Introduction:Injection molding costs are a big deal for plastic product manufacturers who use plastic injection molding . This article gets into the nitty-gritty of plastic injection molding costs , explaining all the different things that affect how much it costs.

Is Injection Molding an Expensive Process?
Is injection molding expensive? It’s not a simple answer. While it’s been proven to be cost-effective for mass production of plastic parts, the machines are expensive, so the initial setup costs can be high.
However, as you scale up production, the overall manufacturing costs go down. So, injection molding is widely considered a cost-effective solution for mass production of plastic parts because the price per part goes down as the volumes go up.

So, the more you make, the cheaper it gets.
What are the Key Factors That Influence the Injection Molding Cost?
There are a bunch of things that can make your costs go up or down, and knowing what they are is key to making the money part of your project work out right.

Part Cost
Part Size
Bigger injection molded parts need more stuff, which costs more money. They also need bigger machines that use more energy and take longer to make stuff, which makes it harder to make stuff.

As parts get bigger, it’s harder to make them perfect, so you have to use fancier, more expensive ways to make them. Plus, bigger parts make more trash, especially in runner systems that produce excess material, further increasing plastic injection molding cost.
Part Complexity
Complex designs often require complex molds with finer details, which increases the initial mold expenses. They may also require advanced machinery and tighter tolerances, which leads to higher operating costs and longer production times.

Complex plastic molded parts often result in increased cycle times due to additional cooling and setup requirements, which reduces overall manufacturing efficiency. In addition, the potential for defects increases with complexity, which leads to higher waste and rework rates.
Part Design for Manufacturability
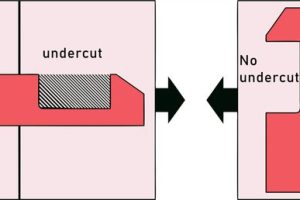
Good parts save money. They use less material, make molds easier to build, and run faster cycles. They do this by having the right wall thickness, being consistent, and not having undercuts.

Bad parts make molds harder to build, run slower cycles, and make more scrap. They do this by having complex shapes and not being designed for manufacturing.
Tooling Costs
The injection mold cost made during the injection molding process depends on the process used to make the mold, the materials used, the complexity of the mold, and the size of the mold cavity.
Choice of Mold Manufacturing Process:

3D Printing: Good for prototyping and complex designs, but may not be strong enough for mass production.
CNC Machining: It’s precise and versatile, but it can take a while and cost more.
Electrical Discharge Machining: It’s good for tiny details, but it might not work as well if the material is hard or complicated.
Mold Complexity
More complex molds, with intricate features, undercuts, or complex geometries, typically have higher mold costs because they’re harder to make. They need special tools and take longer to produce, which means you have to spend more money upfront.

On the other hand, if you have a simpler mold design with fewer complex features, you can reduce the mold cost, making it a more cost-effective option, especially if you don’t need those complex features.
It’s all about balancing your design requirements with your cost considerations to optimize your injection molding costs.
Mold Cavity Size
Bigger molds need to be stronger, which means they cost more. But they can hold more material and make more parts at once.

On the flip side, smaller mold cavities are usually cheaper because they use less material and have a simpler mold design.
You should choose the size of the mold cavity based on your production needs. Getting the right balance between cavity size and part size can help you save on material and mold costs.

Choice of Mold Material
The mold material you choose will affect how much you spend upfront and how well your manufacturing process works.
Different mold materials cost different amounts and last for different lengths of time. Aluminum and 3D printed molds are cheaper and work well if you’re making a small number of things.

On the other hand, when you’re making a lot of parts, you need a mold that’s made out of something strong like steel. Steel molds cost more up front, but they last longer and make each part cheaper.
So, picking the right mold material is a big decision. You have to balance the cost of making parts right now with the cost of making parts over time.
Here are the two most common mold material choices in the industry:

Steel: It’s tough and good for making a lot of parts, but it costs more to get started.
Aluminum: It’s light, doesn’t rust, and is cheaper, so it’s good for some things.
Material Costs
When you choose a specific material, like high-performance plastics, it usually costs more. But if you optimize your design and manufacturing process to reduce material waste, you can save a lot of money overall.

And while using recycled materials might cost a little more up front, it’s a step toward sustainability that could pay off in the long run.
Production Volume
Production volume has a big impact on injection molding. It affects how much raw material you need, how fancy your injection molding machine needs to be, and how strong/durable/whatever your injection mold needs to be. There are three big categories of production volume:

Low-Volume Production
This category needs simple molds, usually made of cheap materials like aluminum or 3D printing materials. It also needs less raw materials and less fancy machines, which means lower overall injection molding costs. But the cost per part is usually higher in low-volume production situations.
Medium- and High-Volume Production
You’ll need a tough steel injection mold because it lasts a long time, can handle multiple materials, and, if possible, a fancy machine. This will make injection molding more expensive.

But the high cost is spread out over the parts, so the manufacturing cost per part goes down. It’s important to note that the cost per part is higher in high-volume production than in medium-volume production. So their manufacturing cost per part is lower.
Equipment Expenses
The machines used in the molding process are special. The cost of a machine depends on how big it is and how complicated it is (usually how much of the work it does by itself), and ranges from $10,000 (small) or less for small-volume injection molding to $200,000 (large) for large-volume injection molding.

