Introduction
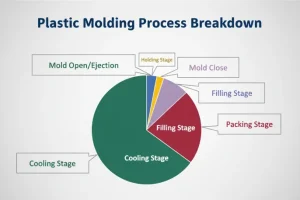
Injection molding, a pivotal technique in contemporary manufacturing, particularly in the domain of plastic goods, epitomizes both efficacy and adaptability. This method is renowned for its ability to shape plastic substances into a plethora of configurations and dimensions, serving myriad purposes across diverse sectors. Fundamentally, injection molding involves the infusion of liquefied plastic at high pressure into a mold, which is the inverse of the intended form.

At the heart of this proficient and complex procedure lies a component termed the injection mold base. Often overlooked yet essential, the mold base is critical to the entire process. Far from being a simple container for the mold, h shaped mold base, it is an intricate structure that underpins, aligns, and expedites the molding operation.
The role of the injection mold base in the fabrication of plastic products is paramount. It governs the accuracy of mold alignment, affects the caliber of the end product, and bears on the productivity of the manufacturing cycle. From mundane objects to sophisticated parts in cutting-edge technology, the caliber of the final plastic item is inextricably linked to the structural integrity and design of the injection mold base.
In summary, the injection mold base forms the bedrock of the injection molding process’s success. Its configuration, material composition, and upkeep are pivotal in determining not only the quality of the plastic item but also the process’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Comprehending the role and complexities of the injection mold base opens a portal to the intriguing realm of plastic manufacturing, where precision engineering converges with material science to fabricate the extensive variety of plastic products that permeate our daily lives.

II. The Essential Role of Injection Mold Bases
The injection mold base plays a vital role in the injection molding process. It serves as the foundation that holds and operates the mold — the hollow cavity where molten plastic is shaped. The mold base is not a single piece but an assembly of various components, each contributing to the molding process. This assembly is crucial for the precision and efficiency of production.
Key Components of a Mold Base
- Mold Plate: The central part of the mold base, providing structure and stability. It forms the core around which other components are arranged.
- Ejector Plate: Houses the ejector pins. These pins are essential for pushing the finished product out of the mold cavity after the plastic solidifies, facilitating smooth production cycles.
- Support Plate: Adds rigidity and support to the mold assembly. It helps bear the pressure during the injection process, maintaining the mold’s alignment and integrity.
Relationship with the Injection Molding Machine
The mold base is intricately connected to the injection molding machine. While the machine injects molten plastic into the mold cavity, the mold base holds and supports the mold in the correct position. This collaboration with standard mold base ensures precise injection of plastic, proper cooling of the mold, and efficient ejection of the final product.
Compatibility and alignment with the injection molding machine are crucial for a mold base. A well-designed mold base fits seamlessly onto the machine and enhances the overall efficiency of the molding process. It plays a significant role in minimizing defects, reducing cycle times, and ensuring consistent quality of molded products.
In conclusion, the injection mold base is a fundamental element in the injection molding process. Its robust construction and precise engineering enable accurate and efficient production of plastic parts, underscoring its essential role in plastic manufacturing.
III. Anatomy of an Injection Mold Base
Exploring the intricacies of an injection mold base unveils the meticulous and intricate engineering involved in its conception. Each constituent element serves a pivotal function, and grasping these functions is essential to fully comprehend the operational dynamics of injection molds.
Cavity Plate and Core Plate:
Deciphering the Mold Cavity’s Intricacies Embedded within the mold base’s core are the cavity and core plates, which collectively sculpt the whole pinpoint gate mold base cavity. The cavity plate molds the external contours of the fabricated item, whereas the core plate shapes its internal structure. This synergistic configuration facilitates the fabrication of plastic components with complex and nuanced details. The craftsmanship precision of these plates is of paramount importance, as it directly influences the fidelity and excellence of the end product.

