Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process that creates complex parts by injecting molten material into molds. It’s widely used in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
Injection molding allows high-volume production of precise parts, using materials like plastics, metals, and ceramics. It’s efficient for producing intricate shapes, minimizing material waste, and maintaining part consistency.
This overview covers the basics of injection molding, but understanding the materials, machine types, and mold designs is key to optimizing your manufacturing processes. Dive deeper to discover how to choose the right setup for your project.
Injection molding is cost-effective for large production runs.True
Injection molding is ideal for mass production due to its low per-unit cost when producing large quantities.
Injection molding is only suitable for plastic parts.False
Injection molding can be used with a variety of materials, including metals, ceramics, and composites, expanding its application beyond plastics.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create a variety of parts, commonly used in industries like automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices.
Injection molding creates parts by injecting molten material into a mold. It is fast, cost-effective, and ideal for mass production, particularly in automotive, electronics, and medical industries. Key benefits include precision, speed, and high-volume efficiency.
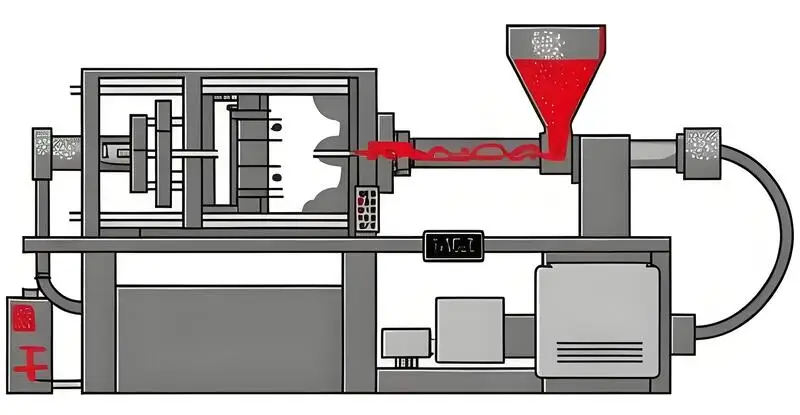
Injection molding, also known as injection molding , is a molding method that combines injection and molding. The advantages of the injection molding method are fast production speed, high efficiency, automation of operation, a wide variety of colors, shapes from simple to complex, sizes from large to small, and precise product size.
The product is easy to update and can be made into complex-shaped parts. Injection molding is suitable for mass production1 and complex-shaped products and other molding processing fields.
When the plastic is completely melted at a certain temperature, it is stirred by a screw, injected into the mold cavity with high pressure, and after cooling and solidification, the molded product is obtained. This method is suitable for mass production of parts with complex shapes2 and is one of the important processing methods.
Injection molding is suitable for large-scale production.True
Injection molding excels in high-volume production due to its efficiency, precision, and ability to create complex parts quickly and consistently.
Injection molding is a low-cost option for all materials.False
While injection molding is cost-effective for high volumes, the initial setup and tooling costs can be expensive, especially for custom designs and small production runs.
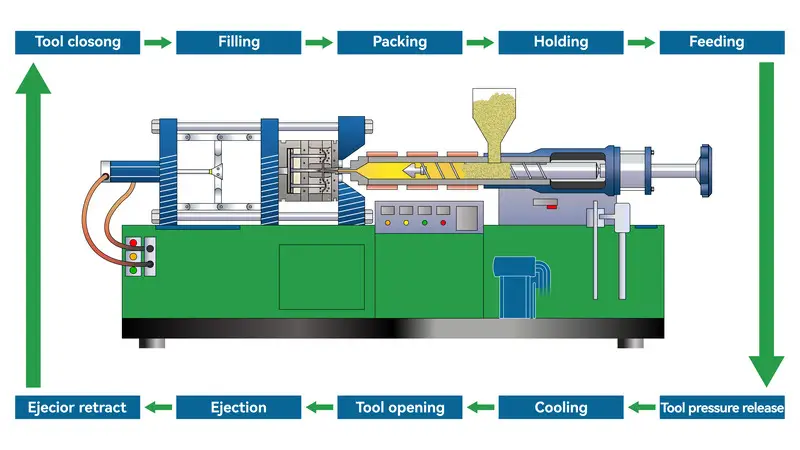
How Does Injection Molding Work?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic3 is injected into a mold to create parts with precise shapes and sizes. It’s widely used for mass-producing complex items.
