Introduction
When you’re designing injection molded parts, there are a lot of things to consider that will affect how well your part functions and how good it looks when it’s done. There are a lot of things that can go wrong when you’re molding parts, like sink marks, flow lines, warpage, and more. So, it’s really important to understand the guidelines for designing parts for injection molding so you can get great results.

In this article, I’m going to give you the ultimate injection molding design rules to help you make the best plastic parts. I’ll also give you some details about process control, some important guidelines for designing molds, and some tips on how to avoid some common design problems.
Injection Molding Design
Injection molding is a process where you melt plastic and shoot it into a mold to make a part. The design of the mold and the part you’re making are really important to how well it works. Here are some reasons why design is important for injection molding.

Determine Manufacturing Complexity
After looking at the design, product designers and engineers can think about all the things that might go wrong when they make the product. The design tells them what to do so they don’t have to guess what to do when they make the product.
Ensure Manufacturing Feasibility
When you’re starting out with a new plastic part design and production process, you don’t know for sure if the part you’ve designed is going to be manufacturable. Injection molding design can help you figure out if the way you’re trying to make the part is going to work. You can figure out if you’re going to have manufacturing problems where the parts get stuck in the mold.

Preventing Part Failures
If you don’t design your injection molded parts properly, they won’t work right. They might not do what they’re supposed to do because of injection defects or other mechanical failures. Injection molding design guidelines will help you pick the right molding parameters and avoid the big problems that will make your parts not work.
Injection Molded Parts Design Considerations
Injection molding is a complex process that requires careful design considerations to ensure successful production. Once the process begins, mistakes caused by design can lead to significant delays and expenses. Therefore, it is imperative to follow proper injection molding design guidelines to avoid these mistakes. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind when designing injection molded parts.

Chamber Wall Thickness
This is one of the big things to think about when you’re designing injection molded parts. Wall thickness affects a lot of things about a part, like how it looks, how it works, and how much it costs. So, you need to figure out the right wall thickness based on how the part needs to work. You need to think about how much stress the part can take and how long it needs to last to figure out the thinnest wall you can get away with.

Parting Line
The parting line is where the two halves of the mold meet to make the final product. If there is any mismatch or misalignment in the parting line design, it may cause flash defects in the molded part. So, it is important to design a simple and straight parting line to minimize these defects.

Draft Angle
The draft angle is the angle on the surface of an injection molded part that allows it to be easily removed from the mold without damage. The required draft angle depends on factors such as wall thickness, material shrinkage, post-processing finishing needs, etc.

Ribs and Bosses
Ribs are used to strengthen the walls of a part where two walls meet at a 90-degree angle. They help make the part stronger and able to hold more weight. Bosses are raised areas on a part that are used to attach and line up other parts. They also make parts stronger in places like screw holes and slots.

Gate Location and Type
The gate in injection molding is a very important part that is directly connected to the plastic part and controls the flow of molten plastic resin into the cavity. The size, shape, and location of the gate have a big impact on the finished product. It affects how strong it is and how it looks.

Ejector Pins
This is a big deal in the injection molding setup. It helps push the part out of the mold after it has cooled enough. They often leave marks on the part. So, you need to design them on a plane that is perpendicular to the direction the pin moves.

Undercuts and Threads
Undercuts and threads are recessed or overhanging features that make the plastic part hard to get out of the mold with one pull. You want to make sure that the part can be ejected with one pull. This will help keep your injection molding costs low. So, when you’re designing injection molded parts, you want to avoid threads and undercuts.

Fillets
To make injection molding better, you want to have rounded features instead of sharp corners and edges. Sharp edges need more pressure to fill, which can damage the part and cause defects when you eject it. Rounded internal and external corners help the plastic flow better, which reduces stress and cracking.

Surface Finishes
Plastic parts can have different surface finishes that affect their texture, appearance, and feel. Choosing the right finish is important during the design phase because it determines the tools and materials needed. Rough finishes require more draft and affect material selection. The mold surface may also need to be prepared to achieve the desired finish. Any imperfection in the mold surface will show up on the molded part.

Material Selection
When you’re making stuff with injection molding, you’ve got a bunch of different kinds of plastic you can use. Each kind of plastic has its own special physical and mechanical properties. The kind of plastic you pick affects how your part works in the world you want it to work in. The main things you think about when you’re picking a plastic for injection molding are how much the plastic shrinks, how well it fits, and how much it costs.

