Custom ABS Injection Molding Factory
ABS injection molding manufacturing and design guide

Resources for The Complete Guide to ABS Injection Molding
What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?

ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a type of plastic that is used in a lot of different things like making stuff, building stuff, and things people buy. It is made up of three different things: acrylonitrile (which makes it strong and hard), butadiene (which makes it tough and not break), and styrene (which makes it shiny and easy to make). ABS has a lot of good things about it, like it is really hard to break, it can be used with a lot of different chemicals (like acid or stuff that is really strong), it can get really hot or really cold and it won’t change shape, it is really good at stopping electricity, and it costs a little bit to make, so it is cheap to buy. It is easy to make things with ABS, like using a machine that squishes it into a shape or using a 3D printer.
ABS has a lot of uses. You can find it in toys (like LEGO bricks), appliances, car parts (like bumpers and dashboards), medical devices (like syringes), construction materials (like pipes and fittings), and electrical parts (like connectors and switches). ABS is made by mixing chemicals together in a big tank. The mixture is then heated up and turned into a solid. This makes ABS strong and long-lasting. ABS can also be melted down and made into something new. This makes ABS a good choice for the environment and for saving money. Overall, ABS is a good plastic that can be used for a lot of things. It works well, doesn’t cost too much, and can be used in many different ways.
What types of ABS materials are there?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer that is used in many different industries because of how strong it is. There are a few different types of ABS materials, and the one you use depends on what you need it to do. Here are the main types:
1. General-purpose ABS:
The most common type is general-purpose ABS, which has good impact resistance, chemical resistance, and processability. It is easy to mold and is suitable for making consumer goods, electronic product housings, automotive interiors, and toys. It is widely used in many industries because of its comprehensive performance.
2. High-impact ABS:
High-impact ABS is designed to enhance impact resistance while maintaining rigidity. It is used in protective gear, tool handles, and external automotive parts that need to withstand high impact forces, performing well in mechanically demanding environments.
3. Flame-retardant ABS:
Flame retardant ABS is a material that has flame retardants added to it. It is used in applications where fire safety is important, such as electrical equipment and car parts. It helps to reduce the risk of fire and keep people safe.
4. Heat-resistant ABS:
Heat-resistant ABS is made to withstand high temperatures without deforming, keeping its mechanical properties. It is often used in parts that need to stay stable at high temperatures, like car dashboards and inside household appliances, so they keep working even when things get really hot.
5. Low-smoke ABS:
Low-smoke ABS is a type of ABS that has been modified with additives to reduce the amount of smoke it emits when it burns. This makes it ideal for applications where there are strict environmental requirements, such as aircraft and medical devices. By reducing the amount of harmful smoke that is released during a fire, this material can help to improve safety.
6. UV-resistant ABS:
UV-resistant ABS is treated to resist degradation caused by ultraviolet exposure. It’s perfect for outdoor applications like outdoor furniture and signage. It extends product lifespan and keeps things looking good.
7. Glass-filled ABS:
Glass-filled ABS is a material that adds glass fibers to enhance its mechanical properties, such as stiffness and impact resistance. It is commonly used in automotive parts and sports equipment that require high mechanical strength to ensure reliability under harsh conditions.
8. Mineral-filled ABS:
Mineral-filled ABS is a cost-effective way to improve performance by adding mineral powders (like calcium carbonate). This material is often used in applications where cost is a concern, but performance is still important.
9. Transparent ABS:
Transparent ABS is a special kind of ABS that is modified to be transparent while still maintaining some impact resistance. It is good for products that need to look good, like display cases and clear packaging, because it looks nice but is still strong.