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold, where it cools and solidifies to form the desired shape. It’s ideal for high-volume production, offering speed and consistency.

Injection molding is a plastic manufacturing process that injects molten plastic material into a mold and then cools and solidifies it.
What is the Basic Principle of Injection Molding?
-
Heating and melting: heating plastic particles or powder until it melts, usually in an injection machine. The melted plastic becomes thick and liquid, and can be pushed into the mold by the injection machine.
-
Filling the mold: Injecting molten plastic into the mold through an injection machine. The injection machine applies high pressure to make the plastic flow and fill the entire mold cavity.
-
Cooling and solidifying: The plastic material in the mold needs to cool down and solidify. The cooling time and temperature depend on factors like the type and thickness of the material. The specific design of the mold can also affect the cooling time and quality.
-
Opening and removing the mold: After the cooling and solidifying4, open the mold and take out the molded part. Usually there is some release agent on the mold to help the molded part easily come out of the mold.
-
Deburring, trimming, and processing: After you take out the molded part, you need to remove the excess plastic material and burrs, and trim and process the molded part. You can do this by hand or machine.
-
Inspection and packaging: Finally, you need to inspect the finished product to make sure its quality meets the requirements, and then package and transport it.
What are the Process Flows of Injection Molding?
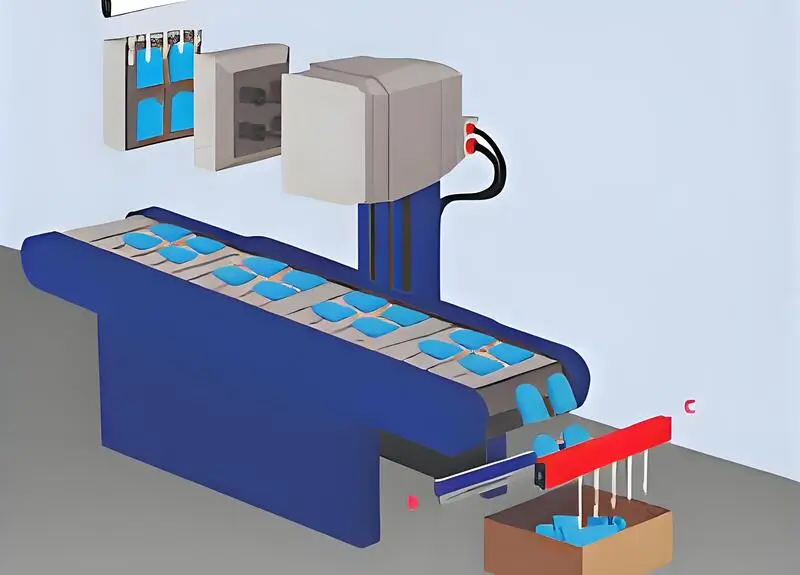
-
Mold preparation: The mold for making the plastic products you want needs to be prepared in advance. This includes designing, making, and installing the mold. The design of the mold should be based on the desired shape, size, and material properties of the product you want. When making the mold, you need to think about things like what material to use and how accurate the mold needs to be.
-
Plastic material preparation: You need to choose and process plastic materials according to the requirements of the products you want to make. Usually, you heat plastic pellets or powder until they melt, and then you shoot the melted plastic into a mold using a machine.
-
Injection: Injection is when you shoot hot plastic into a mold using an injection machine. You have to control the pressure, speed, and temperature of the injection machine to make sure you get the injection right.
