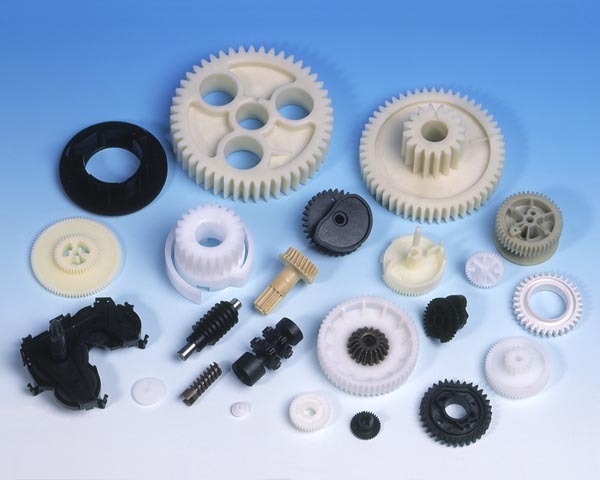
Injection molding materials play a crucial role in determining the quality and performance of molded products, impacting industries from automotive to consumer goods.
The most commonly used injection molding materials include thermoplastics like ABS, polypropylene (PP), and polycarbonate (PC), as well as thermosetting plastics such as epoxy and phenolic resins. These materials are favored for their excellent moldability, strength, and versatility, making them suitable for various applications. Key benefits include cost-effectiveness, durability, and the ability to produce complex shapes with precision.
Understanding the properties and applications of these materials is essential for optimizing your injection molding processes. Explore further to learn how selecting the right material can enhance product performance and reduce production costs.
Thermoplastics are the most common materials used in injection molding.True
Thermoplastics like ABS and PP are widely used due to their excellent flow characteristics, ease of processing, and recyclability.
All injection molding materials are equally durable.False
While many materials used in injection molding are durable, their performance varies significantly based on the type of material and its specific properties, affecting their suitability for different applications.
What is Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)?
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a highly durable, flexible, and abrasion-resistant material, often used in manufacturing for products that require elasticity and resilience. TPU is widely applied in industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods due to its balance of strength and flexibility.
Meaning and Characteristics
TPU is another rubber-plastic blend with very desirable qualities in its polyurethane component. It is very hard and has very good compressive strength, abrasion resistance, and chemical resistance. In addition, these properties don’t change much at extreme temperatures.
But it’s one of the hardest materials to injection mold. It’s so hard and crystalline that it’s difficult to mold. You need experts to handle this injection molding material.
Application
It’s used for protective housings and casings, power tools, casters, inflatable rafts, footwear, and more.
What is Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene (PP) is a durable, lightweight plastic used across industries due to its resistance to heat and chemicals. PP is often found in packaging, automotive components, and textiles. Key advantages include its low cost, recyclability, and high tensile strength.
Meaning and Characteristics
PP is one of the lightest plastics.It has a high melting point and high chemical resistance. Its yield, tensile, compressive strength and hardness are better than those of low-pressure polyethylene. It has outstanding rigidity, good stress relaxation resistance at high temperature (90°C), good heat resistance, and can be used above 100°C.
It will not deform at 150°C without external force. It is very stable in many media except concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Low molecular weight aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons have a softening and swelling effect on it.
It hardly absorbs water, has poor high-frequency electrical properties, and is easy to mold. It is used as general structural parts, corrosion-resistant chemical equipment, and heated electrical insulation parts, and is widely used in automotive interior materials.
PP is one of the lightest plastics1. Its yield, tensile, compressive strength and hardness are better than those of low-pressure polyethylene. It has outstanding rigidity, good stress relaxation resistance at high temperature (90°C), good heat resistance, and can be used above 100°C.
It will not deform at 150°C without external force. It is very stable in many media except concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Low molecular weight aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons have a softening and swelling effect on it.
It hardly absorbs water, has poor high-frequency electrical properties, and is easy to mold. It is used as general structural parts, corrosion-resistant chemical equipment, and heated electrical insulation parts, and is widely used in automotive interior materials.
