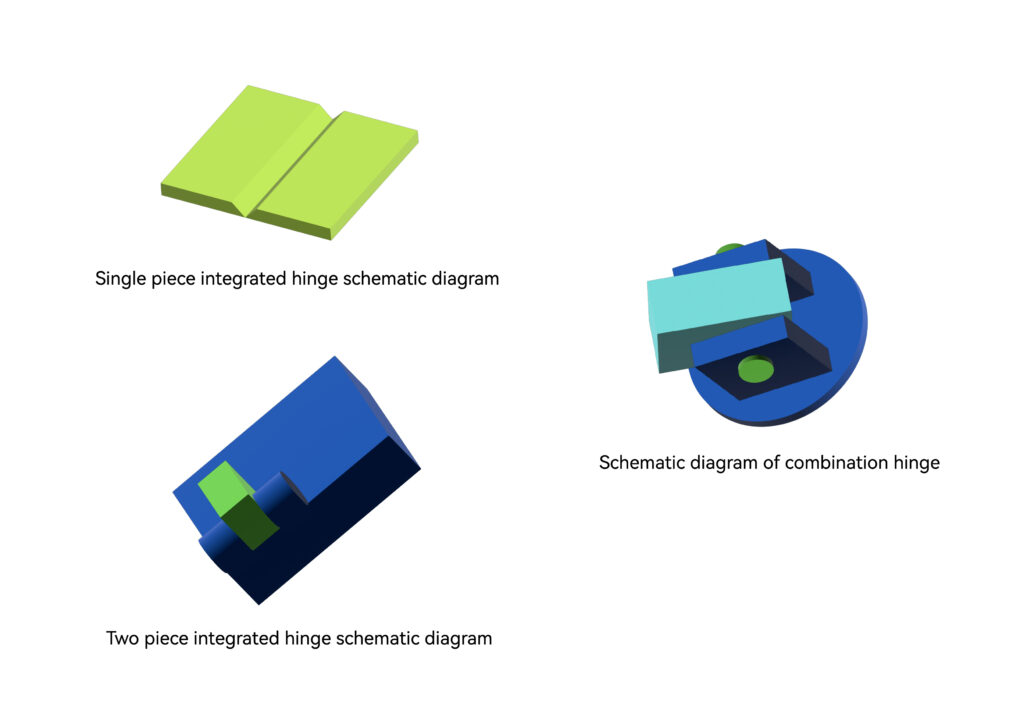
Plastic hinges can be divided into three types: single-piece integrated hinges, two-piece integrated hinges and multi-piece combined hinges. The single-piece integrated hinge is realized by molding two parts as a whole without the need for other additional parts. The two integrated hinges are first processed as two separate plastic parts by molding, and finally connected through assembly. In addition to processing two separate plastic parts, multi-piece hinges also require the use of additional parts, such as rods or metal hinge components. Its advantages are that it can be opened and closed repeatedly, and integrated hinges are usually designed in the box or close to the interior, thus reducing the overall size of the parts; its disadvantage is that the molds for molding require high precision and are generally complex, requiring extensive development experience. Reasonable design of movable hinges.
Insert Molding
Insert molding refers to a molding method in which pre-prepared inserts of different materials are loaded into the injection mold and then resin is injected. The molten material joins and solidifies with the insert to form an integrated product. Threaded inserts are the main way to create threads in plastic parts. This method can provide better connection strength than self-tapping threads. Insert products are not limited to metal, but also include cloth, paper, wires, plastics, glass, wood, wire coils, electrical parts, etc. Insert molding utilizes a combination of the insulation properties of resin and the conductivity of metal to produce molded products that can meet the basic functions of electrical products. In-mold insert injection molding decoration technology is IMD (In-Mold Decoration). IMD is currently an internationally popular surface decoration technology. It is mainly used in decorative and functional control panels of home appliances, automobile dashboards, air conditioning panels, mobile phone casings/lenses, washing machines, refrigerators, etc. It is widely used. IMD is a technology that puts the printed decorative sheet into the injection mold, and then injects the resin on the back of the molded sheet to join the resin and the sheet into an integrated solidification mold.

The main advantage of insert molding is that the easy formability and bendability of resin and the rigidity, strength and heat resistance of metal can be combined to make complex and exquisite metal-plastic integrated products.
Multi-part molding
Multi-part molding, also known as two-color injection molding, refers to a molding method in which two different colors of plastic are injected into the same mold. It can make plastic parts appear in two different colors, and can make plastic parts present regular patterns or irregular moiré-like colors to improve the practicality and aesthetics of plastic parts.