-
Cooling: After you shoot the injection, you have to wait for the plastic to cool and harden. How long it takes and how hot it has to be depends on what kind of plastic you’re using and how thick it is.
-
Mold opening: After cooling, the mold needs to be opened and the molded part taken out. There are many ways to open the mold, including manual, mechanical and hydraulic.
-
Deslagging, trimming and processing: After the molded part is taken out, it needs to be deslagging, trimming and processing to remove excess plastic material, flatten the surface and process the holes required.
-
Inspection and packaging: Finally, we need to inspect the finished product to make sure it’s good enough, then we put it in a box and send it to you.
Injection molding is the fastest method for producing high-volume parts.True
Injection molding allows rapid production of large quantities of identical parts with minimal cycle times.
Injection molding can only be used with plastic materials.False
Injection molding can also be used with other materials like metal, silicone, and rubber, expanding its versatility in manufacturing.
What are the Materials for Injection Molding?
Injection molding uses various materials like thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, and metals. Choosing the right material ensures the durability, strength, and quality of the molded part.
Common injection molding materials include thermoplastics like ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon, as well as thermosets and elastomers. Material choice depends on the part’s required properties such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance.

Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a lightweight, high-strength, durable plastic with excellent corrosion resistance and chemical stability. It is used in a wide range of applications, including automobiles, medical devices, household products, and more. It is popular because it is low cost and easy to process. That’s why it is one of the most commonly used materials in the injection molding industry.
ABS
Polypropylene is a lightweight, high-strength, durable plastic with excellent corrosion resistance and chemical stability. It’s used in a wide range of applications, including automobiles, medical devices, household products, and more. It’s popular because it’s low cost and easy to process. That’s why it’s one of the most commonly used materials in the injection molding industry.
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is a lightweight plastic that’s known for being flexible and cheap. It comes in different types like HDPE and LDPE and can be used in lots of different industries, from packaging and containers to farming stuff and toys.
It’s a plastic that’s really good at not getting messed up by rust, weather, and chemicals, so it’s used a lot in pipes, containers, plastic bags, and other things. Polyethylene can be used in temperatures from -50℃ to 90℃.
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene is a clear, hard plastic that is brittle and often needs to be made tougher or have its molecular structure altered. PS is often used in packaging, food containers and disposable tableware, making electrical housings, daily necessities, video discs and other products. The operating temperature range of polystyrene is -40℃~100℃.
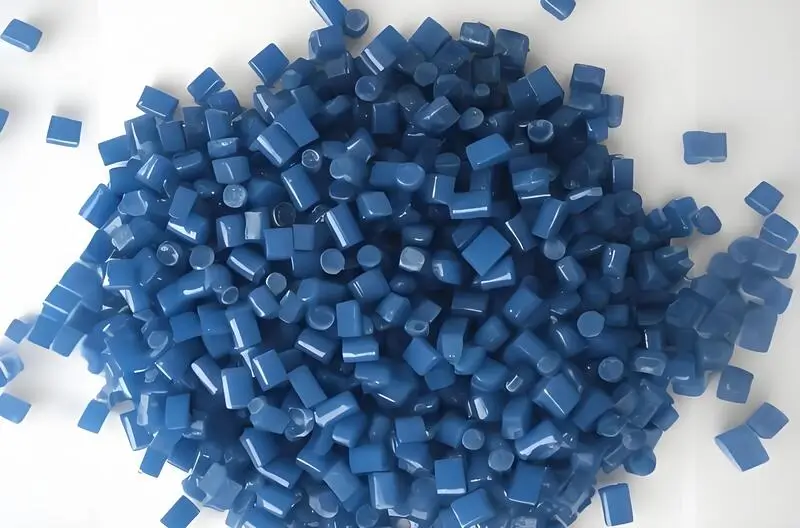

Nylon (PA)
Nylon is a high-strength, heat-resistant plastic with excellent mechanical properties, chemical stability, and impact resistance. It is widely used in the automotive, electronics, toys, clothing, and other industries. The operating temperature range of nylon5is -40℃ to 120℃.
