Introduction: Approximately 80% of plastic parts are manufactured using plastic injection molding.Injection molding has long been considered the only mass production process. With the innovation of industry technology, rapid injection molding is not the only method for mold development.

CAD/CAM/CAE systems reduce design and verification time. In addition to this, new mold varieties were created. Aluminum injection molds and 3D printing molds compete for the manufacturing market. What’s the difference between them? Which mold will make your product more efficient?

Of course, you want to make prototypes faster, cheaper, and look as good as possible. Let’s compare aluminum and what are the differences between 3D printed injection molds.

3D Printed Molds
What is a 3D Printed Mold?
3D printing is a process of using digital files to create three-dimensional objects. First, the computer 3D software slices the parts into digital layers. On the build platform, the feed mechanism deposits material according to the digital layers within a specified range, while the heat source adjusts the shape. The data is processed to build a model by continuously adding material.

What Materials are Used in 3D Printing Molds?
3D printing materials are super important for 3D printing technology. The materials are what make 3D printing possible. Right now, the main materials used in 3D printing are engineering plastics, photosensitive resins, rubber materials, metal materials, and ceramic materials. There are also food materials like colored gypsum materials, artificial bone meal, cell biological raw materials, and sugar that are used in 3D printing.

These materials are made specifically for 3D printing machines and processes. They’re not like regular plastics, gypsum, resins, etc. They come in different forms like powder, filament, sheet, liquid, etc. The particle size of the powder materials used in 3D printing is usually between 1 and 100 micrometers, depending on the type of printer and the printing conditions. The powder needs to be really round so it flows well.

What are the Benefits of Using 3D Printed Molds?
Design flexibility
When 3D printing, you don’t have to worry about things like fixtures and tool interference. You can design for function, including convection channels, integrated structures, and complex features. You can also optimize the shape to reduce weight, simplify manufacturing, improve material utilization, solve problems with difficult-to-machine parts, solve problems with deformation after machining, and create shapes that can’t be made with traditional methods.

Economics of small-batch production
3D printing doesn’t require molds, and it doesn’t require clamping. You don’t have to make a lot of parts to pay for expensive molds. You can make a few parts, or even one part. The economics of low-volume production can reduce the cost of design changes during the development of civil aircraft.

Good production predictability
You can predict how long it will take to 3D print a part and how much it will deform based on the design. You can predict and adjust the deformation by changing the design model. As 3D printing technology and support technology improve, you can control how long it takes to 3D print a part, how good the part is, and how accurate the part is. This means you can measure and control the shape of the part when you design and make a civil aircraft with 3D printing.

Reduce assembly.
Using 3D printing to make integrated parts replaces products that need to be assembled from many parts. This saves the transportation, assembly, fastener installation, welding, and other processes of multiple parts. It also reduces the cost of making parts by eliminating redundant production lines.

Fast to make
In the early design stage of airplanes, it usually only takes a few dozen hours from the time you make a 3D model on the computer to the time you have a physical part. You don’t have to wait for a mold to be made. This means you don’t have to wait for a new mold to be made if you change the shape of the part. You can make changes to the design of the part faster and you can make new parts faster.

What are the Problems with Using 3D Printing to Make Molds?
Accuracy
If the accuracy of the 3D printed mold is not high, there will be layers on the surface, which will affect the use of the mold. Later, mechanical processing or sandblasting is required to remove these layers.

Material restrictions
Technically, the method of building parts layer by layer with materials is different from traditional forging or casting. The microstructure, types of defects, residual stresses, inspectability, post-processing requirements, and structural performance and durability of the materials produced are all different from those of traditional methods.

For complex parts, the material design values may not represent the actual performance of the structure, and it is necessary to verify that the material and process jointly affect the structural performance through structural tests higher than the test piece level.

Limited defect detection
The 3D printing manufacturing process is complex to control. It uses layered manufacturing and layer-by-layer manufacturing processes. The quality of the joints between layers cannot be as uniform as precision forged parts.

3D printing technology is limited by its inherent forming principles. Parts made by 3D printing technology, especially metal parts, have internal manufacturing defects, mainly including voids, micro-cracks, poor melting, and other defects.

The size of these defects is generally less than 20 μm, less than the threshold of general non-destructive testing methods, and these defects are sources of crack initiation, seriously affecting the fatigue performance of the structure.Precision control is difficult In the 3D printing process, there are many factors that affect the quality of the process, from the software and hardware of the equipment itself to the forming materials and forming processes.

Engineering practice shows that the key factors affecting 3D printing accuracy are mechanical control, model data processing, material characteristics, and forming parameter control. These factors control the amount of material added, the size of the 3D printing unit, and the accuracy of system motion, which determine the accuracy of the part in the accumulation direction and the minimum feature manufacturing capability of the part.

Improving 3D printing accuracy requires reducing the amount of material added, controlling the size of the 3D printing unit, and improving system movement accuracy. However, these capabilities are difficult to further improve in short-term research.

Aluminum Molds
What are the Characteristics of Aluminum Molds?
The main characteristics of aluminum molds are light weight, high load-bearing capacity, and high turnover times. During the construction process, they have high construction quality, precision, stability, easy installation, and short construction periods that can save costs.

Their shortcomings are: on-site maintenance and adjustment are not in place and full configuration is required. They have poor adaptability to structural changes, and the cost of projects with many changes is high. When the surface treatment is not good, the aluminum alloy reacts chemically with the concrete, affecting the appearance of the concrete. The fasteners of aluminum molds are prone to conflict with pipeline layout.

What are the Advantages of Aluminum Molds?
Great functional performance
Some prototypes don’t have any mechanical or functional impact, while others need to be used. Pre-production, hybrid, and functional prototype work. Therefore, you need good quality and strength. Aluminum is the metal of choice because it has great properties.