10. ABS Alloys (such as ABS/PC and ABS/PET):
ABS alloys are a mix of ABS with polycarbonate (PC) or polyethylene terephthalate (PET), combining the best of both worlds. This material is great for impact resistance, heat resistance, and optical clarity, making it perfect for high-end consumer goods and electronic housings.
What are the characteristics of ABS?
ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene) is a super useful plastic that can do a lot of things. It’s strong, tough, and can take a hit, plus it’s easy to work with. That’s why you’ll find ABS in all kinds of stuff, from cars to toys. Here are the key characteristics that define ABS material:
1. High Strength and Impact Resistance:
One thing that’s really great about ABS materials is that they’re super tough. They can take a beating and not crack or break, which makes them perfect for stuff that needs to be strong and take a lot of abuse, like car parts and big plastic boxes for machines.
2. High Toughness:
ABS has great toughness, so it can absorb impacts even at very low temperatures, which means it won’t break when you drop it. This is especially important for outdoor products and things you use in cold places.
3. Hardness:
ABS has a moderate surface hardness, which means it can resist scratches and wear. This makes it last longer when you use it to make things that rub together a lot.
4. Heat Resistance:
ABS has good heat resistance and can withstand temperatures of 80-85°C without getting soft or losing strength. But if you go hotter than that, it will start to break down and get brittle. So be careful if you need something that can take a lot of heat.
5. Low-temperature Resistance:
ABS is not only resistant to high temperatures, but it also performs well in low-temperature environments. It remains tough and doesn’t get brittle. That’s why ABS is used in a lot of products that have to work in different temperature environments, like outdoor equipment or things used in cold regions.
6. Good Electrical Insulation:
ABS materials are insulators with very high resistivity and do not conduct electricity, making them particularly suitable for the electronics and electrical fields, especially for components that require insulation protection. Its insulation performance remains stable in environments with significant humidity and temperature fluctuations.
7. Limited Thermal Conductivity:
While ABS is mostly known for its insulation properties, it still has some thermal conductivity, which can help dissipate heat in certain applications, keeping devices at lower operating temperatures.
8. Chemical Resistance:
ABS is resistant to many chemicals, including acids, bases, and salts, which makes it a good choice for applications in the chemical industry where the environment is only mildly corrosive. However, some strong solvents, like acetone or some chlorinated hydrocarbons, can degrade or soften ABS, so be careful when choosing materials for these chemical environments.
9. Solvent Resistance:
In everyday applications, ABS has good resistance to most common household solvents, making it suitable for products such as kitchen utensils and appliance housings, which are not easily damaged by solvent contact.
10. Easy to Process:
ABS is a thermoplastic that can be easily processed into different shapes and sizes, which is great for common processes like injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. It flows well and is very malleable, so you can make complicated molds during production, which speeds up the process and makes it more efficient.
11. Convenient Surface Treatment:
ABS has a smooth surface and good processing performance. Through processes like painting and electroplating, ABS products can look better and be more wear and corrosion resistant, so they’re popular in high-demand aesthetic design applications.
12. Moisture Resistance:
ABS has low moisture absorption, so it keeps its mechanical properties and doesn’t get all wonky in humid environments. That’s why it’s good for outdoor stuff and things that get wet a lot, like gardening tools and boat parts.
13. UV Sensitivity:
ABS is great in many ways, but it doesn’t like the sun. It can turn yellow and get weak if it’s left outside for a long time. So, if you’re going to use ABS outside, you need to do something to protect it from the sun.
14. Recyclability:
ABS is a recyclable plastic, and in both industrial and everyday life, you can reuse recycled ABS materials to make new products. This makes ABS a great choice for many companies looking for environmentally friendly materials.