Nylon, especially nylon 6 or PA 6, is known for being strong, tough, and wear resistant. It’s great for making mechanical parts and is used a lot in things like gears, bearings, and other parts that need to be made fast, last a long time, and be made just right.
Polycarbonate (PC)
PC, or polycarbonate, is known for being see-through, tough, and able to handle high heat. It’s got great optics, strength, processability, thermal stability, and electrical properties. It’s used in electronics, car lights, eyeglasses, and more. It can handle temperatures from -100℃ to 120℃.
Acetal/Polyoxymethylene Resin (POM)
POM, also known as acetal or Delrin, is a super-strong engineering plastic that doesn’t change shape. It’s slippery and doesn’t wear out, and it’s good at resisting chemicals. That’s why people use it to make gears, bushings and other parts that have to be just right.
Cellulose acetate (CA)
Cellulose acetate is a biodegradable plastic that is environmentally friendly and has excellent processing performance and physical properties. It is used in food packaging, toys, medical devices, and other fields. Its operating temperature range is -40℃ to 100℃.
Thermoplastics are the most common materials used in injection molding.True
Thermoplastics are popular due to their ease of processing and versatility across a wide range of applications.
Thermosets are always the best choice for injection molding.False
Thermosets are ideal for specific applications where heat resistance is required but are not always the best choice compared to thermoplastics for general molding tasks.
What are the Types of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process, offering several types for different applications, each with unique advantages in speed, cost, and product quality.
The main types of injection molding include standard, multi-shot, and insert molding. These methods vary in the number of materials used, cycle times, and part complexity. Multi-shot molding allows for different materials in one part, while insert molding involves placing components in molds for overmolding.

Gas-Assisted Injection Molding
Use nitrogen to push the molten plastic out of the way in the mold to make a hollow part, so you use less plastic and make a stronger part.
Liquid Injection Molding (LIM)
Use liquid silicone rubber (LSR) or similar elastomers injected into the cavity under high pressure, which is very suitable for producing flexible parts with complex geometries.
Metal Injection Molding
Metal processing process. After the block is formed from metal powder and binding material, it is formed and cured using injection molding technology, and then the part is post-processed at high temperature. Finally, the binder is removed and the powder is sintered to obtain the product.
Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
Instead of plastics, thermosetting polymers are used. After being pressed in a mold, the mass is mixed with a catalyst and then left to cure. The most common RIM material is polyurethane.
Liquid Silicone Injection Molding
Just like RIM, liquid silicone (rubber) is shot into the mold and then cured. This process can be used to test different material configurations before full production.
Multi-shot molding allows multiple materials in a single part.True
Multi-shot molding uses different injection units to layer multiple materials in one cycle, offering complex, multi-material parts.
Insert molding requires extra molding steps.False
Insert molding uses pre-formed components in molds, reducing the need for additional steps while offering high-quality and durable parts.
What are the Disadvantages of Injection Molding?
Injection molding offers numerous benefits, but it also has its drawbacks, including high initial costs, complex tooling, and limitations on part design flexibility.
The main disadvantages of injection molding include high setup costs, long lead times for mold production, and limitations on design complexity for certain parts. Additionally, it may not be cost-effective for small production runs due to high initial investment.

High Initial Mold Cost
One of the big downsides of injection molding is that it’s expensive to make molds. Designing and manufacturing molds to fit specific part geometries can be very expensive, especially for complex or intricate designs. This initial investment can be a deal breaker for companies with smaller production runs or limited budgets.
Takes Longer toGet Started
Injection molding usually takes longer to set up and start than some rapid prototyping methods like 3D printing. You have to design and build molds, run mold trials, and dial in process parameters before you can start making parts in volume. So the time from concept to finished part can be longer than with faster prototyping methods.