Injection Mold Design Guide
Injection mold design and production is a big deal in plastic part manufacturing. Mold tooling helps define the shape of the intended plastic part. So, all mold components must be in the right condition for smooth injection molding.
Mold Base and Cavity Layout
The mold has to be strong and durable, easy to maintain, and easy to take apart and put back together for repairs and maintenance. The mold tooling has to be precision made so that the cavity and core line up right. The cavity layout of the mold base also has to let you get to the hollow and core inserts easily for maintenance and repairs. This cuts down on defects and makes the parts better.

Cooling System Design
The cooling system is a big deal in injection mold design. It controls the temperature of the mold cavity and plastic material. Cooling is important because it helps solidify the plastic and control shrinkage.
Runner and Gate Design
The runner and gate system controls the flow of molten plastic into the mold cavity. The gate is the entrance for plastic into the cavity, and the runner system guides the plastic to the gate. The gate and runner system design affects the efficiency of the molding process and the quality of the finished product.

Ejection System Design
The ejector system is what gets the finished part out of the mold. When designing the ejector system, you need to think about the shape of the part, how many undercuts it has, and how strong it is. To make sure the part doesn’t get messed up when you take it out, you can use ejector pins, sleeves, or hydraulic ejector systems.
Mold Material and Surface Treatment
The material you use for your mold will affect its life and the quality of your finished part. To get the best performance, your mold material should have a high melting temperature, good thermal conductivity, and excellent wear resistance. Picking the right material can help you reduce cycle time, extend the life of your mold, and reduce the risk of part defects.

Zetar Mold is the best at injection mold services to make your molding process and molded parts better. We do a complete DFM analysis for your injection molding project to make your mold and part design better. This way, you save time and money and get a better product.
Injection Molding Process Quality Control Plastic Parts
Injection molding is a super precise and efficient way to make plastic parts. But if you want to make good plastic parts, you have to control the process really well.

Overview of the Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is the process of melting plastic and then solidifying it under pressure in a mold to give it a shape. This process is done in a continuous cycle and has many steps. After the plastic resin is heated, the gate opens when the mold is under the right amount of pressure. Then, the molten plastic is injected into the mold.
When the molten resin reaches the end of the barrel, the gate closes. The two halves of the mold then close at the same time and are held together by the clamping pressure. After the holding pressure phase, the screw pulls back and the part cools in the mold. After the part cools, the mold opens and the ejector pin or ejector plate pushes the part out. The finished part is then ready for finishing.

Process Parameters and Optimization
Injection molding process control involves monitoring and adjusting multiple parameters to achieve the best results. Here are some of the key parameters to consider:
Injection pressure and speed: These parameters determine how quickly the molten plastic fills the mold cavity. The injection pressure should be high enough to completely fill the mold cavity. However, it should not be too high, otherwise it will cause flash or part distortion. The material should be able to fill the cavity in the shortest possible time without degradation.

Injection temperature: The injection temperature affects how the plastic flows and its viscosity. The plastic should be heated to its melting point and kept at a steady temperature during the injection molding process. You can use thermocouples at different points in the mold cavity to check and control the temperature.
Holding pressure and time: The holding pressure should stop the material from flowing back into the injection device. The holding time should let the plastic cool and harden completely. The time will depend on how thick the walls are and how complicated the part is.
Cooling time: The cooling time should be based on the thermal properties of the material and the wall thickness of the part. Thermocouples can also help monitor the cooling time. You can adjust the time by changing the cooling channel layout or increasing the size.

Ejection: The ejection system should ensure smooth and consistent ejection to avoid damage to the part and the mold. The ejection force should also depend on the size and complexity of the part.
Quality control and inspection is done to make sure that the molded parts are good. There are different things that people do, like process capability studies, visual and dimensional inspections, and functional testing. They help you figure out what is wrong and how to make it better.
Common Injection Molding Design Problems and Solutions

Sometimes, things go wrong when you make stuff with injection molding. These problems can make the thing not work right. Sometimes, the problems happen because of how you make the thing.
Some Typical Injection Molding Design Problems and How to Solve
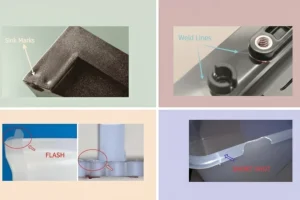
Sink Marks and Warpage
Sink marks are a defect in injection molding that show up as little dents on the flat surface of the molded part. Sink marks are usually caused by shrinkage of stuff inside the molded part, which makes the material sink from the outside to the inside.

