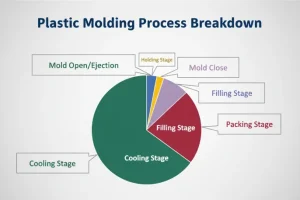
Estimating injection molding costs is essential for budgeting and project planning in manufacturing. Understanding the various factors involved can lead to more accurate forecasts.
Key factors in estimating injection molding costs include material costs, mold design and manufacturing expenses, production volume, cycle time, and labor costs. Material choice significantly impacts the overall cost, while complex molds and higher production volumes may reduce per-unit expenses.
While this overview highlights the main factors influencing injection molding costs, a detailed analysis of each component can help refine your estimates. Dive deeper to understand how specific materials and designs affect pricing in your projects.
Material choice significantly impacts the overall cost of injection molding.True
Different materials have varying costs, and selecting a more expensive material like polycarbonate can increase overall production expenses compared to a cheaper material like polystyrene.
Labor costs are the only factor in estimating injection molding expenses.False
While labor costs are important, they are just one of many factors influencing injection molding costs, which also include material costs, machine time, and mold complexity.
How Much Does Injection Molding Cost?
Injection molding is a big deal for making plastic parts. It’s a great way to make lots of the same thing, and it’s really good at making exactly what you want. It’s cheap and it’s good at making a lot of stuff that’s all the same.

Injection molding is a big deal for making plastic parts. It’s a great way to make lots of the same thing, and it’s really good at making exactly what you want. It’s cheap and it’s good at making a lot of stuff that’s all the same.
The main cost factor for injection molding is the injection mold cost . This is how much it costs to make the mold. The tooling cost depends on things like production volume, part complexity, mold material, and the mold creation process you choose.

For instance, a simple mold made with 3D printing for a small batch can cost as little as $100. On the other hand, a complex molds for high-volume production can cost up to around $100,000 to design and build.
Despite the high startup costs, injection molding has low variable costs because thermoplastic materials are cheap, cycle times are fast, and labor requirements decrease over time due to automation and economies of scale.

As a result, variable production costs stay low, which improves efficiency, while the cost per part goes down as production goes up, spreading the cost across many parts.
What Factors Affect Injection Molding Costs?
The cost of an injection mold isn’t a set number that applies to all situations. It can range widely, from a few hundred dollars to hundreds of thousands of dollars.

The range is quite wide, and the specific amount depends on a variety of factors related to the injection molding process. These factors that reduce the cost of injection molding include:
Equipment
The amount of money you need to spend on an injection molding machine can be very different depending on what kind of machine you want and what you want to make with it.

There are small injection molding machines that are designed for in-house use within a business. On the other hand, large injection molding machines are often used by service providers and manufacturers in high-volume industries.
If you want to get serious about injection molding, you’re going to need some serious equipment. Industrial-grade machines for professional use can cost anywhere from $50,000 to $200,000. And that’s not including shipping. These machines are not for hobbyists or amateurs. They require skilled operators who know what they’re doing.

It’s a big financial commitment for any business, no doubt about it. That’s why a lot of manufacturers outsource their injection molding needs to experts like 3ERP who have state-of-the-art injection molding machinery. Outsourcing is a cost-effective solution that lets customers find the most economical option for their required parts and minimize variable production costs.
Mold (Tooling) Costs
Mold cost is a big deal in injection molding because it’s the cost of making molds and mold bases for each different part you produce. The molding equipment is a one-time investment, but mold cost is a big deal because it determines the overall cost.

Mold costs can vary, depending on the mold making process you choose. There are typically two processes to choose from:
CNC Machining
CNC machining is often used to make metal molds, such as stainless steel or aluminum molds. For example, when machining aluminum molds, we use cutting tools to remove material from an aluminum block. This method ensures excellent precision in the production of aluminum molds.

However, there is a small disadvantage to CNC machining when it comes to the machine cycle time for mold production. These machines require time for tool setup and tool changes for different cutting shapes.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM, short for electrical discharge machining, is a technique used to make molds of complex shapes. It works by using electrical discharges to melt and shape a metal workpiece into the desired mold design.

Like CNC machining, EDM offers high precision. However, unlike CNC machining, EDM is only suitable for creating metal molds and cannot be used with other materials.
3D Printing
3D printing is a powerful solution for rapidly and inexpensively making injection molds. It requires minimal equipment and frees up CNC time and skilled operators for other high-value tasks. Manufacturers can take advantage of the speed and flexibility of in-house 3D printing to create molds that work on both desktop and industrial molding machines.

Plus, product development benefits from being able to iterate designs and test end-use materials before committing to hard tooling for mass production.
SLA 3D printing is a great choice for injection molding. It has a smooth surface finish and high precision that the mold will transfer to the final part, which also makes it easy to demold. SLA 3D prints are chemically bonded, so they’re fully dense and isotropic.

Desktop SLA printers, like those from Formlabs, start at under $5,000 and can be easily integrated into any injection molding workflow because they’re easy to set up, use, and maintain.
Injection Materials
Injection molding is a flexible process when it comes to the materials that can be used as injection molding materials. A variety of plastics, including ABS, PU, PE, PP, and PC, are commonly used in the plastic injection molding process.