Size Limitations
Injection molding can be limited in size, especially for big parts. The size of the injection molding machine and the size of the mold cavity can limit the maximum size of the part that can be made. Making big parts may need special equipment or multiple mold cavities, which makes it more expensive and complicated.

Design Limitations
Injection molding is super versatile for making all kinds of shapes and details, but there are still some things you gotta think about when you’re designing your part. Some shapes, like sharp corners, thin walls6, or deep holes, can make it harder to fill the mold, cool the part, or get it out of the mold.
When you’re designing an injection molded part, you gotta think about things like draft angles, wall thickness, and other stuff to make sure your part can be made and will be good quality. Sometimes you might need extra stuff in the mold or extra steps to make your part if it’s got undercuts or weird shapes inside, and that can make it more expensive and harder to make.
Injection molding has a high initial setup cost.True
The molds required for injection molding are expensive and need to be custom-made, making the upfront investment substantial.
Injection molding is only suitable for large-scale production.False
While it is ideal for large-scale production, injection molding can be adapted for smaller runs by using prototype molds or smaller batch sizes, though cost-efficiency may be reduced.
What are the Advantages of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process that provides precise, high-quality products with minimal waste. It’s used across various industries, including automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
Injection molding offers advantages like fast production, design flexibility, high repeatability, and cost-effectiveness for large-volume manufacturing. It minimizes waste, reduces labor costs, and ensures consistent part quality.
High Precision
Injection molding is a process that can make parts with really tight tolerances and consistent dimensions. It lets manufacturers make parts with complex shapes and intricate details really accurately, so each part is exactly what it’s supposed to be.
Intricate Details
One of the things that makes injection molding so great is that you can make parts with a lot of detail and fancy features. This includes thin walls, fancy patterns, undercuts, threads, and other fancy details that might be hard or impossible to make with other ways of making stuff.
Durability
Injection molded parts are tough. They’re made to be strong. The process makes sure the material is spread out evenly, so the parts are solid and can take a beating. They don’t wear out easily. They don’t break easily. They don’t get messed up by the weather. That’s why you can use them for all kinds of things in all kinds of industries.
Automation
Injection molding is super automated, which makes it go fast and saves money on people. Automated injection molding machines can run all the time with just a little bit of help from people, so the parts always come out the same and you can make a lot of them. This also means you can make parts really fast, so you can get them to people when they need them and make a lot of them if you have to.

Cost-Effectiveness for Mass Production
Although the upfront costs for plastic injection molds can be steep, injection molding is very cost-effective for large-scale production. Once the mold is made, the cost per unit goes way down, making injection molding a great choice for making a lot of the same thing.
Wide Range of Materials
Injection molding can handle a lot of different materials, like thermoplastic material, thermosets, elastomers, and composites. This means that manufacturers can pick the best material for their specific needs, whether it’s mechanical properties, chemical resistance, or how it looks.
Reduced Post-Processing
Injection molded parts usually don’t need much post-processing because they come out of the mold with smooth surfaces and precise dimensions and very little scrap. This means you don’t have to do as much machining, grinding or finishing, which saves time and money. Plus, because injection molding is so consistent and precise, you don’t have as many defects, so you don’t have to do as much rework or fixing.
Injection molding ensures high precision and consistency in mass production.True
Injection molding can produce identical parts with high precision, making it ideal for large-volume manufacturing where uniformity is crucial.
Injection molding is the cheapest method for producing small batches.False
While injection molding is cost-effective for large volumes, the initial setup cost makes it less economical for small batches compared to other methods like 3D printing or CNC machining.
What are the Applications of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is widely used for producing high-quality parts in automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, and packaging, providing precision and efficiency in manufacturing.
Injection molding is used in industries like automotive, electronics, and healthcare for producing complex, durable, and high-volume parts. It’s ideal for creating everything from car components to plastic housings and medical devices, offering high accuracy and low production costs.

