Injection molding plays a critical role in the production of food containers, ensuring both efficiency and safety in the packaging process across the food industry.
Injection molding produces food containers by utilizing high-temperature processes to shape materials like polypropylene and PET. This method not only allows for the mass production of lightweight and durable containers but also ensures compliance with food safety standards. Key benefits include reduced contamination risks and enhanced shelf life for food products.
While this overview highlights the importance of injection molding in food container production, a deeper understanding of material selection and safety regulations is essential for manufacturers. Dive into the specifics of how various molding techniques contribute to food safety and container effectiveness.
Injection molding ensures food safety by preventing contamination.True
The high-temperature processes involved in injection molding minimize microbial growth and ensure that food containers meet health regulations.
All injection-molded food containers are made from harmful plastics.False
Many injection-molded food containers are made from safe, FDA-approved materials like polypropylene and PET, designed specifically for food contact and safety.
Overview of Injection Molding Technology
Basic Principles of Injection Molding
Heating plastic materials until they melt, then injecting the molten plastic into a mold cavity at high pressure where it cools and solidifies. This process is used extensively for manufacturing items from plastics that are both complex in shape and require close tolerances. The advantages of injection molding include fast production speeds, high efficiency, a high degree of automation, and the ability to produce intricate shapes. By designing the molds and controlling process parameters carefully, it is possible to achieve high-quality products with precise dimensions and smooth surfaces. Injection molding is widely used in industries such as household products, automotive parts, medical device, and electronic products.

Basic Process of Injection Molding
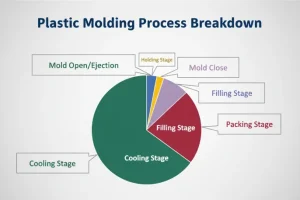
The basic process of injection molding includes the following steps:
1. Feeding: You put plastic pellets or powder into the hopper of the plastic injection molding machine. A screw at the bottom of the hopper turns and moves the plastic into the heating cylinder.
2. Plasticizing: The plastic gets heated and melted in the heating cylinder by both the heat and the turning of the screw. The temperature of the heating cylinder is usually divided into several zones, each with a different temperature to heat the plastic gradually and melt it evenly.
3. Injection: The melted plastic gets injected into the mold cavity through the screw. While injecting, the screw moves forward quickly and pushes the plastic into the mold cavity.
4. Cooling: The plastic cools and hardens in the mold. The time it takes to cool depends on the thickness of the product and the cooling system of the mold.
5. Mold Opening: The mold opens, and you take out the product. After opening the mold, you take out the product either with a robot or by hand.
6. Trimming: You trim and inspect the product, removing any extra material like flash. You check the trimmed product to make sure it meets the standards.

Injection Molding Equipment and Molds
Injection molding equipment comprises primarily of the injection molding machine and the mold, with the former consisting of the feeding system, plasticizing system, injection system, and cooling system whereas it is design and production has direct bearing on product quality and precision.
1. Injection Molding Machine: Injection molding machines come in three types: hydraulic, all-electric, and hybrid. Hydraulic machines provide pressure and stability; all-electrics are efficient and use little energy which is good for the environment too. If you need both precision as well as efficiency then there’s also hybrid models available–these use both types of system (hydraulics plus electrics).
2. Molds: Molds are usually fabricated from top-grade steel in order to resist wear and last longer. When designing a mold, you must take into account the product’s size, shape; its surface finish requirements; and how it will be de-molded too. Quality control also needs to begin right at the start with manufacturing – as any lack of precision here can directly affect (and reduce) overall finished part quality.

Material Selection for Food Containers
Types of Food-Grade Plastics
Common plastics used in producing food containers include:
1. Polyethylene (PE): Known for its excellent chemical resistance and toughness, PE is used for food bags and beverage bottles. Both low-density (LDPE) and high-density (HDPE) variants are used for flexible packaging and rigid containers, respectively.
2. Polypropylene (PP): PP has a high melting point and is heat resistant, so microwavable food containers are made from it. Food storage boxes and tableware are also made from PP, because they remain undamaged if you drop them and are see-through too.
3. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Because PET is transparent and tough, it is commonly used in food packaging and for bottles containing drinks. Such containers keep oxygen and moisture out very well – so their contents stay fresh.

4. Polystyrene (PS): Polystyrene (PS) is used for disposable tableware and food packaging because it is easy to mold and see through. Although this material is rigid with a lot of dimensional stability, products made from it cannot handle much heat- so don’t put hot things in PS containers!
5. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is not widely used in food containers because of concerns about possible harmful chemicals, despite its good resistance to them. If it is used for this application there have to be very thorough checks to make sure no unwanted extras are present as a result of the way it is made.