Causes: Melt or mold temperature too high, holding or injection pressure too low, mold structure design defects, holding or cooling time and pressure not enough.
Solutions: Cool it down slowly and for a long time so it doesn’t get all stressed out. Keep the walls the same thickness so the plastic can flow through the mold in one direction. Use enough pressure and time to cool the stuff near the outside of the part. Make the mold or the material colder.

Flash and Part Sticking
Flash, splatter, or burr is when you have extra molding material that shows up as a thin line on the edge of your part. It usually happens when some material flows out of where it’s supposed to go. Flash is a minor defect, but it can become a major problem if it messes up how your part works.

Causes: Bad design and control of the exhaust system, not enough clamping force, mold design problems and bad molding conditions, too much injection pressure or mold temperature, not enough release agent, not enough cooling time.
Solutions: Make sure the venting channel is big enough, put a lot of clamping force on the plate, don’t leave any gaps, redesign the mold so the molten material flows smoothly and there’s good ventilation, put the right release agent on the mold, use the right injection pressure, mold temperature and cooling time for the material you’re using.

Short Shots and Burn Marks
Short shots are when the plastic doesn’t fill the mold completely. This means that the part you get out of the mold is not complete. Short shots are a big deal because they make your part look bad and not work right.

Burn marks are black or rust-colored marks on the surface or edge of your molded part. They usually don’t affect the part’s integrity, but they become a big problem when they burn the molded part, causing degradation.
Causes: Not enough injection pressure, trapped air pockets that block the free flow of molten plastic, using materials with extremely high viscosity, bad design of gate and runner systems, extremely high melt temperatures.

Solutions: Widen vents or add more vents to get better ventilation, use the right mold temperature to avoid fast and inconsistent material cooling, slow down injection speed to reduce the risk of trapped air, increase injection speed and pressure or use a thinner substrate for better flow.
Air Pockets and Voids
Air pocket defects are some of the most serious defects in injection molding. They show up as trapped air or bubbles in the molded part. These trapped bubbles can cause structural and aesthetic defects. Also, if the initial air in the mold gets hot and compressed tightly enough, it can explode, destroying the molded part and the mold.

Causes: Poor ventilation in the mold, uneven cavity filling, trapped air compression and ignition, insufficient molding pressure, materials prone to voids due to significant changes in density
Solutions: Increase mold temperature, redesign or modify runner system and gate positioning, use materials with lower viscosity to prevent bubble formation, limit cycle time to prevent trapped air compression and ignition, increase injection pressure, effectively exhaust trapped air in the cavity.

Parting Line Mismatch and Deflection
Parting line mismatch is when the two halves of the mold don’t line up right. It makes a visible seam or gap along the parting line of the molded part. Deflection is when the molded part warps or bends out of shape while it’s cooling. Both of these defects can make the part not meet the required specifications. That means more scrap and less productivity.

Causes: Uneven clamping force, changes in the size of the mold parts, too much injection pressure and temperature, the mold gets bigger when it gets hot, not enough time for the part to cool.
Solutions: Make sure the mold is clamped right and lined up right, keep the mold at the same temperature all the time, use the right injection molding settings for the material, and heat the part after it’s molded to get rid of stress.

How to Get Quality Injection Molded Parts
If you want good plastic parts, you need to work with a good plastic parts company. Zetar Mold is a good plastic parts company. We make good plastic parts. We have good people and good machines. We make good plastic parts that look good.
Zetar Mold got you covered with a variety of materials and finishing services to enhance the quality of your injection molds and plastic parts. Our experienced technicians can give you advice on how to optimize your mold design and recommend the right materials and surface finishes for your plastic parts.

We know that injection molding projects can be complicated. That’s why we have a streamlined quote process and provide DFM analysis reports to help you confirm your design concepts before you start manufacturing.
Our experienced engineering team can also support you throughout the manufacturing process. Submit your design files today to get an instant quote and start your injection molding journey.

Conclusion
Injection molding is a versatile and efficient technology that can manufacture high-quality custom plastic parts for a wide range of industries. However, the process is incomplete without following a set of injection molding design guidelines. This will allow you to detailLearn more about what you need and how to complete the process.

The injection molding design rules discussed in this article will help you optimize your process, ensure cost-effective production and reduce cycle times. Design errors are costly. Contact Zetar Mold today for your injection molding design. We are ready to help you achieve better results.