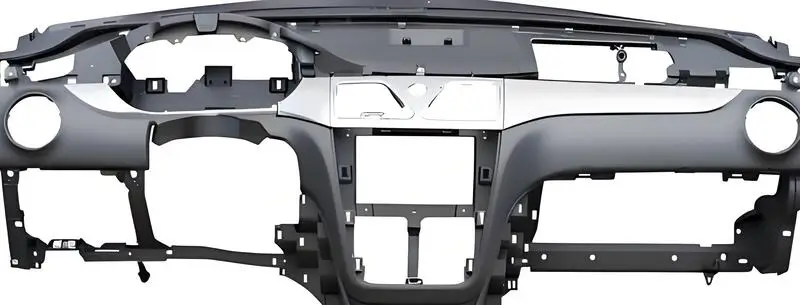
Automotive Industry
The car industry is a big user of injection molding. Injection molding can be used to make lots of car parts, like dashboards, door handles, central control panels, and so on. In the automotive production process, injection molding can greatly improve production efficiency and shorten injection molding cycle.
Injection molding can make car parts faster and make them better. It can make car parts that are more exact and have a better surface finish. This is important because the car market is a high-end market.
Electronic Industry
The electronic industry is another important application area for injection molding. Injection molding can be used to produce a variety of electronic product housings, brackets, sockets and other small parts.

Injection molding can also greatly improve the product\’s protective performance, aesthetics and durability. In the mass production of electronic products, injection molding has the advantages of high efficiency, stability and repeatability, and can meet the needs of large-scale and high-speed production.
Medical industry
Injection molding is also being used more and more in the medical field. It can be used to make all kinds of medical devices, instruments, molds, and so on, like syringes, infusion sets, extracorporeal circulation devices, and so on. Injection molding has a high level of precision, repeatability, and quality control in making medical products, and can make high-quality products that meet medical requirements.
Home Appliance Industry
Injection molding is also widely used in the home appliance industry, such as the manufacture of home appliances like TVs, washing machines, refrigerators, etc. Injection molding can meet the complex needs of various home appliances, while having efficient, stable, and controllable production capabilities.
Injection molding is suitable for high-volume production of plastic parts.True
Injection molding excels at creating large quantities of identical parts, making it ideal for industries requiring high-volume manufacturing.
Injection molding is not cost-effective for producing small batches.False
While injection molding has high setup costs, it becomes cost-effective with large-scale production, reducing per-unit cost significantly over time.
What are Injection Molding Defects?
Injection molding defects can impact product quality and manufacturing efficiency. Understanding common defects helps optimize the production process and reduce waste.
Injection molding defects include sink marks, warping, flash, and short shots. These issues arise due to factors like improper temperature, pressure, or cooling rates, affecting the final product’s strength and appearance.

Warpage
Warpage deformation is when the shape of the injection molded product gets deformed and warps, which means it doesn’t meet the shape accuracy requirements of the product. It’s one of the common and difficult-to-solve product defects in injection mold design and injection production.
The hardness, strength, toughness, stability, and other properties of the material have a big impact on the warpage of the product. If the material properties are bad or don’t meet the requirements, the product will warp after injection molding. If the temperature and speed of processes like heating, cooling, cutting, welding, etc. aren’t controlled right during the production process, the product will warp.
Surface Delamination
Surface delamination is when the surface of the part separates into thin layers, like a peelable coating. This happens because of contaminants in the material or using too much mold release.
Delamination can mess up how strong and good-looking the part is. You can stop it by changing the mold temperature, using less mold release, and making sure the plastic is dry before you mold it.
Sink Marks
Sink marks are those little dents or dimples you see on the surface of molded parts. They happen when the plastic cools unevenly or doesn’t fill the mold completely. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of sink marks, figure out what causes them, and learn how to get rid of them so your parts come out smooth and perfect.