What are the properties of ABS?
ABS, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a thermoplastic polymer that’s used in a lot of stuff. It’s got a bunch of good things going for it that make it useful in a bunch of different industries. Below are the key properties parameter of ABS:
| Property | Metric | English |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.882 - 3.50 g/cc | 0.0319 - 0.126 lb/in³ |
| Water Absorption | 0.0250 - 2.30 % | 0.0250 - 2.30 % |
| Moisture Absorption at Equilibrium | 0.100 - 0.300 % | 0.100 - 0.300 % |
| Water Absorption at Saturation | 0.00950 - 1.03 % | 0.00950 - 1.03 % |
| Maximum Moisture Content | 0.0100 - 0.150 | 0.0100 - 0.150 |
| Linear Mold Shrinkage | 0.000 - 0.0290 cm/cm | 0.000 - 0.0290 in/in |
| Linear Mold Shrinkage, Transverse | 0.00200 - 0.00900 cm/cm | 0.00200 - 0.00900 in/in |
| Melt Flow | 0.0800 - 125 g/10 min | 0.0800 - 125 g/10 min |
| Electrical Resistivity | 1500 - 1.00e+18 ohm-cm | 1500 - 1.00e+18 ohm-cm |
| Surface Resistance | 1000 - 2.00e+17 ohm | 1000 - 2.00e+17 ohm |
| Dielectric Constant | 2.70 - 3.80 | 2.70 - 3.80 |
| Dielectric Strength | 15.7 - 53.0 kV/mm | 400 - 1350 kV/in |
| Transmission, Visible | 0.000 - 90.0 % | 0.000 - 90.0 % |
| Processing Temperature | 170 - 270 ℃ | 338 - 518 ℉ |
| Nozzle Temperature | 180 - 310 ℃ | 356 - 590 ℉ |
| Adapter Temperature | 200 - 300 ℃ | 392 - 572 ℉ |
| Die Temperature | 200 - 295 ℃ | 392 - 563 ℉ |
| Melt Temperature | 149 - 323 ℃ | 300 - 613 ℉ |
| Mold Temperature | 10.0 - 120 ℃ | 50.0 - 248 ℉ |
| Injection Velocity | 200 - 240 mm/sec | 7.87 - 9.45 in/sec |
| Roll Temperature | 60.0 - 150 ℃ | 140 - 302 ℉ |
| Drying Temperature | 60.0 - 120 ℃ | 140 - 248 ℉ |
| Moisture Content | 0.0100 - 0.300 % | 0.0100 - 0.300 % |
| Dew Point | -29.0 - -17.8 ℃ | -20.2 - 0.000 ℉ |
| Injection Pressure | 4.14 - 130 MPa | 600 - 18900 psi |
| Vent Depth | 0.00254 - 0.0510 cm | 0.00100 - 0.0201 in |
Can ABS materials be injection molded?
Yeah, ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene copolymer) can be injection molded, and injection molding is one of the most common processes for making ABS parts. ABS is a tough, impact-resistant plastic that’s used a lot in cars, household appliances, and electronics.
Advantages of ABS materials:
① Great Flowability: ABS has great flowability, which makes it perfect for complex mold designs.
② Great Dimensional Stability: ABS can keep its dimensions and shape even after it cools.
③ Great Impact Resistance: ABS is known for its great impact resistance, which makes it perfect for applications that need impact resistance.
④ Low Warpage: ABS is less likely to get deformed or warped during the molding process, which makes sure the product looks good and is high quality.
Challenges in ABS Injection Molding Process:
① High shrinkage rate: ABS shrinks a lot when it cools down, which makes it hard to get the right size.
② Flashing: Sometimes, when you’re making something out of ABS, you get extra plastic where you don’t want it. Then you have to fix it.
③ Warping issues: If you don’t make the mold right or you don’t do the process right, your thing will get bent.
What are the key considerations for ABS Injection Molding?
ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene) is a common plastic that’s used in a lot of different industries, like electronics and automotive. If you want to make sure that you’re getting good ABS injection molded parts, you need to pay attention to a few things:
1. Material Preparation:
① Moisture Control: ABS plastic sucks up moisture, and too much moisture can make it look bad and not work as good. So, dry it at 80-90°C for 2-3 hours, and keep the moisture below 0.1%.
② Material Selection: Choose the right ABS material based on your product requirements (like impact-resistant, heat-resistant, electroplating grade, etc.). If you’re using recycled material, make sure you don’t use more than 30% recycled material, or it’ll affect the quality of your finished product.
2. Mold Design:
① Reasonable Mold Design: To reduce warping, shrinkage, and other issues, mold design should make sure the material flows evenly and doesn’t get stuck. The draft angle setting helps parts come out smoothly, and the gate position should be good so the material doesn’t have to go too far.
② Mold Cooling: Cooling is very important. It is recommended to use water-cooled molds and design cooling channels reasonably to make the cooling effect consistent and prevent product deformation.
3. Injection Molding Process Parameters:
① Injection Temperature: The injection temperature for ABS usually ranges from 200°C to 275°C. Different grades of ABS materials have different injection temperatures. For example, impact-resistant ABS is 220°C to 260°C, while electroplating grade is 250°C to 275°C.
② Injection Pressure: Injection pressure has a big impact on the quality of the molding. Generally, the injection pressure is between 50 MPa and 100 MPa. If the pressure is too low, the mold won’t fill up completely. If the pressure is too high, the mold will stick.
③ Injection Speed: Injection speed is super important. If it’s too fast, you’ll get too much stress and the part will shrink and warp. If it’s too slow, you’ll get short shots or little black specks.
4. Cooling Time and Holding Time:
① Cooling Time: If the cooling time is too short, the product will have internal stress; if the cooling time is too long, the production efficiency will be affected. Reasonable cooling time is to ensure that the plastic in the mold can be cooled and solidified, generally controlling the cooling water temperature at 75-85°C.
② Hold Time: Controlling the hold time between 2-5 seconds will help the plastic fully solidify, preventing the product from deforming or flowing back.

