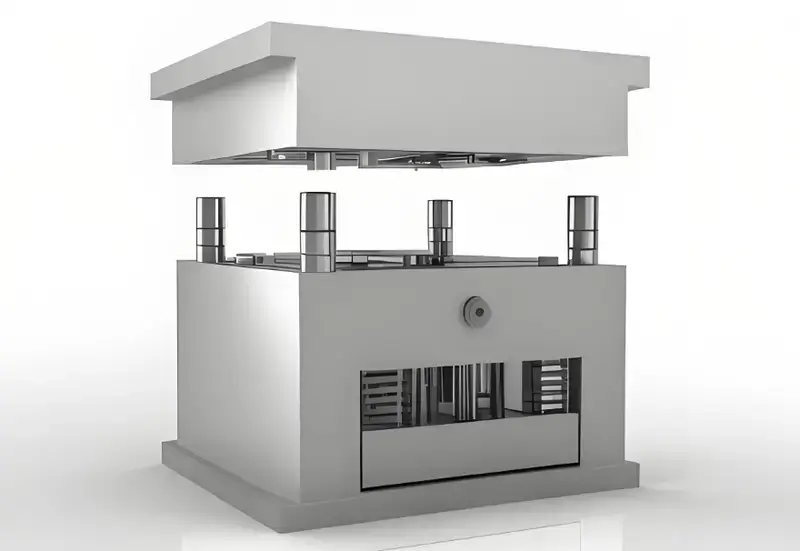
Plastic injection molds are essential tools in manufacturing, allowing for the mass production of precise plastic parts with high efficiency and quality.
Plastic injection molds shape plastic by injecting molten material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into a part. Benefits include high precision, speed, and cost-effectiveness in large-scale production.
To fully leverage the power of injection molds, understanding the types, materials, and maintenance is key. Continue reading to learn how these factors impact your production quality and cost.
Injection molds are ideal for high-volume production.True
Injection molds are designed for large-scale manufacturing, making them cost-effective for mass production due to their high speed and precision.
Injection molds are always cheaper than other manufacturing methods.False
While injection molding is cost-effective for large runs, its initial mold creation cost can be high, making it less ideal for small production runs compared to alternatives like 3D printing.
What is the Injection Molding Process?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create precise, high-quality parts. It’s essential in industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods.
Injection molding is a process where molten plastic is injected into a mold to form various parts. It offers fast production times, high precision, and is ideal for mass production of components like automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer goods.
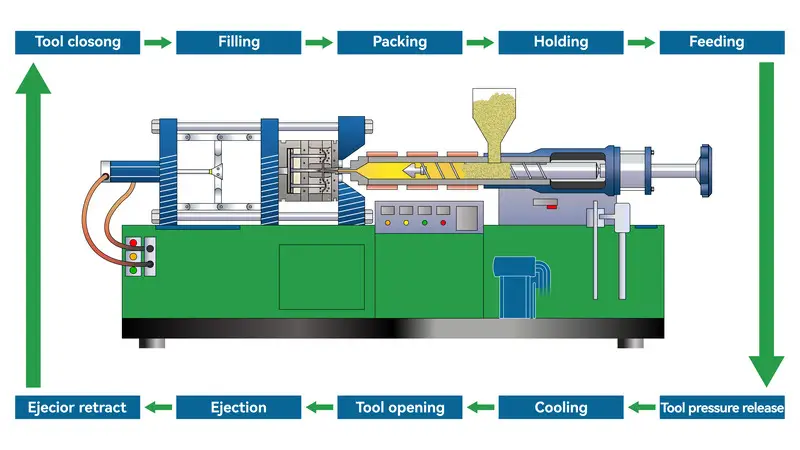
Raw Material Preparation
Some of the treatment activities that may be carried out before molding, include drying, mixing and coloring of the plastic raw materials. Raw material preparation is fundamental to the injection molding process and directly impacts the quality of injection molded parts.
Melting
Raw materials used in making the plastics are heated and softened through the injection molding heated cylinder. In this case, when it is necessary to heat screws or plungers, plastic pellets or plastic resin are melted and evenly mixed. Melting is the most significant phase of the injection molding and the phase is directly tie to the quality of the molded parts.
Injection
The molten plastic is forced by the injection molding machine to flow through the injection molding machine nozzle and into the mold cavity adopting to the shape of the part. Injection is a very important stage in the injection molding process and a function of injection influences the quality of the molded parts (surface finish, hardness, wall thickness, etc.).