But it’s got a high coefficient of thermal expansion, which means it doesn’t work well in high temperature applications. It’s also hard to handle when you’re injection molding it. It degrades under ultraviolet (UV) light and it’s flammable after you injection mold it.
Application
Some of the things you can make with it are food containers, carpets, toys, and home appliances.
What is Nylon Polyamide (PA)?
Nylon Polyamide (PA) is a high-performance thermoplastic used in applications requiring high strength and impact resistance, such as automotive parts, textiles, and electrical components. It offers excellent wear resistance, high tensile strength, and can be used in both dry and wet environments. Common grades include PA6 and PA66, with PA6 being slightly more flexible and PA66 having better strength and heat resistance.
Meaning and Characteristics
Nylon is a great material. It’s tough, heat resistant, and has good surface friction/wear properties. It’s a natural compound and it’s also made synthetically.
The synthetic kind is great for injection molding. “It also has vibration dampening properties, so it’s good for making noise dampeners. The common grades are.
Nylon 11 : A bio-based polymer with good impact strength, dimensional stability, and UV resistance. It also has very low water absorption.
Nylon 12 : It is very similar to Nylon 11, but has slightly lower impact strength, but higher abrasion and UV resistance.
Nylon 46 : It is ideal for high temperature applications that require high impact strength, abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and electrical resistance.
Nylon 66 : A good alternative to metal parts. It has high stiffness, strength, wear and abrasion properties, and fatigue resistance.
Injection molding nylon can be a challenge because it shrinks a lot. You have to design the mold with the right amount of space and angles. Also, nylon doesn’t like acids and bases.
Application
Nylon is used to make gears, bearings, guitar strings, waterproof and wear-resistant fabrics, and ropes.
What is Polystyrene (PS)?
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer derived from the monomer styrene. It is widely used in products like disposable cutlery, CD cases, and packaging materials. PS is valued for its rigidity, affordability, and ease of processing. It can be solid or foam, with foam PS often used for insulation and packaging due to its lightweight nature.
Meaning and Characteristics
PS is one of the few brittle injection molding materials2. It is super light, doesn’t care about moisture or chemicals, and is great for injection molding because it shrinks the same amount all over when it cools down.
Polystyrene is clear and transparent, can be easily dyed, and has a density that is only lower than PP and PE. It has excellent electrical properties, especially good high-frequency characteristics, second only to F-4 and PPO. In addition, it is second only to methacrylate resin in terms of light stability, but its radiation resistance is the strongest among all plastics.
The most important feature of polystyrene is that its thermal stability and fluidity when molten are very good, so it is easy to mold and process, especially injection molding, and is suitable for mass production. The molding shrinkage is small, and the dimensional stability of the molded product is also good.
PS is used to make things like toys, electrical appliances, and containers. It’s also important in the medical devices because it doesn’t break down from gamma radiation, which is how medical equipment is sterilized. So things like petri dishes and culture kits are all injection molded with PS.
What is Polycarbonate (PC)?
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable, transparent plastic known for its excellent impact resistance and heat tolerance. It is commonly used in applications such as eyewear lenses, medical devices, automotive parts, and electronics. Key properties include high tensile strength, light transmission, and resistance to heat and UV radiation.
Meaning and Characteristics
PC has excellent impact toughness and creep resistance, high heat resistance3 good low temperature resistance, brittle temperature of -100℃, bending tensile strength comparable to nylon, high elongation and elastic modulus, and excellent impact strength.
It is colorless and transparent, has good colorability, higher heat resistance than nylon and polyoxymethylene, better creep resistance and electrical insulation, good corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Application
PC has great toughness, crack resistance, and impact resistance. It is transparent. It also has the great quality of keeping its mechanical properties and appearance over a wide temperature range.
So it works well in high temperature environments. Medium (and internal stress) requires higher the formation conditions. PC is known to be harmful to the human body, especially the reproductive system. Fragmentation. After injection molding, acrylic parts are easy to change and finish.