Weld Lines
Meld lines or weld lines are lines where two streams of molten resin meet during the process of passing through the mold. These lines are usually formed around holes in the geometry. As plastic flows around a hole, a visible line forms where the two flows meet.
Weld lines are bad. They make parts weak. You can get weld lines if the resin is too cold, if you inject too slow, or if you don’t have enough pressure. You can get rid of weld lines by changing the mold. You can take out the baffles.
Flow Lines
Flow lines are complex patterns that are often discolorations, streaks, or part variations in the surface. These marks are a visual representation of the molten plastic’s progress through the plastic injection mold. When plastic moves at different speeds, it solidifies at different rates, creating these lines.
If you see flow lines, you might have a problem with injection speed or pressure. You can minimize this defect by making sure the wall thickness is consistent and the gate is in the right place.
Short Shots
A short shot is when the resin doesn’t fill the mold all the way, so you end up with a part that’s not complete and you can’t use it. Things like flow restrictions in the mold, small gates, gates that are blocked, air bubbles getting trapped, and not enough injection pressure can all cause short shots.
Understanding these issues is critical to optimize the injection molding process and ensure complete, consistent part production.
A short shot is when the resin doesn’t fill the mold all the way, so you end up with a part that’s not complete and you can’t use it. Things like flow restrictions in the mold, small gates, gates that are blocked, air bubbles getting trapped, and not enough injection pressure can all cause short shots.
Bubbles
The gas in the bubbles (vacuum bubbles) is very thin and is a vacuum bubble. Generally speaking, if bubbles are found at the moment of mold opens, it is a gas interference problem. The formation of vacuum bubbles is due to insufficient plastic filling or too low pressure. Under the rapid cooling of the mold, the fuel at the corner of the cavity is pulled, resulting in volume loss.
If the temperature, pressure, speed, and other parameters of the injection molding machine are not well controlled, bubbles will be generated in the injection molded parts.

If the temperature is too high or the pressure is too low, the raw material will not flow smoothly, which will produce bubbles; if the speed is too fast or too slow, the gas in the injection molded parts will not have time to be discharged, bubbles will be generated.
Black Spots
Black spots on injection molded parts are caused by impurities, foreign matter, or degradation products mixed into the plastic during the injection molding process. This results in black particles or spots on the surface or inside of the plastic parts. The size, distribution, and density of the black spots are related to the nature and quantity of the impurities or foreign matter.
Sink marks occur due to uneven cooling in injection molding.True
Sink marks appear when thicker areas of a mold cool more slowly than thinner sections, causing surface depressions.
Warpage always occurs from temperature issues.False
Warpage can also result from uneven part design or mold cooling, not just temperature issues.
Conclusion
Injection molding is the most popular manufacturing method in the world. It’s used to make everything from car parts to medical devices to toys. It’s fast, it’s efficient, and it can make parts with complex shapes and features that would be impossible to create with any other method.
In this article, we’ll explain what injection molding is, how it works, and why it’s so popular. We’ll also talk about the different types of injection molding, the different materials you can use, and some of the problems you might run into. and the injection unit is integral to the injection molding process, playing a critical role in the quality, efficiency, and repeatability of the molded plastic parts produced.
-
Learning about the benefits of injection molding for mass production can help businesses make informed decisions for their manufacturing needs. ↩
-
Exploring how injection molding manages complex shapes can provide insights into its versatility and application in various industries. ↩
-
Understanding the role of molten plastic can enhance your knowledge of the injection molding process, leading to better product design and manufacturing efficiency. ↩
-
Exploring the impact of cooling and solidifying on part quality can help in optimizing the injection molding process for higher precision and durability. ↩
-
Learn about PA6, PA66, PA12, and PA1010 are four kinds of nylon injection molding process introduction: NylonPolyamide (PA for short) is a plastic composed of polyamide resins. ↩
-
Learn about What are the benefits of thin wall injection molding : One of the most critical factors in thin-wall injection molding is the maintenance of uniform wall thickness throughout the part. ↩