Packing (or Holding)
After the injection, the pressure is applied on the plastic inside the mold cavity to counterbalance the shrinkage resulting from cooling, ensuring the dimensions and surface quality of the part. Packing step is an important one in the injection molding and directly contributes the quality of the molded parts.
Cooling
The plastic inside the mold cavity is cooled and solidified with the help of the cooling system of the mold to produce the final plastic part. Annealing or cooling is a very important step that takes place in injection molding and determines the quality of the molded components.
Mold Opening
The injection machine then moves the two halves of the mould the movable mould and the fixed mould apart and opens the mould. Mold opening is one of the important stages within plastic injection molding process and molds directly influence the quality of molded parts.
Ejection
In the aided method of formative processes for the production of molds, when the material is molded, an ejection system1 is used to eject the molded part from the mold in order to undergo the other processes. Ejection is considered as one of the most important parts of injection molding manufacturing process and plays a direct role to the quality of molded parts.
Injection molding produces high-quality parts in large volumes.True
Injection molding provides consistent quality and precision, making it ideal for producing large quantities of identical parts with minimal waste.
Injection molding is suitable for all types of plastics.False
Not all plastics are suitable for injection molding; materials with high melting points or certain chemical properties may require specialized molding techniques.
What are the Applications of Injection Molds?
Injection molds are essential in manufacturing, used to create parts across industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods, providing high precision and efficiency.
Injection molds are used to produce high-quality parts in industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods. They ensure accuracy, reduce waste, and improve production speed by efficiently shaping plastics and other materials.

Automotive Sector
The injection molds are utilized to manufacture automobile components both external and internal, dashboards, bumpers headlights and so on, enhancing the looks, efficiency and safety in automobiles. The automotive sector places high demands on injection molds, requiring high precision, strength, and wear resistance.
Electronics Sector
Electronics products-the housing of a diversity of electronic equipments, connectors, sockets among the many which are created by injection mold are precise and reliable. The electronics sector needs injection molds that have great accuracy, stability and heat conductivity.
Appliances Sector
The injection molds are applied to create housings, panels, buttons, and other elements of home appliances to improve their appearance quality and service life of electrical products. The appliances sector requires injection molds that are precise, hard wearing and possess a high gloss finish.
Medical Sector
Injection molds apply to the manufacturing of many types of medical products including syringes, infusion sets, surgical instruments, sharing accessories and other consumables guaranteeing the safety and sanitary requirements for medical products. A medical sector involves injection molds that are precise, clean and resistant to corrosion.
Daily Necessities Sector
The injection molds assist in manufacturing of daily use articles like; bottles, containers, toys among others undergoing through different consumers tastes and trends. The daily necessities sector demands injection molds with high precision, glossiness, and production efficiency.
Injection molds are essential for high-volume production.True
Injection molds allow mass production of precise and consistent parts at a fast rate, making them vital for industries requiring high output.
Injection molds are only used for plastic parts.False
Injection molds can also be used for metals, silicone, and other materials, making them versatile in various manufacturing sectors.
What are the Basic Components of an Injection Mold?
Injection molds are crucial for producing precise, high-quality parts. Understanding their basic components can help optimize the molding process and improve efficiency.
Basic components of an injection mold include the mold cavity, core, sprue, runner, and ejector system. These elements work together to shape and eject plastic parts efficiently during the molding process.
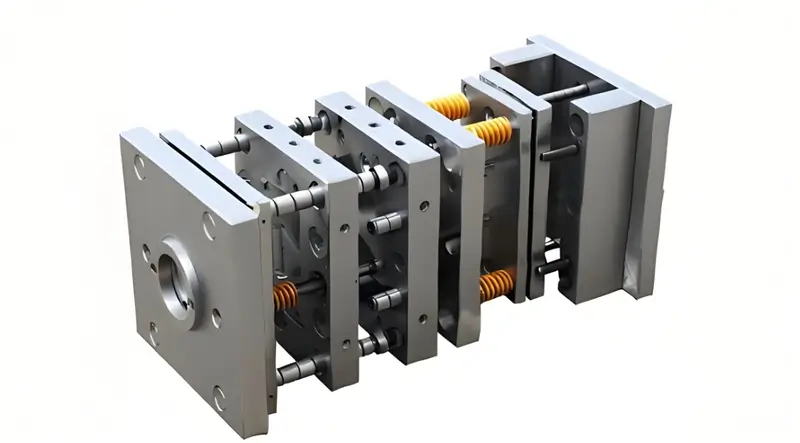

Movable and Fixed Molds
Injection molds2 are mainly classified into moveable and fixed molds, which are situated on the moveable and fixed platens of the plastic injection molding machine respectively.