5. Post-molding Processing and Inspection:
① Post-molding Processing: ABS finished products may need trimming, deburring, and other treatments to make sure they are smooth and look good. For electroplating grade products, you also have to bake the surface to get rid of surface marks.
② Quality Control: After molding, we need to strictly check the appearance, size, and performance of the product to ensure that the product meets the quality requirements. Common inspection methods include non-destructive testing and visual inspection.
6. Nozzle and Temperature Control:
Nozzle Temperature: The nozzle temperature should be controlled within a reasonable range, typically set slightly lower than the melt temperature to avoid overheating or decomposition of the melt, causing surface defects in the product.
7. Cost and Time Management:
Cost Optimization: Optimize the flow, reduce material, labor, and equipment costs. Manage production time effectively to shorten production cycles and improve efficiency.

Resources for The Complete Guide ABS Injection Molding Manufacturing
Design guidelines for ABS Injection Molding
When you’re designing ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) injection molded parts, you need to keep these key guidelines in mind to make sure you get the best moldability, structural integrity, and aesthetics.
1. Part Geometry:
Keep the design of parts as simple as possible. Avoid complex geometries like sharp corners, thin walls, or areas with significant cross-sectional changes. Also, avoid small holes or cavities. Use rounded corners and smooth edges to reduce stress concentration and avoid sudden changes in wall thickness and cross-sectional dimensions. This will help ensure a smoother molding process.
2. Wall Thickness:
It’s important to keep the wall thickness consistent in your parts. Avoid designs with thin walls (<0.5 mm) or thick walls (>2 mm). The ideal range is between 1.143 mm and 3.556 mm. This helps you get uniform cooling, reduce warping or deformation, and improve dimensional stability and mechanical properties. Thinner walls not only make your parts faster to produce, but they also make them stronger.
3. Gate Position and Design:
Where you put the gate and how you design it is important. You want to put the gate where the material fills the part evenly and comes out easily. This will help keep the part from warping, getting dents, or having holes. A good gate is in the middle of the part and looks the same on both sides. It has smooth round edges and is the right size to make sure the part doesn’t move when you make it.
4. Draft Angle:
The draft angle is important because it helps parts come out of the mold easily, without sticking or damaging the mold. For ABS parts, the draft angle should be between 1° and 2°. For every inch of depth, the draft angle should increase by about 1.5°. For features like ribs, the draft angle should be at least 0.5° to make sure the parts come out of the mold smoothly.
5. Rib and Boss Design:
Ribs and bosses are great for making parts stronger and stiffer. Ribs should be about half the thickness of the wall, and bosses should be big enough to hold screws. Ribs should be at least 0.5 mm thick, and they should be no taller than 2-3 times the wall thickness. Use rounded transitions to keep the material from getting stressed out.
6. Hole and Cavity Design:
When designing holes and cavities, consider a minimum hole diameter of 1 mm and a maximum depth of 2-3 times the wall thickness. Using smooth rounded edge designs can reduce stress concentration and enhance the durability of the parts. To ensure processing stability, avoid designing excessively small holes or complex cavities.
7. Material Flow and Cooling:
When you design parts, you need to consider the flowability of the material and the cooling process. Make sure the material can flow well and cool down well to avoid warping or deformation problems. The design of the cooling water channels in the mold should ensure uniform cooling, avoiding shrinkage or internal stress caused by uneven cooling.
8. Ejection and Demolding:
To make it easier to get parts out of the mold, make sure you have smooth, rounded surfaces and use draft angles so the parts don’t stick or get damaged. Avoiding sharp corners and edges also helps the parts come out better and look better.
9. Color and Texture:
When designing parts, think about their color and texture requirements. This includes things like matching or contrasting colors, surface texture effects, and how rough or smooth the surface should be. The surface treatment you choose should look good and work well, so the part does what it’s supposed to do.
10. Tolerances and Dimensions:
When designing tolerances and dimensions, you need to be careful to make sure the parts will work and fit with other parts. Think about how the parts might change size when they are made and add up the tolerances so the parts will fit together right.
How to Perform ABS Injection Molding: A Step-by-Step Guide
ABS injection molding is a widely used plastic processing technology in various industries. It has excellent mechanical properties and good processability, and is used to produce various complex parts. The following are the detailed steps of ABS injection processing, from raw material preparation to finished product packaging, each step is very important.