Plastic injection molding costs usually range from $1 to $5 per kilogram. The final cost of the injected material depends on the quantity required, which is determined by the design specifications.
Besides plastics, there are other materials that can be used for injection molding, such as different metals and liquid silicone. These other materials give you more choices and flexibility when you’re making stuff.

Design Complexity
If you want to design a complex part with multiple cavities and high mold finishes, it’s going to cost you more money. These designs require a lot of research, development, and technical expertise. You can hire a professional designer or outsource the design to a specialized company. But both options are going to cost you money.
Labor or Service Costs
The equipment that goes with injection molding is usually self-regulating and relies on automation to do its job. CNC machines, EDM machines, and 3D printers rely on the specifications of the CAD design to produce the mold.

Injection molding machines also rely on automation to inject the material into the mold, while industrial IM machines are usually autonomous to cool and eject the finished product.
Labor Costs Include:
Setup costs: Setup labor is all about the time it takes to get the equipment ready to make the mold and finished product.

Repair costs: Repair and maintenance tasks include replacing parts that don’t work and using tools to do maintenance stuff.
Monitoring Costs
Even though machines do most of the work, you still need someone to watch the machines when you’re making plastic parts. You have to pay that person, and that cost is part of the cost of making plastic parts.

When you make parts in your own factory, you include that cost in your labor cost. When you have someone else make your parts, you have to pay them to watch the machines, and you have to pay them to make the parts.
Part Size
The bigger the thing or part you want to make, the bigger the mold you need to make it. Bigger parts need more stuff to make them. Bigger molds cost more money than smaller molds.

Part Design
When you have a complex part design with complex geometry, you need a complex mold to make it. Molds have two sides: the A side and the B side. The A side is the pretty side, the side you see. It needs to be smooth and look good. The B side has all the hidden stuff that makes the part work.

It has ribs, bosses, and stuff like that. The B side is usually rougher than the A side. Molds with complex A and B side designs cost more to make than simple molds. If you have a complex design with undercuts, you might need slides and cores, which make the mold cost more.
Production Volume
The number of products you’re making with injection molding determines the production technology and the quality of materials you use to make the mold. If you’re making a low-volume project, you might use a 3D printed mold or a low-grade machined aluminum mold.

If you’re making a high-volume project, you’ll use a high-grade steel mold or even multiple molds to keep the process going without wearing out the mold and affecting the quality of the parts you’re making. This affects the cost of the mold, but of course, the increased cost of high-volume molds is spread out over more parts, which generally means a lower cost per part.
Part Volume and Cavity
Part volume refers to the size of the hole in the mold. The more holes or hole size a mold has, the longer it takes to press. Increasing the press time slows down the process, which costs more.

How is the Injection Molding Price Calculated?
Basic Composition
Molds are important for making all kinds of industrial products. They’re a must-have for developing and producing industrial products. But molds aren’t usually sold directly. Instead, they’re made to order.
The buyer and seller negotiate a deal. Injection molds are high-tech products. They’re made in small quantities. That means you need to have good production management, equipment, and people. One of the biggest problems in making a mold is figuring out how much it costs.

When you’re figuring out how much to charge for a molded part, you need to think about the technical value and the extra cost of getting it done fast (which we call the rush charge). So, the price of a mold is the cost of the material plus the cost of making it plus the overhead plus the profit plus the tax plus the technical value.
The rush charge is the cost of the mold plus the profit plus the tax plus the technical value plus the crash charge. The mold cost is the cost of the material plus the cost of making it plus the overhead.

The cost of making it includes the cost of the machine work, and the overhead includes all the other costs and expenses that aren’t machine work that you have to pay for when you make a mold.
Empirical Calculation
The price of molds is made up of several parts: material cost, design cost, processing cost and profit, value-added tax (VAT), trial mold cost, packaging and transportation cost. Usually, each part accounts for a certain proportion of the total mold cost as follows .
Material Cost
The cost of materials and standard parts accounts for about 15% to 30% of the total mold cost.

Processing Fee and Profit
This part usually accounts for 30% to 50% of the total cost, including the cost of processing the mold and the required profit margin.
Design Fee
The cost accounts for about 10%-15% of the total mold, which is used to pay for the costs associated with the design process.

Mold Trial Fee
For big and medium-sized molds, the trial cost is usually controlled within 3% of the total mold cost, and for small precision molds it is within 5%.
Packaging and Transportation Fee
The packaging and transportation fee can be calculated based on the actual amount or at a fixed rate of 3% of the total mold cost.

Material Coefficient
To figure out how much the mold material costs, you need to know how big the mold is and how much the material costs right now. The mold price is the material cost times a number that depends on what kind of mold it is .

For plastic molds: The mold price is usually 6 times the material cost.
For die-casting molds: The mold price is generally 10 times the material cost.
Mold Price Estimation
First, you need to think about what the customer wants and decide what kind of material to use and how to heat treat the mold.