Higher heat resistance
Aluminum prototypes can handle extreme temperatures better than cheaper options like plastic. So, it’s less likely to degrade during the manufacturing process.

Better aesthetics
Whether you’re using 3D printing or CNC machining technology, metal prototypes look better. Plus, even as a non-functional prototype, it looks better than a plastic part.

Cost-effectiveness
Aluminum prototypes and metal parts are much cheaper compared to plastic parts. This is because the physical properties of metal reduce the frequency of parts replacement. This reduces manufacturing costs in the long run.

Test accuracy
Prototypes produced by processes such as CNC machining have high precision. In addition, aluminum alloys have excellent quality and can produce parts for market inspection.

More suitable for mass production
Once engineers create an aluminum prototype, customers can use it for production. It’s easier to turn metal prototypes into finished products. However, if the prototype is made of plastic, it cannot be converted to metal for mass production.

What are the Limitations of Aluminum Molds?
Limited service life
Due to its softer nature, aluminum molds have a limited service life, especially when undergoing high-pressure forming processes or abrasive materials.

Heat resistance
Aluminum has lower heat resistance. This limitation may limit the types of materials that can be used during the molding process, as some materials require higher temperatures than aluminum can withstand.

The Difference Between 3D Printing and Aluminum Molds
What are the Differences Between 3D Printing and Aluminum Molds?
Manufacturing and molding methods
The manufacturing and molding methods of the two are different. 3D printing technology is a technology that uses adhesive materials such as powdered metal or plastic to print and construct objects layer by layer. It is realized using a digital technology material printer. By accumulating and adding up bit by bit, the final work is printed. For aluminum mold manufacturing, 3D modeling software is used to draw mold drawings, and the molding effect is achieved through continuous adjustments.

Accuracy of precision
The precision accuracy of the two is different. The precision accuracy of 3D printing involves many factors. The accuracy of the 3D printer, the quality of the selected materials, and the accuracy of the 3D model drawings all determine the accuracy of the product. The precision accuracy of aluminum molds mainly depends on the user’s actual needs to confirm the precision.

Turnaround time
Turnaround time is the time between the start of mold development and the time the part is ready for production. The design methods and calculations for the two molds are actually different, but the manufacturing stage is where significant changes occur.

Aluminum molds are made from aluminum blanks using CNC machining and finishing operations. In some cases, additional electrical discharge machining (EDM) is required if the cavity must have sharp corners that cannot be obtained by milling. Usually, processing is mainly mechanical processing, no heat treatment is required, and almost no specialized tools are required. The average aluminum mold is produced in 10 to 15 days.

3D printed molds are created using a metal sintering additive manufacturing process. Many fine metal powders are sintered together layer by layer to form the cavity of an injection mold. The main advantage of this process is that it requires little manufacturing preparation and requires no tools. The average time to create such a mold is only 2-3 days.

Stability
Stability is basically how many parts a mold can make before it gets too old. Important to know if you want to make a batch of product.

Aluminum tools are made of softer materials, but some aluminum alloys are really strong. This means the mold can make up to 5,000 parts. The average is 100-2000 copies.
3D printed molds are the worst for stability. There are a lot of problems with sintering chambers. It’s porous and not as strong as a solid blank. Now, 3D printed cavities can make batches of 50 to 200 parts.

Cycle time
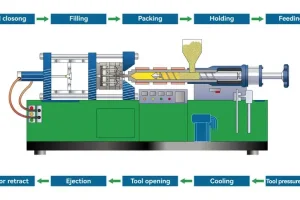
Cycle time is the time it takes to produce one part. It is the sum of the injection time, cooling time, and ejection time. The injection time is the time it takes to fill the mold with plastic. The cooling time is the time it takes for the plastic to cool and solidify. The ejection time is the time it takes to remove the part from the mold.

Aluminum molds have a cycle time of 44-70 seconds. This is quite impressive when we start talking about thousands of parts.3D printed molds have a cycle time of 150-250 seconds.
Part accuracy and surface finish
Part quality is one of the most important factors. After all, this part will serve as an integral part of a larger mechanism and may be presented to future investors. The part must look professional.

The accuracy of aluminum injection molds only depends on the ability to process and polish them. However, the accuracy of 3D printed molds depends on the additive manufacturing process. AM involves the melting and cooling of materials, and thermal deformation can significantly reduce accuracy. Modern technology can produce steel and aluminum mold cavities with tolerances up to IT6, as well as 3D printed molds with tolerances up to IT9.

Flexibility
Flexibility is crucial with pre-production prototypes when you’re only testing how the final product will look and operate. Once you have completed initial prototyping using certain materials, you will need to test the materials you initially selected for your product, as well as test your manufacturing procedures.

Most of the time, you will encounter some problems that will make you modify the design. For example, during running tests, some defects were discovered or the injection process resulted in porous parts. That’s when you want to change the design as well as the mold. Different mold materials have different flexibility

Aluminum molds are made from softer materials, and their cavities are typically manufactured as separate parts that fit into the mold base. Therefore, it is much easier to remove the cavity and make adjustments.

Modifying 3D printed molds is difficult because it requires machining parts of the cavity, and the surface finish will be uneven because machining provides a better surface finish. It is easier to completely remake the mold, which doesn’t take much time, but it does bring with it the undesirable additional expense of prototyping and pre-series testing.

Conclusion
Originally created as a method of rapid prototyping, also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing has evolved into a true manufacturing process. 3D printers enable engineers and companies to produce prototypes and end-use products simultaneously, offering significant advantages over traditional manufacturing processes.

In summary, the main differences between 3D printed molds and aluminum molds include different manufacturing molding methods, different strength accuracy, different turnaround times, different stability, different manufacturing times, different part accuracy and surface finish, and different flexibility.