-
Movable Mold: The movable mold is the mold component that is mounted on the movable platen of the injection machine, during the injection molding cycle. The primary purpose of the movable mold is to provide the cavity of the part’s formation along with the mold that is fixed. The movable mold sometimes may have side core and internal insert for producing the complex shaped articles.
-
Fixed Mold: The fixed mold is the mold part installed on the fixed platen of the injection machine, typically not moving during the machine\’s operation. In the fixed mold, the primary purpose is to create the mold cavity together with the movable mold and, at the same time, establish a gate system to admitted the molten plastic into the cavity. Fixed mold structure is normally less complex though they must provide a rigid construction due to the high pressure that is created by injection moulding process3.
Mold Base
Mold base is the general setup where movable and fixed molds are mounted and secured, mainly made up of front and rear plates, fixed and sliding plates and so on. The main function of the mold base is to ensure the positional accuracy and rigidity of mold components to withstand the high pressures and temperatures generated during injection molding.
-
Front Plate: It is at the front end of the mold, usually fixed together with the fixed mold, which plays the role of supporting and positioning of the fixed mold. The design of the front plate must consider the arrangement of the cooling system to ensure uniform mold temperature.
-
Rear Plate: The rear plate is positioned at the rear part of the mold and usually combines with the movable mold to establish the support and location of the latter. The rear plate needs sufficient strength and rigidity to withstand the movement of the movable mold and the pressure during injection molding.
-
Movable Plate: The Movable plate is the mold plate that is installed on the movable portion of the injection machine used to immobilize the Movable mould. The movable plate has to have excellent parallelism and smoothness to let the movable mould slide on the injection machine consecutively.
-
Fixed Plate: Fixed plate is the mold plate on the fixed part of the injection machine responsible for fixing and supporting the fixed mold. The fixed plate requires high accuracy and stiffness to ensure the stability of the fixed mold on the injection machine.
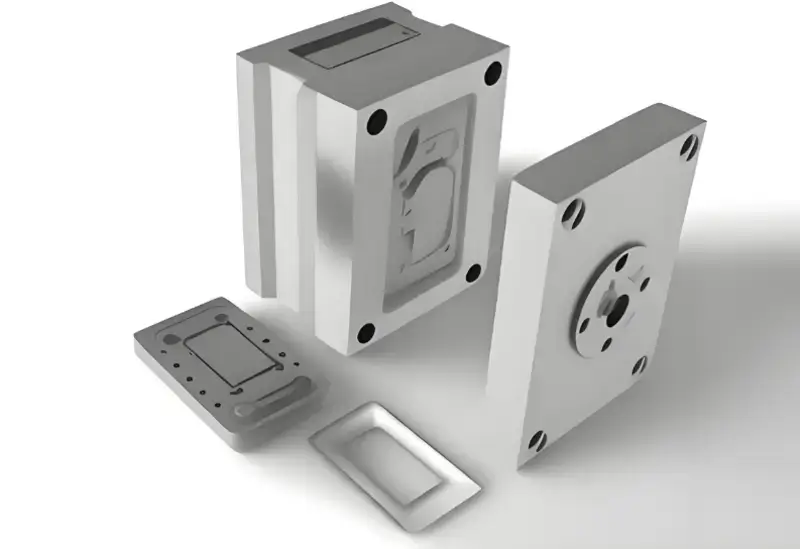

Cooling System
The cooling system is a crucial part of the mold mainly concerned with temperature regulation of the mold to improve part quality and production rates. They are the cooling channels, water pipes and the cooling devices. The water which is cooled circulates through the passages of the mold to ensure that the mold does not become excessively hot.
-
Cooling Channels: Cooling channels are water flow channels which established in mould to provide even flow of cooling water in number of section of mould for the purpose of cooling. Cooling channel design has another challenge of equal water flow and cooling influence on mold temperature in the different areas.
-
Cooling Pipes: Cooling pipes are pipes that link cooling channels and cooling devices and using them water is transported. The location of cooling pipe should take decided on the structural framework and cooling performance of the mould so that the cooling water can be smoothly supplied.