Once you’ve decided on the material, you need to make a rough plan for the mold. You need to think about how much the mold is going to weigh (including the core and cavity materials) and how much it’s going to cost to heat treat it. You also need to think about how much the mold base is going to weigh.

Next, let’s talk about the processing cost. The processing fee for the mold core is generally 1.5-3 times the price of the core material, depending on its complexity. The processing fee for the mold base is usually equal to the cost of the substrate.
You should also consider the cost of potential risks, which is usually 10% of the total price you’ve calculated so far.

Finally, you should also include a design fee of 10% of the total mold cost.
How to Estimate and Quote the Price of Injection Molds?
The mold is a high-tech product with a specific purpose. We should not put the emphasis on low price or even sell at a loss. We should focus on high quality and competitive price.
We emphasize the quality, precision and service life of the mold, but not the cost of the mold. If you choose a low-priced mold, it may be difficult to guarantee the quality, precision and service life of the mold.

If mold manufacturing and product development/production belong to the same accounting unit or are financially interrelated, the mold price should be quoted at the mold cost price. The mold price estimate should only consider the basic cost of the mold, temporarily excluding other costs and profits.
Later, after the mold is put into production, the added value of the mold fee can be extracted from the profits generated as compensation. However, it should be noted that this initial quotation cannot be regarded as the actual price of the mold, but as the mold cost in the early development stage.

In the future, after you’ve successfully developed your product and made money from it, you should go back to the mold maker and get the mold paid for. Those two things together make up the final price of the mold.
At this point, the price of the mold might be higher than what you originally paid for it, and your return on investment (ROI) might be a lot higher, maybe ten or a hundred times higher than what you originally paid for the mold. But depending on the situation, your ROI might be zero.

What are Some Tips for Reducing the Cost of Plastic Injection Molding?
Eliminate Undercuts
Avoiding or limiting undercuts can make the design and ejection of the mold easier, thereby speeding up production and reducing costs. Undercuts complicate the design of the part. They also make it more difficult to remove it from the mold.
When undercuts are present, the mold must include complex mechanisms, such as slides or lifters, to release the item from the mold cavity. This adds complexity and length to the mold design and production process.

For simpler plastic injection mold builds, another option is to use sliding closures and pass-through cores or modify parting lines and draft angles. This saves on tooling expenses by avoiding the need for additional mold components, which increases production costs.
Reduce Decorative Effects
Do you really need smooth or shiny surfaces for your project? If they don’t make you more money, you might want to get rid of them.

Choosing a simpler surface finish can reduce post-processing and injection mold complexity, thereby reducing costs. Although good-looking parts are nice, making them look better often requires bead blasting, EDM, or high mold polishing, which increases mold costs.
Using a Core-Cavity Method
The core-cavity method machines the complex internal parts of a device housing into a solid core. The final part is then formed by molding the mold material around this core.

The core-cavity method is consistent throughout the production process and allows you to make complex internal features exactly the same every time. It also lets you get away with less draft and makes it easier to get a smooth finish, good venting, and easy demolding.
Adhere to Lean Design
Lean design is a product design methodology that emphasizes reducing waste, increasing efficiency, and simplicity throughout the product development process. It aims to reduce unnecessary complexity and cost while creating products that meet customer expectations.

Design things to be efficient and simple. Don’t make things complicated or add extra stuff that needs special tools. This will save you money on materials and making things.
Apply DFM Analysis
Design for manufacturability is a process that helps you find any design flaws that may increase the complexity and manufacturing cost of your plastic injection molding process. By addressing these issues, you can save yourself time and money.

Remove Unnecessary Features
Look at the part design and see if there is anything that doesn’t really add to the usefulness or look of the product. You can make the mold design simpler and save money on making the part by getting rid of stuff that doesn’t need to be there.
Some stuff on your part might not be needed. Like, you don’t need to have all these fancy textures and stuff on the surface. You don’t need to have all these ribs that don’t do anything. You don’t need to have all these logos and stuff that are embossed on the part. You can get rid of all that stuff. It’ll make the mold easier to build and it’ll save you money on the mold.

Series Molds/Multi-Cavity Molds
Multi-cavity molds, also known as series molds, are a type of mold design that can make multiple identical or related parts in one molding cycle. Series molds have multiple cavities in the same mold base, so you can make multiple parts at the same time instead of using a different mold for each part.

This way, you spend less on tools and labor and make more stuff faster, so it costs less to make each one.
Summary
Calculating the plastic injection molding cost involves many factors, including mold cost, injection molding equipment, material selection, design complexity, labor and service costs, etc. Mold cost is usually the biggest expense in injection molding, which is affected by production volume, mold complexity and manufacturing process.
Equipment investment, material cost and labor cost also have a big impact on the total cost. By simplifying the design, reducing complex decorative effects, applying lean design and DFM analysis, and using multi-cavity molds, the cost of injection molding can be effectively reduced, and efficient production and quality control can be achieved.
Injection mold cost calculator can help users accurately estimate the total cost of injection molding based on the complexity of the insert molding and the mold size.