Characteristics and Advantages of Food-Grade Plastics
Food-grade plastics must meet the following characteristics:
1. Non-toxic and Harmless: Containing no harmful substances, materials should also pass any necessary checks to show they are safe for use with food – so that nothing unwanted gets into your meal.
2. Heat Resistance: They must withstand high temperatures, suitable for hot foods or microwave heating. Materials like PP maintain stability at high temperatures without deforming or releasing harmful substances.
3. Corrosion Resistance: They should resist acids, bases, and other chemicals, preventing material corrosion by different types of food.
4. Good Mechanical Properties: They should have good strength, toughness, and wear resistance, enabling long-term use. PP and HDPE are notable for their durability under repeated use and washing.

Safety and Environmental Considerations
If you’re choosing food-safe plastics, think about safety and environmental effects. Pick recyclable, biodegradable options for less environmental impact. PET and PE are highly recyclable and important for “closing the loop.” While biodegradable plastics such as PLA cost more right now, their advantages will likely matter more down the road.
Ensuring Safety and Health in Food Container Production
Selection and Inspection of Raw Materials
The initial phase in guaranteeing the safety of containers is to select food-grade plastic raw materials of a superior quality. Each one of these materials needs to pass rigorous checks to comply with the necessary food safety standards, for example those laid down by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the US or EU regulations covering food-contact articles. It is essential to choose reputable suppliers when purchasing materials and then carry out quality assessments not only on each batch as it arrives but also at regular intervals thereafter. These tests should include an examination of chemical composition plus evaluations relating to physical properties and hygiene criteria.

Control of the Production Environment
In order to stop food containers becoming dirty during production, the area where the containers are made needs to be really clean! It’s important that the space is regularly tidied and disinfected. Regular cleaning and disinfection of the production area, along with air filtration systems to keep the air clean, are essential. Access to the production area should be strictly controlled, and operators must wear clean work clothes and gloves to avoid contaminating the products.
Monitoring the Production Process
During production, it is important to have strict control over a number of parameters – among them temperature, pressure and cooling time. One should also employ cutting-edge automated equipment as well as monitoring systems which work in real-time: this way all indicators can be checked continuously making sure that product quality remains consistent. Injection moulding machines need to be kept in perfect condition too; they must therefore undergo regular maintenance alongside calibration (both of these help achieve optimal performance).

Inspection of Finished Products
The produced food containers must undergo rigorous quality inspections, including visual checks, dimensional measurements, and physical performance tests. Additionally, microbiological testing ensures the products are hygienically safe. Random sampling of finished products should be sent to third-party laboratories for chemical composition analysis and microbiological testing to verify compliance with safety standards.
Standards and Certifications
All companies that make food containers need two certifications: One is ISO 9001 Quality Management System certification, and the other is ISO 22000 Food Safety Management System certification. There are additional certifications for products — like passing muster on being safe to store edibles (FDA) or checking off a list about what can be in contact with food per European Union rules. Making sure everything meets up-to-date standards involves having outside groups come in regularly to check both how things are being produced as well their quality level.

Design and Innovation in Injection Molding Processes
Mold Design and Optimization
Mold design is central to the plastic injection molding process, directly impacting the quality and efficiency of the finished product. Optimization can be achieved through:
1. Runner Design: Ensuring the mold cavity fills evenly is key with runner design. This reduces problems like air bubbles and uneven cooling. If you use hot runners, production efficiency and product quality can be boosted even more.
2. Cooling Systems: Production becomes more efficient when cooling takes less time, something that effective cooling systems help achieve. Channels that cool both quickly and uniformly because their layout and dimensions have been optimized will also mean there is less chance of either deformation or stresses becoming locked into products as they cool.
3. Demolding Design: Products need to leave the mould without being damaged or changed in shape. Demolding design can make this more likely. Mechanisms such as inclined ejectors and push rods can help with demolding.

Optimization of Process Parameters
Process parameters significantly affect the quality of the final product. Optimizing temperature, pressure, and speed enhances performance and consistency.
1. Temperature Control: Controlling the temperature of the heating cylinder and mold is super important. Too hot or too cold can mess with the plastic’s flow and the product’s mechanical properties. You want to set the temperature based on the material’s characteristics and the product’s requirements.
2. Pressure Control: Injection pressure impacts the filling quality and product density. Proper injection pressure ensures even filling of the mold cavity, avoiding bubbles and uneven cooling.
3. Speed Control: Injection and cooling speeds must be fine-tuned depending on the product’s size and structure. While faster injection can make a process more cost-effective, it might also create problems like uneven cooling or warping. Experimentation and adjustment are needed to find the optimal speed parameters.