What is acrylic (PMMA)?
Acrylic (PMMA) is a versatile, durable plastic known for its clarity and weather resistance. It is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, construction, and signage. Acrylic is prized for its high impact resistance, optical clarity, and ease of fabrication, offering an ideal balance of durability and versatility.
Meaning and Characteristics
Acrylic, also known as poly(methyl methacrylate), is a thermoplastic material that’s lightweight, strong, and clear. It’s not flexible, but it doesn’t chip easily.
One of the best things about acrylic is that it’s easy to work with. After you mold it, you can easily change and finish acrylic parts.
PMMA has some notable disadvantages. First, it scratches easily, which not only affects how clear it is but also how it looks. Second, it gets greasy easily, which affects how clear it is and how it feels. Third, it doesn’t do well in really hot or really cold temperatures.
Application
People use acrylic for things like display cases, cases for solar panels, windows, and so on.
What is Thermoplastic Rubber (TPE)?
Thermoplastic Rubber (TPE) is a flexible, durable material that combines the characteristics of rubber with the ease of plastic processing. It can be molded, extruded, and recycled, making it ideal for use in automotive seals, medical components, and consumer goods. TPE offers benefits such as excellent elasticity, resistance to wear, and the ability to be reprocessed for various applications.
Meaning and Characteristics
TPE is different from other injection molding materials because it is a plastic-rubber blend. It has a low melting point. It combines the best of both worlds. It is flexible, can be stretched a lot, is strong, and is recyclable. Plus, the best part is that it is cheap compared to most rubber alternatives.
However, it is not good for use at high temperatures because it loses some of its material properties. Also, you shouldn’t stretch it too much for too long because it will creep.
Application
It has a wide range of uses. It’s good for making gaskets, hoses, shoe parts, shock mounts, bumpers, and so on.
What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a durable plastic with excellent impact resistance and thermal stability. It is commonly used in the production of automotive parts, toys, and electrical components. ABS can be easily molded, making it ideal for injection molding applications.
Meaning and Characteristics
ABS is made from three chemicals: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Each chemical has different properties: acrylonitrile is strong, heat-resistant, and resistant to chemicals; butadiene is tough and can withstand impacts; styrene is easy to process, shiny, and strong.
ABS is a shapeless material. When the three chemicals are mixed together, they make a terpolymer with two parts: one part is a continuous mix of styrene and acrylonitrile, and the other part is a mix of polybutadiene rubber. The properties of ABS depend on how much of each chemical is used and how the two parts are mixed together.
This allows for great flexibility in product design, allowing hundreds of different grades of ABS materials to be produced on the market. These different grades of materials provide different properties, such as medium to high impact resistance, low to high gloss, and high temperature deformation characteristics.
ABS materials have extremely high processability, aesthetic characteristics, low creep and excellent dimensional stability, as well as high impact strength.Uses, typical applications: water meters and other commercial stuff, cable casings, mechanical cams, sliding mechanisms and bearings.
Cars (dashboards, tool hatches, wheel covers, mirror boxes, etc.), fridges, high-strength tools (hairdryers, blenders, food processors, lawn mowers, etc.), phone cases, typewriter keyboards, recreational vehicles (e.g. golf carts) and jet skis.
Processing conditions for injection molds: Drying: ABS material is hygroscopic and needs to be dried before processing. The recommended drying condition is at 80-90°C for at least 2 hours. The material temperature should be guaranteed to be less than 0.1%.
Melting temperature: 210-280C; recommended temperature: 245.Mold temperature: 25 … 70C. (Mold temperature will affect the finish of plastic parts, and lower temperatures will result in reduced finish. Injection pressure: 5001000bar.
Injection speed: medium speed, ABS plastic combines the characteristics of three components, acrylonitrile has high hardness and strength, heat resistance and corrosion resistance, butadiene has impact resistance and toughness; styrene has high gloss, easy to color and easy to process.