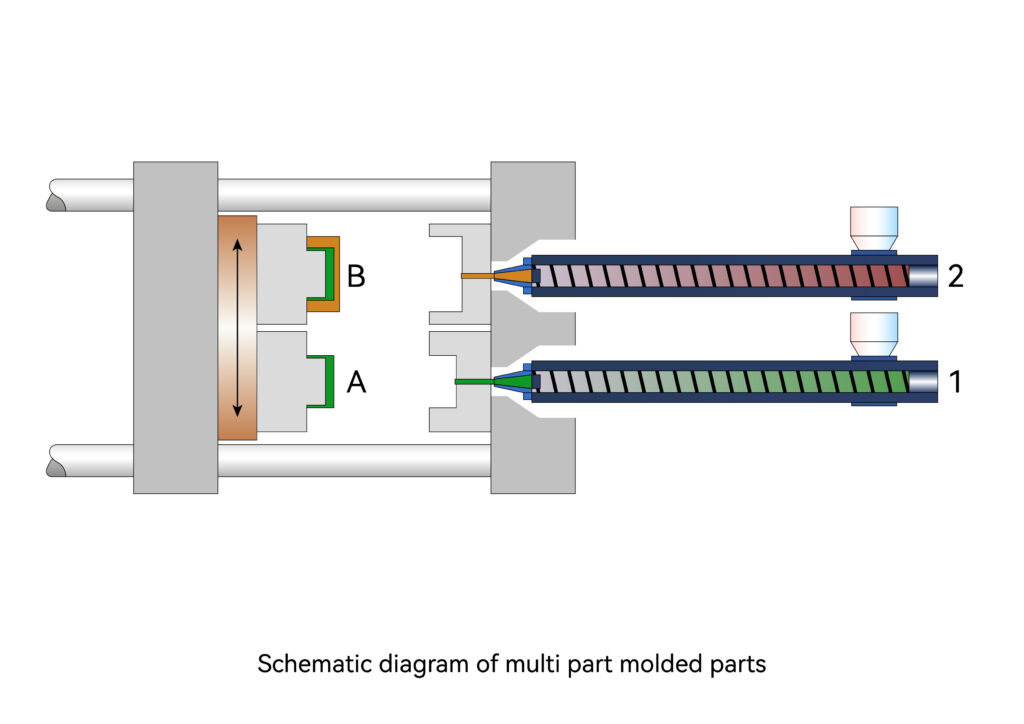
The figure below shows the principle of two-color injection molding. It has two barrels, and the structure and use of each barrel are the same as ordinary injection molding barrels. Each barrel has its own channel connected to the nozzle. When forming at the nozzle, after the molten material is plasticized in the barrel, the molten material enters the front sequence of the nozzle through the opening and closing valve and discharges the proportion of material. Injected into the mold cavity from the nozzle. A variety of plastic products with different color mixing effects are available.
Molded thread forming
Molded threaded connection refers to directly forming threads on plastic parts through the design of injection molds, thereby achieving threaded connections with other threads with the same tooth profile, nominal diameter and other parameters.