Automation and Intelligence
As Industry 4. 0 becomes more prevalent, injection molding is being automated and made smarter. This means fewer mistakes are made (which can lower quality) thanks to things like intelligent controls alongside advanced machinery – both working together in order make production quicker!
1. Automated Production Lines: Automated production lines carry out activities such as injections, cooling, demolding and trimming. These processes mean there is less need for human involvement in tasks, making them more efficient overall as well as ensuring each product is made the same.
2. Intelligent Monitoring Systems: Intelligent monitoring systems check things like speed and temperature while goods are being made: if they notice anything unusual, these systems can make small changes so that production stays constant and product quality remains high.Big data and artificial intelligence can also be used to improve how products are produced.
3. Big Data and Artificial Intelligence: By analysing lots of information at once, computers may be able to work out better ways for example setting machines or which ingredients to use. In some cases analysis might show up a problem with production that keep happening – managers could then look at making particular changes in order solve this ongoing issue.

Future Trends and Challenges
Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection
As environmental awareness grows, food container production and use are shifting towards sustainability. Future plastic injection molding processes will increasingly use renewable and biodegradable materials to minimize environmental impact while enhancing recycling and reuse rates to promote a circular economy.
1. Renewable Materials: Use of renewable materialsUsing bio-based plastics instead of regular plastics made from petrochemicals can help reduce our dependence on these resources while also cutting down on environmental pollution. One example is polylactic acid (PLA) – a versatile bioplastic that degrades well and has good mechanical properties.
2. Biodegradable Materials: These days there are food containers which break down naturally when you throw them away (biodegradable), again helping to reduce the environmental impact of waste. Some are now being made with PLA or polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA).
3. Recycling and Reuse: Improving the recycling and reuse rates of food containers minimizes resource waste and environmental pollution. Containers made from recyclable materials like PET can be collected and processed into new products.

Technological Innovation and Smart Manufacturing
Future injection molding processes will continue to evolve towards technological innovation and smart manufacturing, employing advanced technologies and equipment to improve efficiency and quality.
1. 3D Printing Technology: When it comes to mold manufacturing and small-scale production, 3D printing really shines. That’s because it allows for the quick creation of intricate molds which in turn means products can be developed faster and with cheaper molds overall.
2. Smart Manufacturing: Smart manufacturing is another game-changer: think technologies that make production lines both automated and intelligent (so they can self-optimize in real time). One major plus here is the internet of things (IoT), which links disparate devices and processes together, meaning you can enabling real-time monitoring and data analysis.
3. New Material Development: Developing new materials enhances the performance and functionality of food containers. For example, developing antibacterial, preservative, and fresh-keeping plastic materials increases food container value and meets consumer demands.

Market Demand and Competition
Because people are more and more worried about their health and food safety, the market for containers that can be used to store food is growing. This means companies that make these things need to keep getting better at what they do and how they do it, so they can make everybody happy and stay ahead of the other guys.
1. Quality Control: Having strict quality control and management systems in place makes sure that your products meet all the rules and regulations. Certifications like ISO 9001 and ISO 22000 make your products better and safer.
2. Brand Building: Building your brand and promoting your products makes more people know about you and buy your stuff. Talking to your customers and finding out what they want and what they think helps you make better products and come up with new ideas.
3. International Development: Selling your stuff in other countries and working with companies from other countries makes more people know about you and buy your stuff. Working with companies from other countries means you can learn from them and get better at what you do.

Conclusion
Injection molding plays a crucial role in the food and beverage sector, particularly in the production of food and beverage containers. This manufacturing process, widely utilized for its efficiency and precision, is essential not only in producing everyday items but also in the medical industry. Medical injection molding is pivotal in creating a range of producing medical devices and surgical instruments, that are integral to the medical sector. The production of plastic injection molded products ensures the availability of high-quality, durable, and safe components. Injection molding services cater to both the food and medical sectors, ensuring that the plastic injection molded parts used in food containers adhere to strict health and safety standards, thus ensuring patient safety in the medical field and consumer safety in the food and beverage industry.

Injection molding is crucial for making food containers. Through choosing the right materials, closely monitoring production and using clever design, it’s possible to produce safe environmentally-friendly items– that keep food fresh . With advances in technology and changes in what people want these products do more than ever before; there may also be scope for further developments such as personalisation along with being able tell if its contents are still okay to eat.