1. Raw Material Preparation:
① Selection of ABS Pellets: Start by picking the right ABS grade for your parts’ application requirements, with an emphasis on impact resistance, heat deflection temperature, weatherability, and color considerations. Make sure the material you choose meets your final product’s performance requirements.
② Drying ABS Pellets: ABS is hygroscopic, so it needs to be dried at 80-90°C for 1-2 hours to get the moisture content below 0.1%. This is important because if you don’t dry it properly, you’ll get bubbles and voids when you’re injection molding, and you’ll end up with parts that have a rough surface.
③ Preheating Treatment: To make the material flow better, preheat the ABS pellets to 180-200°F (82-93°C). This will help the material flow better during injection molding and make the finished part have a better surface finish.

2. Mold Design and Preparation:
① Mold Design: The mold design should comprehensively consider the geometry of the parts, material characteristics, and production requirements. Pay attention to the uniformity of the wall thickness to avoid deformation and dents in the parts. Ventilation design is also important. Make sure the mold can be well-vented during injection to reduce bubbles and incomplete filling. In addition, the mold design should consider the shrinkage rate of the material to ensure the dimensional accuracy of the finished product.
② Mold Preparation: Before you start injection molding, you need to check the mold to make sure it’s clean and doesn’t have any problems. You can put some release agent on it to help the part come out easier. Once the mold is hot, you can put it on the machine to get it ready. This way, you’ll be all set and can make parts faster.

3. Machine Settings and Calibration:
Parameter Settings: The settings of the injection machine are key to ensuring the smooth progress of ABS injection molding, typically recommended as follows:
① Injection Pressure: 10,000-20,000 psi (690-1380 bar).
② Injection Speed: 10-50 mm/s (0.4-2.0 in/s).
③ Holding Pressure: 5,000-10,000 psi (345-690 bar).
④ Cooling Time: 10-30 seconds.
⑤ Machine Calibration: To make sure the quality of the final product, the temperature control system of the injection machine needs to be calibrated to make sure the processing temperature is within the processing range of ABS, achieving precise control and stable production.

4. Injection Molding Process:
① Material Loading: Load the ABS pellets into the hopper of the injection machine. Make sure the pellets go into the machine evenly so it doesn’t get clogged up and stop working.
② Injecting Process: The ABS beads are melted in a high-temperature environment of 180-240°C, and then injected into the mold cavity under high pressure, ensuring that the molten material can fully fill the mold and avoid early cooling that leads to insufficient filling.
③ Holding Pressure and Cooling: After the plastic is injected, the machine will hold pressure to make sure the plastic fills the mold cavity completely and to avoid any voids. After that, the parts will cool and harden inside the mold. The cooling time depends on how thick and how complicated the parts are. Normally, it takes 1-3 minutes to make sure the parts are completely solidified.
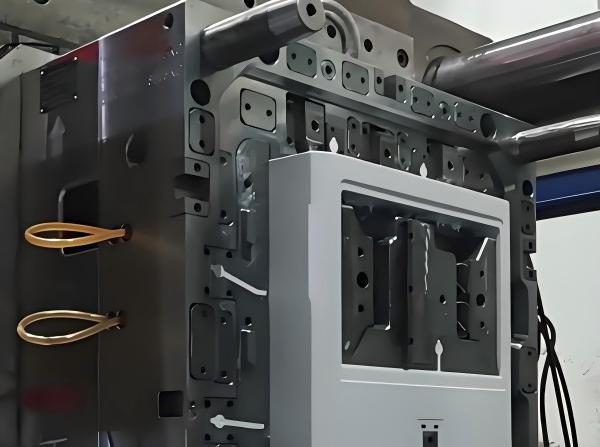

5. Mold Opening and Ejection:
① Mold Opening: After cooling is done, the machine will slowly open the mold. Be careful not to open the mold too fast, or you might mess up the parts. This is especially important for parts with a lot of details or thin walls.
② Ejection: The machine will push the molded ABS parts out of the mold while removing any excess material (like flash) from the surface or parting line to make sure the parts look good.