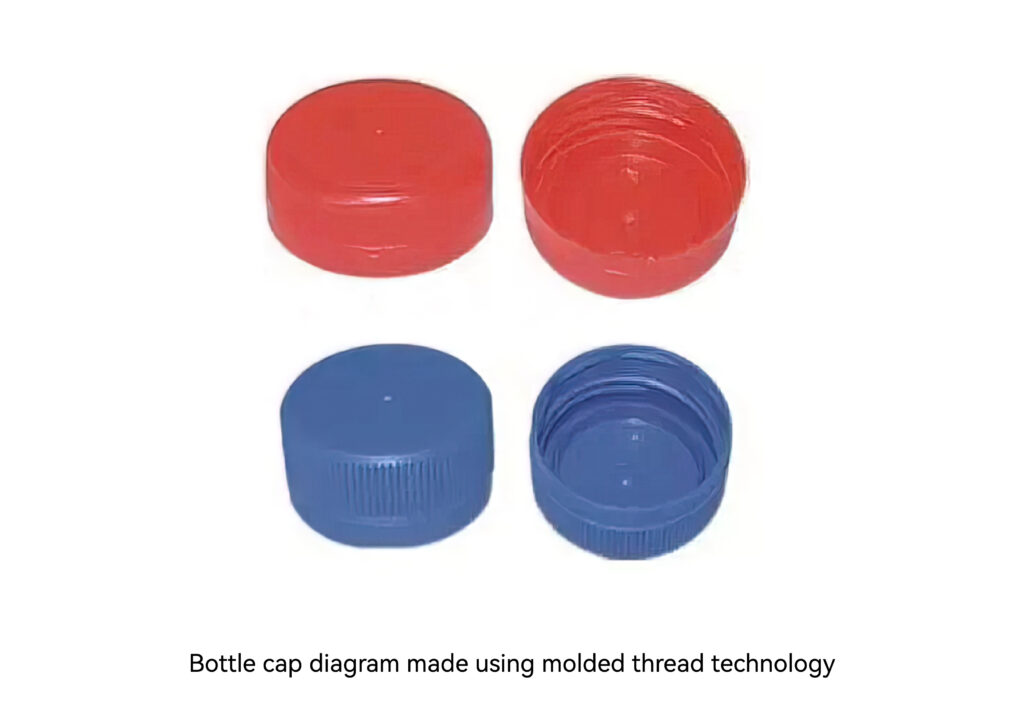

The threads on plastic products are divided into two types: external threads and internal threads. External threads usually use sliders to demould, while internal threads use twisting methods to demould. Among them, the external thread structure is relatively simple. After the product is formed, parting line marks will be left on the plastic product. If the parting line marks are obvious, it will affect the appearance of the product and the coordination of the threads. The principle is to slide open by the action of the inclined guide pillar, and then the ejection pin ejects the product. Internal thread molds can be divided into:
1. Forced thread removal structure (non-rotating type).
2. Non-forced thread removal (rotary type). Currently, molded threads are mainly used in the production of bottle caps.
Tapping thread connection
Plastic tapping threaded connection refers to drilling and then tapping holes in plastic parts to form threads, and then using the threads to connect to other parts. This method is similar to that in metal.
Its advantage is that the process does not have any requirements on the shape of the plastic parts, and accurately positioned holes can be obtained through precision machine tools.
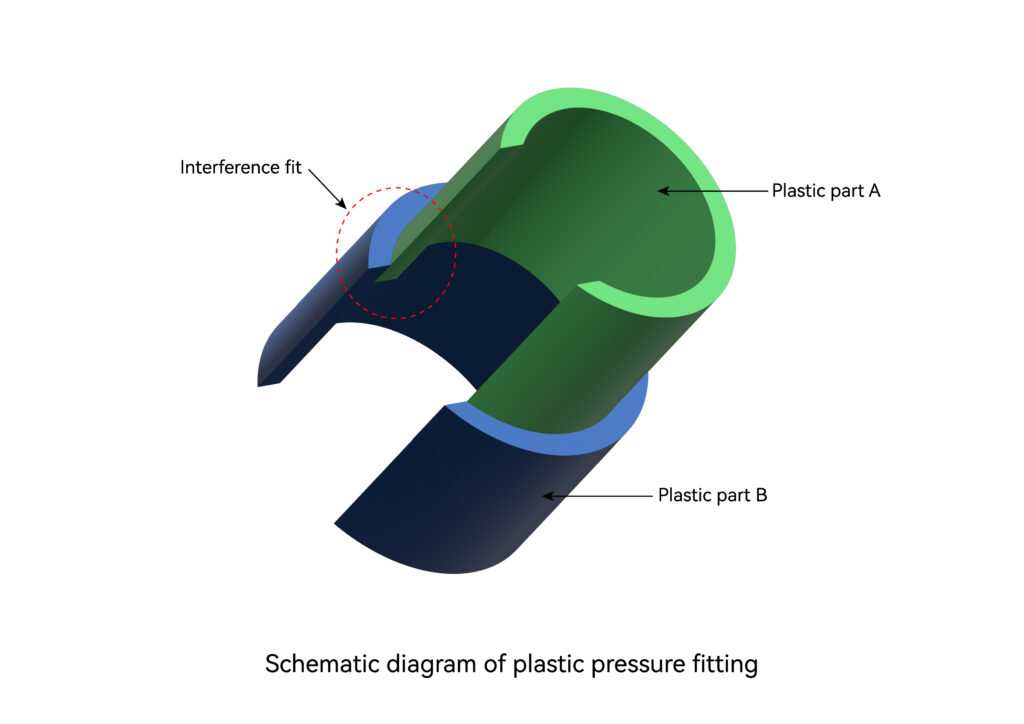
Pressure Fit
Pressure fit is also called force fit, interference fit and shrink fit. The shaft and hole whose assembly relationship is an interference fit are assembled together under a certain pressure. The hole can also be heated to enlarge the hole or cool the shaft. The assembly between the two parts is performed by reducing the size of the shaft. After assembly, an interference fit occurs when the two parts return to the same temperature. It utilizes the elastic deformation of the hole and shaft of the connected plastic parts, and can transmit a certain torque or axial force after assembly.