Ejector System:
Ejector Pins and Ejector Plate’s Crucial Contribution Post the injection and cooling of plastic within the mold cavity, its ejection is imperative for the continuance of the process. Here, the ejector system plays a crucial role. Comprising an ejector plate and pins, this system propels the pins forward upon the mold’s opening, thereby extricating the solidified plastic part from the cavity. The efficacy and dependability of this system are essential for a consistent production rhythm and the safeguarding of the molded parts’ integrity.
Runner System:
The Critical Role of the Runner Stripper Plate in Gate Mold Bases The runner system, especially pertinent in gate mold bases, is another fundamental aspect of the mold base. It orchestrates the flow of molten plastic from the nozzle of the injection molding machine to the mold cavity. Within this mechanism, the runner stripper plate plays a pivotal role. As the mold opens, this plate aids in the expulsion of the runner – the conduit for the plastic’s entry into the mold cavity. This system’s efficiency is vital in multi-cavity molds to ensure a uniform distribution of plastic across all cavities, thereby guaranteeing consistent quality of the produced items.

In summation, every component of the injection mold base, from the cavity and core plates to the ejector and runner systems, collaborates to guarantee efficient and precise production of plastic parts. An understanding of these elements and their roles enhances the appreciation of the sophistication and precision inherent in the injection molding process.
IV. Diverse Mold Base Types for Injection Molding Applications
The realm of injection molding is characterized by its multifaceted nature, necessitating a spectrum of mold base types to accommodate a variety of production exigencies and design criteria. Comprehending the assortment of available mold bases and their designated uses is paramount for the judicious selection of an apt mold base for any specific endeavor.
Delineation of Various Mold Base Types Conventional Mold Bases:
Predominantly utilized in the industry, these mold bases are crafted for uncomplicated tasks. Their versatility renders them apt for a broad spectrum of products, making them a staple choice for numerous standard injection molding operations.
Pinpoint Gate Mold Bases:
Tailored for scenarios demanding meticulous control over the injection site of molten plastic. The pinpoint gate facilitates a more refined and immaculate injection process, rendering these bases ideal for products necessitating elevated aesthetic qualities or possessing elaborate details.
Lateral Gate Mold Bases:
Employed when the gate’s placement is required on the flank of the molded item. This mold base variant is frequently selected for larger components or in situations where the gate’s visibility in the final product is not a primary concern.
Specialized Mold Bases:
I-Form, T-Form, and H-Form I-Form Mold Bases: Optimal for straightforward, linear objects. The ‘I’ configuration allows for streamlined injection and ejection, enhancing efficiency in fabricating elongated, slender products.
T-Form Mold Bases:
Engineered for items necessitating molding from bifurcated directions. This architecture is often employed in intricate components where undercuts or unique features are imperative.
H-Form Mold Bases:
Suited for items needing a central injection locus, frequently utilized in symmetrical components or where an equitable mold fill is crucial.
Principles for Mold Base Selection Based on Parting Requisites and Production Objectives Choosing an appropriate mold base entails a thorough evaluation of several elements:
Mold Parting Requisites:
The very t shaped mold base parting type, whether a straightforward straight pull or an elaborate multi-parting line, significantly influences the mold base design. This choice affects aspects such as ease of production, maintenance, and overall expenditure.

Production Objectives:
Parameters like production volume, cycle duration, and quality standards are pivotal in mold base selection. For high-volume output, a more durable and efficient mold base is essential, whereas for lower volume or prototype production, a more economical and simpler mold base may suffice.
Design Specifications:
The product’s design, encompassing its dimensions, form, and intricacy, greatly sways the mold base choice. Features such as undercuts, threads, or detailed intricacies might necessitate specialized mold bases for optimal production efficacy.
Grasping the variety of mold bases and their applications is vital for attaining desired results in plastic injection molding. An astute selection not only guarantees the quality and functionality of the end product but also enhances the production process in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
V. Selection and Configuration of Substrates in Mould Foundations
The efficacy and durability of a mould base in injection molding are profoundly affected by the choice of materials and the strategic considerations in its design. Grasping the nuanced relationship between substrate selection, surface texture, and architectural elements is crucial for forging mould foundations that are both efficient and long-lasting.
Criticality of Mould Substrate Iron Alloys and Specialized Steel Compositions:
Prevalently, various forms of steel, encompassing pre-hardened steel offering a harmonious blend of affordability and resilience, and custom steel alloys engineered for heightened resistance to abrasion or corrosion, are employed in mould bases. The selection of steel influences the foundation’s robustness, longevity, and its capacity to endure the strenuous pressures and temperatures encountered during the injection molding operation.
Attributes of Mould Substrates: Distinct grades of steel present unique attributes, such as thermal conduction, rigidity, and fusion capabilities. These attributes must be in congruence with the specific demands of the molding procedure, considering the type of polymer being shaped and the projected production scale.
Impact of Surface Texture on the Final Artefact Quality of Surface: The texture of the mould base’s surface, especially the cavity and core plates, directly impacts the surface quality of the molded item. A superior texture can diminish the necessity for post-molding refinement processes and enhance the visual appeal of the product.
Techniques for Finishing: Methods like burnishing, embossing, and applying protective layers are utilized to attain the desired surface quality. The selection of these techniques is contingent upon the final product’s requirements, such as sheen, texture, or resistance to abrasion.
Design Strategies for Optimal Thermal Conductivity and Cooling Ducts Thermal Conductivity: In injection molding, proficient thermal management is vital to regulate the cooling pace of the molten polymer. Effective thermal conductivity ensures consistent quality of parts and shortens cycle durations.
Design of Cooling Ducts: Cooling conduits are incorporated into the mould base design to dissipate heat from the mould cavity. The configuration, dimension, and spacing of these conduits are critical for achieving uniform cooling. Insufficient cooling can result in distortion, surface flaws, or extended cycle durations.