6. Quality Inspection:
① Defect Inspection: The produced parts must go through a thorough quality inspection. We need to check for warping, dents, bubbles, flash, color differences, or any other surface defects.
② Dimensional and Functional Testing: You also need to test the dimensions and functions to make sure the parts meet the requirements in the drawings. If necessary, test the mechanical properties and other important parameters to see if the products are stable and can last long in real life.

7. Post-molding Processing:
① Trimming and Surface Treatment: If you’re looking for a product with a high surface treatment requirement, you might need to do some secondary processing. For example, you might need to sand, polish, or spray your product. Sanding can remove any surface irregularities, while spraying can add color or a functional coating to your product.
② Assembly and Packaging: If you need to assemble the molded parts, you should do it according to the design drawings. During this process, you must strictly control every step to make sure the assembled products meet the requirements for use. Finally, you should package the qualified products according to the requirements and store them for transportation.
What are the advantages of ABS Injection Molding?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a material that’s used in a lot of different industries because it’s really good at what it does. Here are some of the main reasons why people like to use ABS for injection molding:
1. Outstanding Mechanical Properties:
ABS has great impact strength and toughness, especially maintaining good performance even in low-temperature environments. This allows it to effectively absorb energy in automotive parts manufacturing, protecting the safety of passengers inside the vehicle. Its tensile strength and flexural strength reach 46 MPa and 74 MPa, respectively, showing great mechanical performance.
2. Excellent Processability:
ABS materials are easy to process and suitable for mass production. They have excellent flowability and ease of processing, allowing for precise replication of complex shapes and functional components. Additionally, ABS materials can be post-processed, such as painting and electroplating, to meet diverse design needs.
3. Good Chemical Resistance:
ABS has good resistance to various chemicals, so it can withstand chemical corrosion in special environments. This characteristic makes it perform well in manufacturing components that need chemical resistance.
4. Aesthetic Flexibility and Ease of Finishing:
ABS materials have a smooth surface, which makes them easy to paint and print, allowing for molding into various colors and finishes to meet the aesthetic requirements of products. Its surface gloss can reach up to 90%, giving the products an outstanding appearance.
5. Heat Resistance and Dimensional Stability:
ABS materials have excellent heat resistance, maintaining dimensional stability in high-temperature environments. This allows them to maintain reliable performance when applied to products that require high temperatures and harsh environments.
6. Low Cost and High Productivity:
ABS materials are cheaper than other engineering plastics, so production costs are low. ABS injection molding can make a lot of parts at once using fast injection machines, so it’s fast and efficient.
7. Recyclability:
ABS is an eco-friendly material that can be recycled, which is in line with the current manufacturing industry's call for sustainable development and helps to cut down on waste and resource use.
What are the disadvantages of ABS Injection Molding?
ABS injection molding has its pros and cons. Here are some of the drawbacks and limitations of ABS injection molding:
1. Brittle and Poor Fatigue Resistance:
ABS materials are super brittle and can easily crack or break under impact or pressure, and they have poor fatigue resistance when you put a lot of heavy loads on them for a long time or keep stressing them over and over, so they’re likely to fail.
2. Low Heat Distortion Temperature:
ABS has a pretty low heat distortion temperature. It can get soft or bendy when it gets hot, so it’s not great for high-temperature stuff.
3. Sensitive to Moisture:
ABS is sensitive to moisture and can easily absorb moisture, which can make it brittle or discolored.
4. Difficult to Bond:
Because of its low surface energy, ABS is tough to bond well with other materials like adhesives or coatings.
5. Prone to Warping:
ABS parts have a tendency to warp or deform during the molding process, especially if the mold design is bad or the material isn’t dried enough.
6. Limited Chemical and Solvent Resistance:
ABS has limited resistance to certain chemicals and solvents (like acids and bases), so it can corrode or dissolve in harsh chemical environments.