Snap Connection
A buckle is a mechanism used for embedded connection or overall locking between one part and another part. It is usually used for the connection of plastic parts, and its material is usually composed of plastic materials with a certain degree of flexibility. The biggest feature of the snap connection is that it is easy to install and disassemble, and can be disassembled without tools.
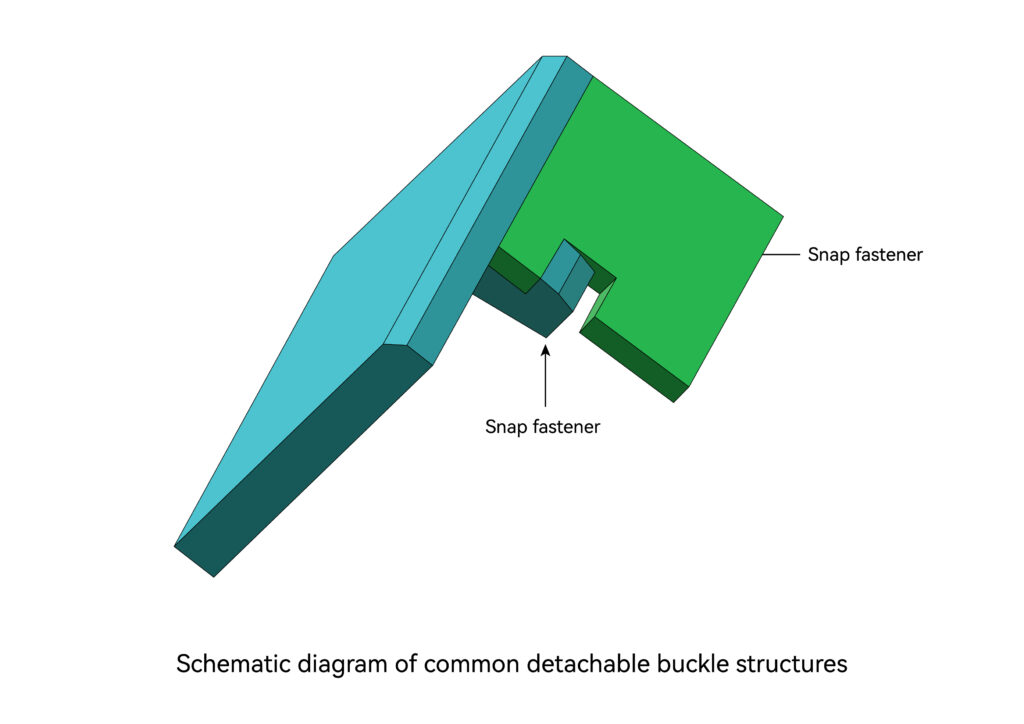
Generally speaking, buckles are composed of positioning parts and fasteners. The function of the positioning piece is to guide the buckle to reach the installation position smoothly, correctly and quickly during installation. The function of the fastener is to lock the buckle with the base body and ensure that it does not fall off during use. According to different use occasions and requirements, fasteners are divided into removable fasteners and non-detachable fasteners. Removable fasteners are usually designed so that when a certain separation force is applied, the buckle will disengage and the two connecting parts will separate. This kind of buckle is often used to connect two parts that need to be frequently disassembled. Non-detachable fasteners require artificial deflection of the fastener to separate the two parts. They are mostly used to connect and fix the parts without disassembling them during use.
Plastic Riveting
The rivet welding process is used in particular to join parts made of different materials (e.g. plastic to metal). There are rivet posts on one part that extend into holes in the other part. Then through the cold flow or melting of the plastic, the rivet posts are deformed to form rivet heads, which mechanically lock the two parts together. By changing the design of the welding head, a variety of different rivet head designs can be obtained.