-
Cooling Devices: Cooling devices typically include cooling towers, chillers, etc., used to provide cooling water. The selection and configuration of cooling devices need to be optimized according to the cooling requirements of the mold and production environment to ensure cooling efficiency and energy savings.
Gate System
The gate system relates to the system of channels which bring molten plastic from the injection machine nozzle to the mold cavity, the main and sub-runners, the gate, and cold slug.
-
Main Runner: Main runner is the channel extending from the nozzle of the injection machine and reaching to the sub-runner, where the molten plastic enters into the mold. The design of the main runner must take into account the flow characteristics to ensure smooth flow.
-
Sub-runner: It is a connecting passage between the main runner and gate4which helps to carry molten plastic to several cavities of a mould. According to the requirement of the sub-runner structure, its design must take into account there distribution of the molten plastic as well as flow resistance to guarantee equal filling of all the cavity.
-
Gate: The gate is the thin entrance linking the sub-runner and the mold cavity, which allows the supply of hot plastic into the mold cavity. The design of the gate needs to consider the flow rate of molten plastic and filling effect to ensure the surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the part.
-
Cold Slug Well: The cold slug well is a hole located at the end of the main runner, used to store residual plastic after cooling, preventing it from entering the mold cavity. The design of the cold slug well needs to consider cooling effects and mold structure to ensure part molding quality.
Venting System
The venting system is required for removing air and volatile gases for formation of defects such as bubbles and scorching on the molded products. This is normally in form of vent grooves, vent holes, and vent valves.
-
Vent Grooves: Vent grooves are low width grooves which are provided on the surface of the mold cavity to help the air and gases to exit the mold cavity. It becomes important to measure the flow of the gas through the vent grooves in relation to the ability of molds to influence the quality of the surface finish of the part and the attainable accuracy of dimensions.
-
Vent Holes: Through vents are small openings made on the mold which are used in exhaust of air and gases. Thus, an optimal location and size for ventilated openings regarding the effectiveness of gas discharge and the mold structure must be determined to provide appropriate surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the part.
-
Exhaust System: The exhaust valve is a device for regulating and controlling the product, which can release gas and automatically control the in and out process. In order to produce plastic parts with higher surface quality and dimensional accuracy, there are high requirements for the efficiency of the exhaust valve and mold structure. The design of the exhaust valve needs to consider the effectiveness of gas exhaust and the structure of the mold.
Ejection System
The ejection system is used to push out the molded plastic parts from the mold. It normally includes ejector pins and plates, ejector rods, and the ejector systems.
-
Ejector Pins: Ejector pins are components that directly contact and eject the plastic parts, usually slender cylindrical bodies. Ejector pins must be designed in concordance with the shape and size of the plastic parts so that they can eject easily.
-
Ejector Plate: The ejector plate is a supporting component of the ejector pin and is used to position and fix the ejector pin. The most important aspect of the ejector plate design is the number of ejector pins included and the location of the ejector pins.
-
Ejector Rods: Ejector rods are parts which link ejector plates or mechanisms, driving the movement of ejector plates and ejector pins. When designing ejector rods they have to factor in the force and stroke of ejection to allow efficient ejection.
-
Ejector Mechanism: Ejector mechanism is a mechanical device of injection molding machines where through hydraulic or mechanical force it enhances the process of propulsion of the ejector rod. The design of the ejector mechanism needs to consider the force and stroke of ejection to ensure effective and efficient ejection. The design and optimization of the ejection system are critical aspects of mold design, directly affecting the molding quality and production efficiency of plastic parts.
The core and cavity are essential for shaping the molded part.True
The core forms the interior, while the cavity creates the exterior shape of the molded part, both being fundamental to part accuracy.
Ejector systems are not critical in injection molds.False
Ejector systems are vital for removing finished parts from the mold, ensuring smooth and consistent production.
What is the Mold Material?
Mold materials are the substances used to create molds for manufacturing processes like injection molding. Choosing the right material is essential for mold durability, precision, and efficiency.
Mold materials are typically made of steel, aluminum, or specialty alloys. Steel is preferred for long-lasting molds, while aluminum is often used for shorter production runs due to its cost-effectiveness. Material choice impacts mold performance and cost-effectiveness.