The characteristics of the above three components make ABS plastic a thermoplastic with comprehensive properties of strong quality, toughness and high rigidity.
Change the ratio of the three components of ABS, and its properties will change accordingly to meet the requirements of various applications, such as high resistance ABS, heat-resistant ABS, high gloss ABS, etc. ABS plastic is easy to process.
It can be formed by injection, extrusion, thermoforming and other methods. It can be processed by sawing, drilling, kneading, grinding and other methods. It can be combined with organic solvents such as chloroform, and can also be subjected to surface treatments such as coating and electroplating.
ABS plastic is also an ideal choice for wood substitutes and building materials. ABS plastic has high strength, light weight, high surface hardness, very smooth, easy to clean, dimensionally stable, good creep resistance, and suitable for electroplating.The application field of ABS plastic is still expanding. ABS plastic is widely used in industry.
ABS injection products are usually used to make shells, boxes, parts, toys, etc. Well, small water absorption, small friction coefficient, good chemical resistance, and no more than nylon. Make it an ideal choice for dense applications.
Application
In addition, its performance can also be stable at extremely low temperatures. Various copper parts of the device, pole and sprayer. In addition, its applications include kitchen knives, gears, furniture, and ball bearings.
What is Polyoxymethylene (POM)?
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a versatile plastic known for its exceptional mechanical properties, such as high tensile strength, low friction, and dimensional stability. It is commonly used in applications requiring precision, such as gears, bearings, and automotive components. POM is available in two main forms: homopolymer and copolymer, with the homopolymer offering superior strength and rigidity.
Meaning and Characteristics
POM has good comprehensive properties. It has high tensile strength, impact toughness, rigidity, fatigue strength, creep resistance, good dimensional stability, low water absorption, low friction coefficient, good chemical resistance, and performance is no less than nylon.
It has poor thermal stability, is easy to burn, and will age if exposed to the atmosphere for a long time.
POM is great for things that need to be really precise. It’s stiff and rigid, so it doesn’t change shape much. It’s also slippery and smooth, so it’s good for things that rub together a lot. It works well even when it’s really cold.
Application
It is more desirable when plastic injection molding hard automotive parts such as handles and switches. It can be used as bearings, gears, cams, valves, pipe nuts, pump impellers, small parts of the chassis, car dashboards, carburetors, boxes, containers, rods, and various copper replacement parts for sprayers.
In addition, its applications also include kitchen knives, gears, furniture, and ball bearings.
What is Polyethylene (PE)?
Polyethylene (PE) is a lightweight, flexible plastic made from polymerized ethylene monomers. It’s commonly used in packaging, containers, and various plastic products due to its resistance to chemicals and low cost. There are several types of polyethylene, including low-density (LDPE) and high-density (HDPE), each offering unique properties for different applications.
Meaning and Characteristics
PE is divided into three major categories with different densities: high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
Generally, PE grades are ductile, have good impact strength and creep resistance (can withstand mechanical loads for a long time without deformation). In addition, they are resistant to chemical reactions.
Application
HDPE is stronger and harder. So, you can use it to mold things like kettles, bathtubs, and pipes. On the other hand, LDPE is more flexible. It’s a great packaging material and has a billion-dollar product in the packaging industry (shopping bags, foils, films).
Conclusion
The commonly used injection molding materials and plastic materials suitable for injection molding include PE, PP, PS, ABS, PC, PA, POM, PBT, PMMA, etc., this plastic material are thermoplastic and suitable for hot injection molding. In this article, we introduce a variety of injection molding materials, focusing on their advantages and disadvantages in injection molding.
-
Learn about Polypropylene: Polypropylene is the lightest of all commercial plastics with a good balance of properties …… ↩
-
Learn about What You Need to Know About Common Injection Molding Material : Common injection molding materials include thermoplastics such as ABS, polypropylene …….. ↩
-
Learn about Polycarbonate (PC) : Polycarbonate possesses excellent impact strength, high heat resistance and good dimensional stability. ↩