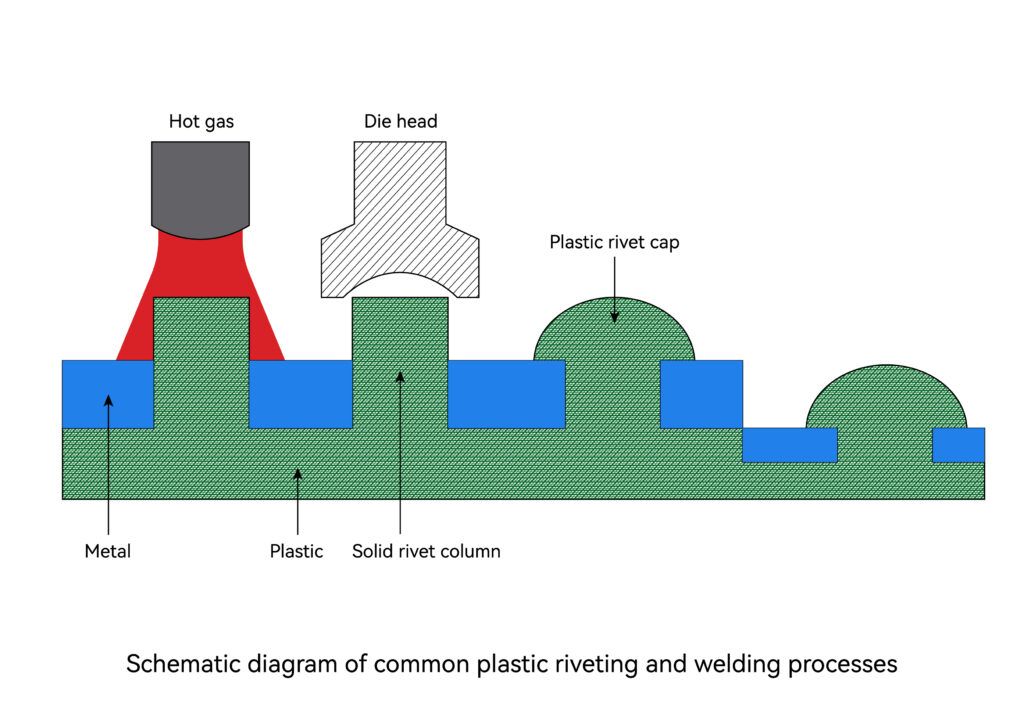
Cold rivet welding: In cold rivet welding, high pressure is used to deform the rivet posts. The cold flow causes large stress in the rivet area, so it is only suitable for plastics with good ductility.
Hot riveting welding: In hot riveting welding, the compression welding head heats up, so less pressure is required to form the rivet head on the rivet post, and less residual stress is created in the rivet head. Can be used on a much wider range of thermoplastic materials than cold riveting, including glass-filled materials. The quality of its joints depends on the control of process parameters: temperature, pressure and time.
Hot gas riveting welding: In hot gas riveting welding, the rivet column is heated by a flow of superheated air, and heat is transferred through the air pipe around the rivet column. The independent cold welding head is then lowered, compressing the rivet post.
Ultrasonic riveting: In ultrasonic riveting, the rivet posts are melted using the ultrasonic energy provided by the welding head. During the continued pressure of the welding head, the molten rivet stud material flows into the cavity within the welding head, forming the desired rivet head design.
Plastic parts welding process: The plastic weld principle is the same. First, heat the butt surfaces of the two weld plastics to be welded until they melt, then increase the butt pressure on the plastic welding rods surface, and maintain the pressure stably for a certain period of time until the welding surface solidifies, that is, the welding is successful.
Induction Welding rod
Mainly using high-frequency equipment, high-voltage rectification, self-excited high-frequency electronic tubes oscillate to instantly generate electromagnetic wave current electric fields, and use the processed PVC, TPU, EVA, PET and other plastics and plastic materials to produce polarized friction among the internal molecules of the plastics and plastic materials in the electromagnetic wave electric field. Generate heat and add a certain amount of pressure to achieve the welding effect on the plastics and plastic products that need to be heat-sealed and welded.