7. Prone to Discoloration:
ABS materials can turn yellow or change color when exposed to UV light or heat for a long time, so they’re not good for outdoor use unless they’re treated with UV stabilization.
8. Flammability:
Standard ABS plastic does not have good flame retardancy and can release a lot of smoke when it burns, so it can’t be used in places where fire safety is important.
9. Release of Harmful Gases:
During the processing and welding of ABS, toxic gases may be released, so operations should be conducted in well-ventilated environments to ensure safety.
10. Noise and Vibration Issues:
ABS parts can create noise and vibration when they get hit or squeezed, so they’re not good for things that need to be quiet.
11. Higher Costs for Complex Designs:
Because mold design and tooling are complicated, the upfront costs for making ABS parts can be high, especially for intricate designs, which jacks up production costs.
12. Limited Recyclability:
ABS can be recycled, but its complex molecular structure and additives make recycling it kind of hard.
Common issues and solutions in ABS Injection Molding
There are a lot of things that can go wrong when you’re doing ABS injection molding. Here are some common problems, what causes them, and what you can do about them.
1. Short Shot:
Short shot is when the mold doesn’t fill up all the way, so you end up with incomplete parts. This usually happens because you don’t have enough pressure or speed when you’re injecting the plastic, the material isn’t viscous enough, or the mold design is bad (like if you have really narrow gates or not enough vents). To fix short shot, you need to make sure you have enough pressure and speed to get the plastic to flow all the way through the mold. You also need to make sure the mold is at the right temperature so the plastic doesn’t cool down and solidify too early while you’re injecting it, so you get a good part.
2. Warping or Deformation:
Warping or deformation is when the shape of a molded part gets all messed up after it cools down. This usually happens because the mold design is bad, the cooling is bad, or the material temperature is bad. To fix warping, you need to make sure the mold cools down evenly by designing the cooling system right. You also need to make sure the material temperature and injection speed are right to reduce stress when you mold it. You can also use stuff to make the part not stick to the mold, so it doesn’t warp.
3. Dents or Voids:
Dents or voids are caused by insufficient material flow and improper gate positioning, which can affect the appearance and strength of molded parts. Optimizing the design and size of the gate can ensure good material flow and avoid local flow issues. Also, adjusting the mold temperature to make sure the material stays flowable throughout the injection process is an important strategy to solve this problem. This comprehensive approach can effectively improve the quality and reliability of molded parts.
4. Air Pockets:
Air pockets are bubbles that get trapped inside molded parts, which can weaken them. They happen when the mold doesn’t have enough vents or the walls of the part aren’t the same thickness. To fix this, add vents to the highest points of the mold so air can escape better. Also, redesign the mold so the walls of the part are the same thickness. This will help get rid of air pockets and make better parts.
5. Brittleness or Cracking:
ABS brittleness or cracking issues are often related to improper material selection, unsuitable processing conditions, and insufficient drying. To effectively reduce brittleness, first select ABS materials suitable for specific applications. Additionally, optimize drying conditions to ensure that the material reaches appropriate moisture levels before molding. Properly set injection temperature and cooling conditions to ensure good material flowability, avoiding cracking due to excessively high or low temperatures.
6. Flashing:
Flashing is when extra material comes out of the mold where it’s not supposed to, making the part look bad and not work right. It usually happens because the mold isn’t closed tight enough or there’s something wrong with it. You can fix this by making sure the mold is closed tight enough so the two halves of the mold fit together and the plastic doesn’t come out. You can also fix this by checking the mold to make sure it’s not messed up and fixing it if it is. That will help make your parts good and not have flashing.
7. Flow Lines:
Flow lines are wavy patterns that show up on the surface of molded parts. They happen when the material flow is inconsistent, which is usually caused by low mold or material temperatures and slow injection speeds. To fix flow lines, you can raise the temperature of the mold and material, and make sure you’re injecting the material at the right speed and pressure. This will help the material flow smoothly through the mold, and make your molded parts look and work better.
8. Delamination:
Delamination is when the layers of your material don’t stick together right, which makes weak spots in your parts. This usually happens because your raw materials are dirty or you’re mixing stuff that doesn’t go together. To stop delamination, dry your material really good before you use it and keep your mold clean so you don’t get anything from the last time you ran it in there. You can also make your layers stick together better by using the right amounts of stuff and doing the right things to your material when you’re making it. That’ll make your parts better.
9. Ejection Difficulties:
Ejection problems are when parts don’t come out of the mold smoothly after molding. This is usually because the mold design is bad or the ejection system isn’t good enough. You can fix this by making sure the mold is designed right so the parts come out right and the parting lines are in the right place. You can also fix this by changing the temperature of the material and how fast it goes into the mold. You can also use stuff to make sure the parts don’t stick to the mold, so they come out right and you can make more parts faster.
10. Material Degradation:
ABS materials can degrade when they come into contact with chemicals, heat, or UV light. This can make the material not work as well, which can make the product not as good. One way to stop this from happening is to use ABS materials that have been treated to stop UV light from hurting them. You can also stop the material from getting too hot or being around chemicals and use stuff to help the material come out of the mold. This will make the material last longer and make the product work better.
11. Difficulties in Material Recycling:
When we choose the wrong materials or process them the wrong way, we end up with waste that’s hard to recycle. But if we pick the right ABS materials and process them the right way, we can recycle them easily. And if we set up our processes right, we can make less waste and be more efficient. That’s how we can keep making stuff and keep the planet healthy.
What are the applications of ABS Injection Molding?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) injection molding is used in many industries because it’s versatile, durable, and cost-effective. It’s an essential material in modern manufacturing. Here are some of the main applications of ABS plastic:

1. Automotive Industry:
ABS plastic is used a lot to make lightweight parts like dashboards, interiors, and door panels. These parts need to be tough and last a long time, but they also need to look good to people. ABS is light, so it helps cars use less gas, and it can take the place of heavy metal parts.

2. Household Appliances:
Because of its high strength and good chemical resistance, ABS is often used to make the housings of household appliances like vacuum cleaners, coffee machines, and microwaves. The low production cost and efficient manufacturing process make household appliances more competitive in the market.

3. Consumer Electronics:
In the consumer electronics game, ABS plastic is used all over the place. You’ll find it in computer cases, keyboards, printers, and all sorts of other parts on electronic gadgets. It’s great for these things because it’s a good insulator and it can take a hit without breaking. That means it keeps the important parts inside safe from getting messed up.
4. Medical Devices:
In the medical field, ABS plastic is used a lot to make things that need to be cleaned and sterilized, like nebulizers and medical device parts. ABS is good for medical stuff because it doesn’t change when it touches chemicals, it’s smooth, and it’s easy to clean. That’s important in medical places because it makes medical stuff safer and more reliable.

5. Construction and Construction:
Because of its excellent chemical and physical resistance, ABS plastic is often used in the production of pipes and fittings. Whether in residential or commercial plumbing systems, the toughness and durability of ABS make it a great choice.

6. Toys and Games:
Lots of toys, like LEGO bricks and different plastic games, are made from ABS material. ABS is great for toys because it can be molded into complex shapes and still be strong. This makes toys safe and long-lasting, which is why ABS is so popular for kids’ toys.

7. Prototyping:
ABS is a popular choice for rapid prototyping because it’s easy to work with and has great moldability. It can make complex shapes and is cost-effective, which is great for design and development.

8. Industrial Machinery Parts:
ABS panels, covers, and protective devices are used a lot in industry. ABS plastic is tough and easy to look after, so it’s a big part of industrial equipment that has to last in tough conditions.

What are the types of injection mold?
Key Takeaways – Injection molds come in several major types: single-cavity, multi-cavity, family, stack, and overmolding, each optimized for different production volumes and part requirements. – Single-cavity molds offer the

What Are Injection Molding Ejector Pins and How Do You Design Them Right?
Key Takeaways – Ejector pins are the mechanical components that push finished parts out of the mold cavity after cooling, and their design directly impacts part quality and cycle time.

What Causes Injection Molding Warpage and How Can You Fix It?
Key Takeaways – Warpage occurs when differential shrinkage creates internal stresses that bend or twist a molded part after ejection. – The top causes include uneven cooling, inconsistent wall thickness,
Optimization Solutions Provided For Free
- Provide Design Feedback and Optimization Solutions
- Optimize Structure and Reduce Mold Costs
- Talk Directly With Engineers One-On-One