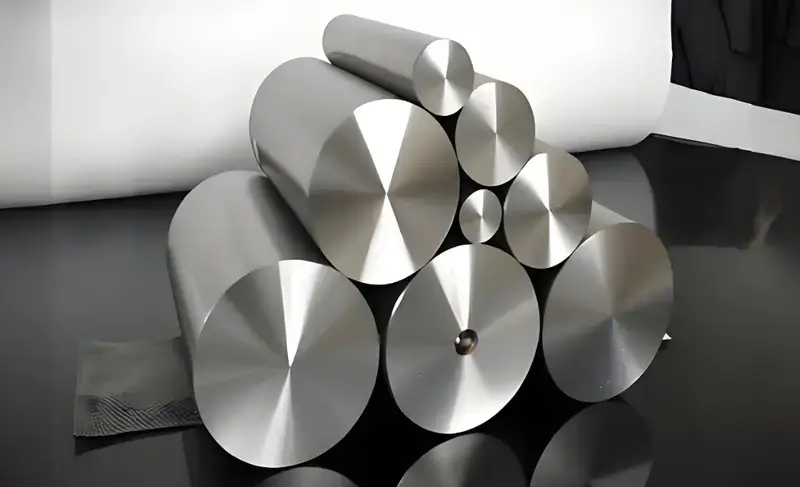

Mold Steel
Mold steel has high tensile strength, high hardness, and good fatigue and wear properties. Thus, most of the injection molds are produced from mold steel. Some of the most regularly used mold steels are P20, 718, H13 and so on Mold steels’ choice depends on several factors such as the mold usage life and cost of production.
Beryllium Copper Alloy
Beryllium copper alloy is a good heat conductor and wear resistant, commonly used for making core components of molds, such as mold cavities and slides. The selection of beryllium copper alloy needs to consider the cooling effect of the mold and production efficiency.
Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloy products are superior in light weight, high speed heat conductivity, which can be used for making prototype mold and small batch production mold. As for the issues with aluminum alloy selection, it’s necessary to take into account the mold service time as well as the cost of production.
Steel is the best material for all molds.False
Steel is durable and ideal for long runs but can be expensive. Aluminum is a more cost-effective option for shorter production cycles.
Aluminum molds are cheaper than steel molds.True
Aluminum molds are lighter and easier to machine, making them a cost-effective choice for low to medium production volumes.
What are the Mold Designs?
Mold designs are crucial blueprints in the injection molding process, determining the shape and functionality of the final product. They influence production efficiency and part quality.
Mold designs dictate the geometry and functionality of molds used in injection molding. Key types include single-cavity, multi-cavity, and family molds. Efficient design reduces production time and material waste.
Mold Cavity Design
Mold cavity design is the patterns and standards of the shape and size of the mold of the plastic products, number of cavities, the layout, tolerance etc. Mold cavity design has to comply with the shape and dimension of the plastic parts to ensure molding quality.
Runner System Design
The runner system design involves the layout of the channel where the molten plastic flows from the mold to the parting line5, the size, position and direction of the main runner, branch runner and gate, etc. For the design of the runner system, it is very necessary to emphasize the flow characteristics of the molten plastic and the structure of the mold.
Cooling System Design
Mold cooling water ways means the design of cooling systems such as the layout, and sizes of the channels as well the type of cooling medium used. Cooling system design needs to consider the cooling effect of the mold and production efficiency to ensure molding quality.
Venting System Design
Venting system design refers to the design of gas discharge channels inside the mold cavity, including the layout and size of vent grooves and vent holes. When working on venting system design, one has to assess the performance of the gaseous discharge and the mold structure in regard to molding quality.
Ejection System Design
Ejection system design refers to the design of plastic part ejection devices, including the arrangement of the number of ejector pins and their positions, size of ejector plates and ejector rods. Design factors related to ejection systems require evaluations that are focused on the efficiency of the ejection in relation to molding quality.
Mold design affects the quality and cost of the final product.True
Efficient mold designs reduce defects, improve part quality, and streamline production, leading to cost savings.
Mold designs are the same for every product.False
Each product requires a unique mold design based on its shape, size, and function, which may vary widely depending on the industry and application.
How is the Mold Manufacturing ?
Mold manufacturing involves creating molds used in injection molding to shape plastic, metal, or other materials. It’s crucial for producing high-quality, precise components across multiple industries.
Mold manufacturing refers to designing and creating molds for injection molding processes. These molds are made from durable materials like steel and aluminum to ensure accuracy and longevity in high-volume production. Mold quality directly impacts part precision and cycle efficiency.