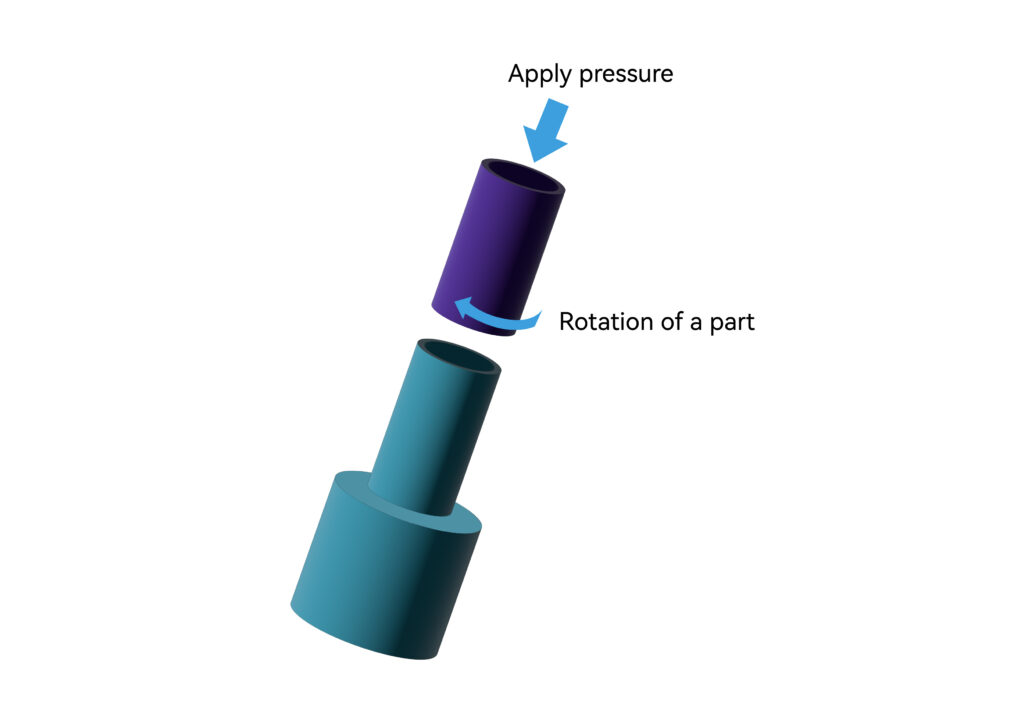
Spin Welding
Rotary friction plastic welding machines are generally used to weld two round thermoplastic workpieces. During welding, one workpiece is fixed on the bottom mold, and the other workpiece rotates on the surface of the fixed workpiece. Because there is a certain amount of pressure acting on the two workpieces, the heat generated by the friction between the workpieces can melt the contact surface of the two workpieces and form a solid and airtight combination. Among them, positioning spin welding rotates at a set time and stops at the set position instantly, becoming a permanent fusion.
Hot Plate Welding
Hot plate welding refers to placing the edges of two plastic components to be connected on a hot plate controlled by a thermostat and heating until the surface melts, the correct welding temperatures is important and then using a small pressure to press the softened two melted plastic surfaces together to achieve the connection of the plastic components. Plastic welding is a technique used to join pieces of plastic together. The process is similar to metal welding , but instead of melting metal, plastic welding process melts the plastic to create a bond.
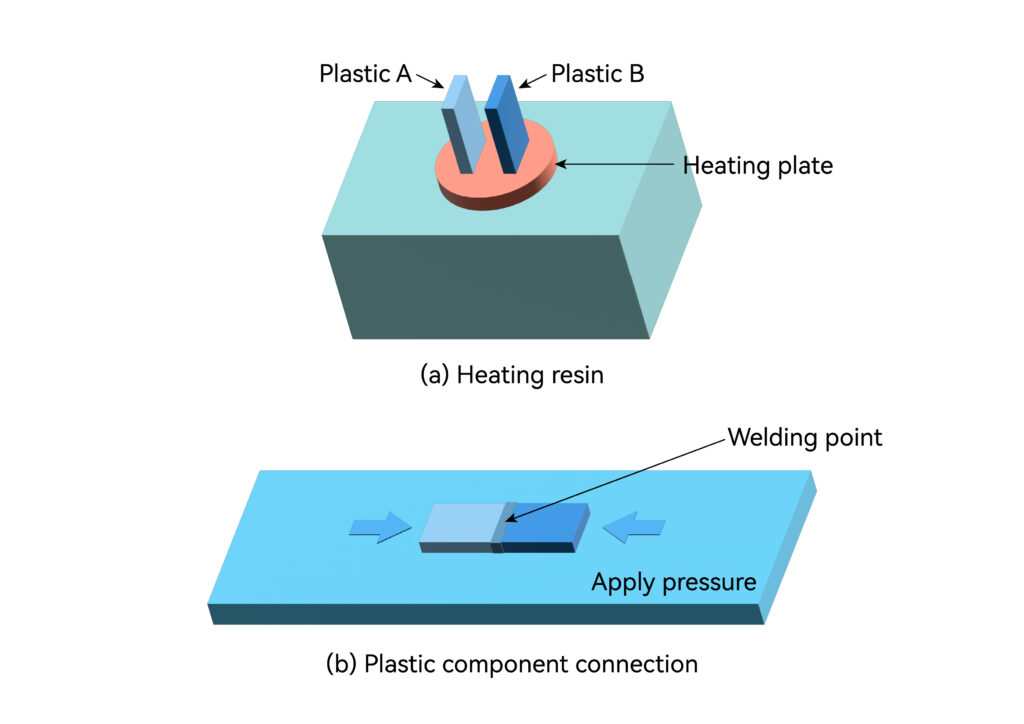
In addition, there is a commonly used hot plate heat sealing process. First, the two parts that need to be connected are stacked together, and the heat sealing plate is heated using electric heating tubes and other means. The heat sealing plate is lowered to the upper part of the two parts, and at the same time, a certain amount of force is applied to the heat sealing plate. With the pressure, the heat-sealed plate melts the contact area of the two parts and then solidifies to join them together. This process is mainly used for the sealed connection between polymer resin film materials and plastic parts.