Medium-sized molding machines ($50,000 or more) can also be customized for medium-volume molding. Also, you need to think about the different kinds of injection molding machines and how they affect cost:
Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines
Hydraulic molding machines use hydraulic pumps to control the machine during the molding process. They have high durability, consistent injection and ejection, and affordable initial purchase costs. However, they consume too much energy and are not precise.

Electric Injection Molding Machines
Electric injection molding machines use electric servo motors to control the machine during the molding process.

They consume less energy, are accurate, have low operating and maintenance costs, and are easy to use. However, they require a high initial investment cost and require routine maintenance.
Hybrid Injection Molding Machines
Hybrid injection molding machines are a combination of these two types of machines. They are characterized by energy saving, high precision, and repeatability.

However, they require a lot of maintenance procedures due to the use of hydraulic pumps and electric motors, and the initial investment cost is very high.
Instead of buying the machines, businesses outsource the project to injection molding service providers. So they no longer have to bear the high cost of purchasing the machines, but instead need to bear the service costs of the service provider.

Labor Costs
Labor costs include a few costs related to human operators:
Setup costs include the cost of configuring and setting up the injection molding machine. It takes a lot of time due to the accuracy and technical expertise required for such processes.

Repair costs include replacing faulty parts, tools, and multiple components during the molding process.
Even though injection molding machines are automated most of the time, operator costs are important.
Surface Finishing
Surface finishing includes processes like annealing, sandblasting, powder coating, etc., where the parts are made to look better or work better. They are not part of the injection molding process itself.

However, many service providers will give you a discount if you use them for injection molding and surface finishing.
There are also extra services, which can be manufacturing processes like machining and drilling, assembly services like sonic welding, and decoration like pad printing, which make the cost of injection molding go up.

Note: Not all parts require surface finishing or other secondary operations. So, make sure you need those services to improve overall production efficiency and reduce material waste.
Part Packaging
The cost of packaging depends on whether it’s consumer packaging (i.e., something you recognize and throw away) or more expensive shipping packaging. Consumer packaging is good for products that are ready to use.

But bigger manufacturers can use automated packaging, which can reduce damage and mistakes.
Part Inspection Requirements
There are two types of part inspection costs: standard and specialized. Standard inspection is an internal process where trained personnel check for part defects (cosmetic defects or critical defects) and the quality verification team determines the possible causes.

Specialized inspection involves inviting professional engineers to inspect the product. Therefore, specialized certification costs more, and sometimes injection service providers charge a fee to provide certification.
What are the Best Practices to Reduce Injection Molding Costs?
There are a few things you can do to save money on plastic injection molds cost without sacrificing quality. By doing these things, you can make your production more cost-effective and efficient.

Simplified Mold Design
Simplified mold design helps shorten the cycle time of the molding process, improve production efficiency, and low cost injection molding . They also minimize material waste by reducing rejection rates and scrap.
Additionally, simpler molds are easier to maintain, which extends their life and reduces the frequency and cost of repairs and replacements.

To make mold design simpler, you need to get rid of stuff you don’t need, make the part shape better, and think about using parts that are already made. You can use computer tools to find and get rid of stuff you don’t need, so you can make a mold that works good and doesn’t make bad parts.
Reducing Unnecessary Part Features
This approach simplifies injection mold tooling design, which reduces manufacturing costs, as complex molds are more expensive to make. Also, reduced part complexity means reduced material usage, which directly saves costs.

Also, simpler designs can reduce molding cycles, increase productivity, and reduce labor and energy costs.
This also means less maintenance for the mold. Importantly, such simplified designs often produce parts with greater structural integrity and consistent quality, which means fewer defects.

To effectively cut the fat, you need to do a deep dive into your design, focusing on optimizing part geometry for functionality and manufacturability.
This might mean rethinking the need for certain aesthetic elements, combining multiple components into a more efficient design, or tweaking part dimensions to get rid of redundant or non-critical features.

The goal is to strike the right balance between what a part needs to do and what it costs to make.
Optimize Material Selection
While high-performance plastics may have specific advantages, they are often more expensive. Analyzing the functional requirements of a part and selecting cost-effective materials that meet those needs can result in significant cost savings without compromising quality.

Eliminate Cosmetic Appearance
In some applications, how a part looks doesn’t matter. Skipping fancy details can make parts faster and easier to make, which can save money. This is especially true for parts that don’t have to look good.
Reuse Molds
Getting the most out of a mold is a smart way to save money in injection molding. By using a mold for multiple production runs, you can spread the cost of the mold over a larger number of parts, which lowers the cost per part.

If you take good care of your mold and do regular maintenance, you can make it last longer, which saves you money in the long run.
Choose Insert Molding
Insert molding is when you put a pre-molded part, or insert, into the mold before you inject. This lets you put multiple parts into one mold, so you don’t have to do extra steps to put them together.

When you do it all in one step, you run the machine for less time and you don’t have to do as many repeats and cycles.
Plus, you don’t have to put different parts together that were designed separately, which saves time. By putting all the steps together, insert molding saves time and money.

Conclusion
Knowing the cost of plastic injection molding process is crucial for optimizing your manufacturing process. By understanding the various factors and components, you can make informed decisions.

In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about injection molding costs and how to use them. If you’re looking for a quality injection molding service provider, Zetar Mold offers top-notch products at competitive prices.