Material Preparation
Regarding the specific mold design requirements, choose appropriate mold and carry out processing including stress-relieving treatment and tempering treatment. Preparation of material is one of the elementary processes in the manufacturing of a mold, as it decides the quality and life span of the mold.
Rough Machining
Turning, milling, planing, and grinding are the machining operations to be used in making molds as the primary roughing or shape creating techniques on mold materials6. The accuracy and efficiency of rough machining directly affect the manufacturing cycle and cost of the mold.
Heat Treatment
Carry out other heat treatment processes of quenching and tempering in mold to increase hardness and wear resistant. The heat treatment quality markedly affects the service life and molding quality of the mold.
Finish Machining
Accurately polish the mould by the method of fine machining such as CNC tooling, EDM, wire cutting etc. , make sure that the molded part is within the tolerance limits stated in the design and possesses the surface finishes as provided. The fine machining accuracy and surface roughness of the precision casting molds will directly impose an impact on the molding quality of the plastic parts.
Assembly and Debugging
Compile multiple members of the mold, debugging and trial molding in order to test the mold and inspect the accuracy and performance of different parts. Assembling is the last process of the mold and debugging; directly impacting the mold’s operational effectiveness and production efficiency.
Mold manufacturing ensures precise product shapes.True
Molds are designed to deliver exact shapes, ensuring uniformity and consistency in mass production.
Mold manufacturing is always time-consuming and expensive.False
While mold creation can be costly, advances in technology and design optimization have made the process more efficient and cost-effective over time.
How to Maintain and Maintain the Mold?
Proper mold maintenance is essential to ensure consistent product quality and extend the lifespan of your molds in injection molding processes.
Regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of molds prevent defects and downtime. Maintenance schedules should focus on removing debris, checking wear, and ensuring proper cooling channels. Timely repairs can reduce costly delays and improve mold performance.

Cleaning
Cleaning of the mold should be done frequently to ensure that it gets rid of the plastic residues, oil stains and other impurities that may be on the surface of the mold so as to keep the mold clean and smooth. Cleaning as one of the most fundamental activities of mold management directly relates to the mold’s performance efficiency and its useful lifespan.
Lubrication
Grease all the moving parts of the mold for minimization of friction between themoving parts thereby lengthening the durability of the mold. Mold lubrication is also one of the essential processes of mold management since it impacts the functionality and durability of the mold.
Rust Prevention
The mold should be treated with rust and corrosion prevention, especially when the mold is not used for a long time. Rust prevention is one of the basic work of mold maintenance, which determines the operation efficiency and service life of the mold.
Inspection
Perform routine checks on various regions of the mold, and replace or correct severely, worn out features to avoid breakdowns in the production processes. Mold inspection is the primary process of mold maintenance with significant impact on the operational efficiency as well as the durability of the mold.
Proper mold maintenance extends mold lifespan.True
Regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection prevent wear and tear, extending the mold's service life and ensuring consistent part quality.
Mold maintenance requires constant professional oversight.False
While professional oversight is beneficial, proper routine care by operators can ensure mold longevity without constant expert involvement.
Conclusion
Functioning as one of the crucial means in the work of the plastics processing industry, injection molds exhibit intricate structures and diverse function. In this article, the author gives the simplest and accurate definitions of various components of injection molds and their roles namely movable and fixed molds, mold frames, cooling systems, runner systems, venting systems and the ejection systems amongst others.
Also, the article presents the selection of mold material, the designing, manufacturing, maintenance, and care of molds, and the areas of using the injection molding processes and injection molds. It is believed that this article has offered the reader sufficient and profound knowledge regarding injection molds aiming at helping the reader as a reference for the design, manufacture, and application of injection molds.
-
Learn about Types of Ejection System in Injection Molding : An ejection system is very important as it is what clears the crate for another injection. ↩
-
Learn about The Eight Types of Injection Molds : In mold types commonly encountered, we find the two-color mold, overmolding, and family mold. ↩
-
Learn about Injection moulding process considerations : Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process that can be used to produce a variety of parts and products. ↩
-
Learn about Sprues,runners and gates of plastic mold : Sprues,runners, and gates fulfill the function of conveying the plastics melt from the nozzle of the injection unit to the individual cavities. ↩
-
Learn about How do I find the parting line of a mold? The parting line of a mold is the line or plane at which the two halves of the mold meet and separate during the injection molding process. ↩
-
Learn about Plastic Injection Mold Materials : Injection molds can be made of steel, aluminum, or beryllium copper. ↩