Hot Gas Welding Rod
There are three methods of hot gas welding technique for fabrication welding of thermoplastic: spot welding, permanent hot gas welding and extrusion welding. Their basic principle is the same. The wind generated by the motor takes away the heat generated by the electric heating wire, thereby obtaining flowing hot air, so that the two plastic parts to be welded and the plastic welding rod are heated to a molten state and bonded together, thereby achieving welding purposes. Spot welding is used to hold the pieces together before permanent welding.

Spot welding is a temporary welding of materials that does not require a welding rod and requires the use of a spot welding gun.
Permanent welding uses a correct welding rod made of the same material as the part being welded. The welding tip moves rapidly back and forth in a fan shape over the welding area until the V-shaped groove and the welding rod are softened enough to be welded, usually pressed together with a hot roller. Extrusion welding refers to filling resin or feeding it from a funnel in the form of pellets or giving it in the form of a welding rod on a barrel, and then extruding it from a single-screw melting chamber driven by a motor, and heating it with an electric heating ring or hot gas. The joint surface is heated with a hot gas preheater connected to the extruder, and finally the filling resin and the welded parts are melted and connected together.
Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding uses an ultrasonic generator to convert 50/60 Hz current into 15, 20, 30 or 40 KHz electrical energy. The converted high-frequency electrical energy is converted again into mechanical motion of the same frequency through the transducer, and then the mechanical motion is transmitted to the weld rod through a set of horn devices that can change the amplitude.
The welding head transmits the received vibration energy to the joint of the workpiece to be welded. In this area, the vibration energy is converted into heat energy through friction, causing the contact surface of the two plastics to melt weld line rapidly. After a certain pressure is applied, they fuse. into one. When the ultrasonic waves stop working, let the pressure continue for a few seconds to solidify and form, thus forming a strong molecular chain to achieve the purpose of welding, and the welding strength can be close to the strength of the raw material. Ultrasound can be used for welding plastics, but also to process fabrics and films.

The main components of an ultrasonic welding system include ultrasonic generator, transducer/horn/welding head trio, plastic welding tools and frame.
The quality of ultrasonic weld plastic depends on three factors: the amplitude of the transducer welding head, the applied pressure and the welding time. The welding time and welding head pressure can be adjusted, and the amplitude is determined by the transducer and horn.
Vibration Welding
There are six process parameters in the vibration welding process: welding time, holding time, welding pressure, amplitude, frequency and voltage.
Vibration welding is divided into: linear vibration welding, orbital vibration welding and angular vibration welding.
Linear vibration friction welding uses the frictional heat energy generated at the contact surface of two workpieces to be welded to melt the plastic. Thermal energy comes from the reciprocating movement of a workpiece on another surface with a certain displacement or amplitude under a certain pressure. Once the desired degree of welding is reached, the vibration will stop, while a certain amount of pressure will still be exerted on the two workpieces, allowing the newly welded parts to cool and solidify, thereby forming a tight bond.
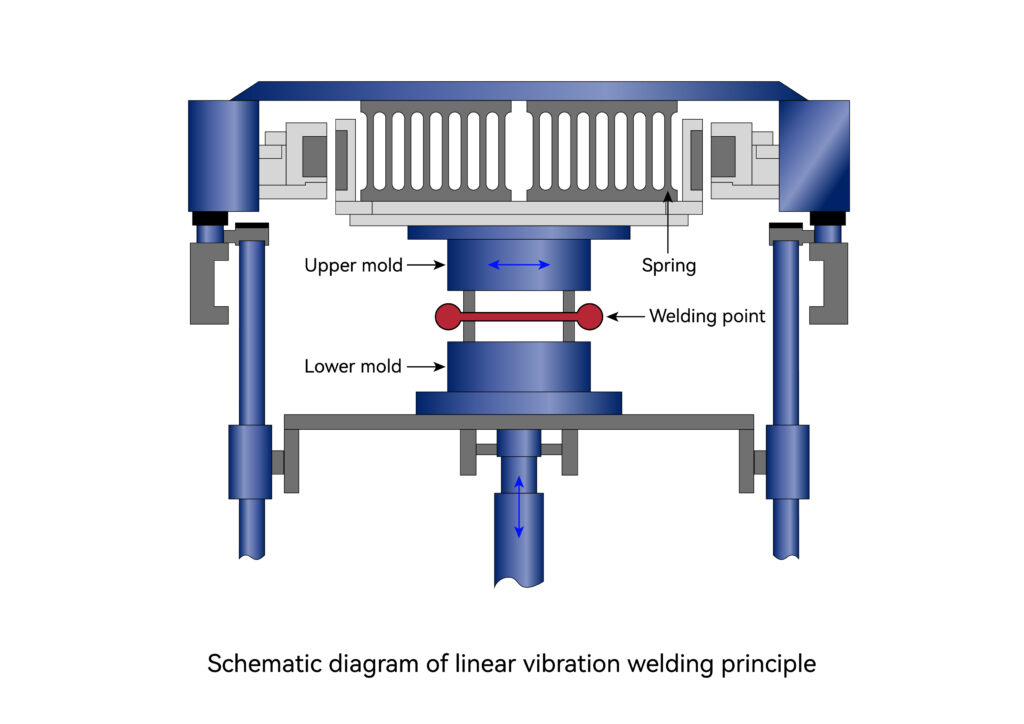
Orbital vibration friction welding is a welding method that utilizes frictional heat energy. During orbital vibration friction welding, the upper workpiece performs an orbital motion – a circular motion in all directions – at a fixed speed. Movement can generate heat energy, causing the welded portion of the two plastic parts to reach the melting point. Once the plastic begins to melt, the movement stops and the welded portions of the two workpieces solidify and join firmly together. Small clamping forces will result in minimal deformation of the workpiece, and workpieces up to 10 inches in diameter can be welded using orbital vibration friction.
Angle vibration welding refers to the rotational movement of a workpiece around a fulcrum. Currently, there are few commercially produced angle vibration welding machines.
Laser Welding
Laser welding technology is a technology that uses the heat generated by a laser beam to melt the plastic contact surfaces and thereby bond thermoplastic sheets, films or molded parts together.
It first appeared in the 1970s, but due to its high cost, it could not compete with earlier plastic bonding technologies, such as vibration welding technology and hot plate welding technology. However, since the mid-1990s, due to the decline in the equipment costs required for laser welding technology, this technology has gradually become widely popular.

Laser welding technology can come in handy when the plastic parts to be bonded are very precise materials (such as electronic components) or require a sterile environment (such as medical devices and food packaging). Laser welding technology is fast and is especially suitable for assembly line processing of automotive plastic parts. In addition, for complex geometries that are difficult to bond using other welding methods, laser welding technology can be considered.
The main advantages of laser welding are: the welding equipment does not need to be in contact with the bonded plastic parts; it is fast; the equipment is highly automated and can be easily used for processing complex plastic parts; there will be no flash; the welding is firm; High-precision welds can be obtained; vibration-free technology; can produce air-tight or vacuum-sealed structures; minimize thermal damage and thermal deformation; can bond resins of different compositions or colors together.
Hot Wire Welding
Hot wire welding, also known as resistance welding, uses a wire to transfer heat between two connected plastic parts to melt the surface of the plastic parts and apply a certain amount of pressure to join them together.

The metal wire is placed on a surface of the parts to be connected. When current passes through the metal wire, its resistance is used to cause the metal wire to generate heat and transfer the heat to the plastic part. After welding, the metal wire remains in the plastic product, and the part extending beyond the joint is cut off after welding. Generally, grooves or other positioning structures are designed on the parts to ensure that the metal wire is in the appropriate position.