Thermal Dilatation: The design must also take into account the thermal dilatation characteristics of the mould material. As the mould undergoes temperature fluctuations during the molding cycles, materials expand and contract. Appropriate design and material choice ensure these changes do not impinge on the mould’s precision or the final product’s quality.
In summation, the substrates used for mould bases, along with their surface textures and design strategies, are pivotal in the triumph of the injection molding process. Electing suitable materials and design elements is indispensable for attaining peak performance, durability, and quality in molded plastic products.
As we culminate our in-depth examination of the quintessential role of plastic injection molding machine bases within the plastic injection molding cosmos, it becomes manifestly evident that these elements transcend mere structural functionality. They are indispensably integral to the entirety of the procedure, decisively influencing the caliber, efficacy, and triumph of plastic product fabrication.
Recounting the Paramount Importance of Injection Mold Foundations
Indispensable for Exacting Precision and Superior Quality: Serving as the skeleton of the plastic injection molding odyssey, injection mold bases offer crucial support and alignment to the mold cavities and cores. Their meticulous design and construction are paramount in achieving exact replication of component designs and upholding the apex of quality standards in the resultant wares.

Augmenting Process Efficiency: Surpassing the realms of quality, the configuration of mold bases markedly affects the operational efficiency of the manufacturing saga. They play a pivotal role in streamlining cooling and ejection processes and accommodating diverse gate typologies, thus directly swaying cycle durations and production throughput.
The Consequential Influence of Mold Base Selection on Manufacturing
Dictating Quality and Efficiency: The choice of a mold base is a consequential decision impacting the overarching quality and efficiency of the manufacturing journey. Considerations like material selection, design intricacies, and mold base variants (be it standard, pinpoint gate, side gate, etc.) demand meticulous deliberation to align with specific product requisites and production ambitions.
Custom Tailoring for Application Specificity: Variegated applications necessitate divergent mold base configurations. Ranging from conventional forms to bespoke I-shaped, T-shaped, and H-shaped foundations, each archetype fulfills a distinct objective. Opting for an apt mold base not only enhances the quality of the end product but also assures a more streamlined and efficacious manufacturing course.
In essence, the injection mold base stands as a pivotal linchpin in the plastic injection molding process. Its design, material composition, and operational capabilities profoundly sway the overarching success of plastic product manufacturing. An astutely selected and masterfully crafted plastic injection mold base can engender notable enhancements in product quality and manufacturing efficiency, emphatically underscoring the crucial role these components occupy in the expansive domain of plastic injection molding.

Conclusion:
The Integral Role of Injection Mold Bases in Plastic Injection Molding As we conclude our exploration of injection mold bases in the plastic injection molding process, it’s clear that these components are far more than just structural elements. They are, in fact, vital to the entire process, playing a significant role in determining the quality, efficiency, and success of plastic product manufacturing.
The injection mold base is a cornerstone of the plastic injection molding process. Its design, material composition, and functionality have a profound impact on the overall success of plastic product manufacturing. A well-chosen and expertly designed mold base can lead to significant improvements in product quality and manufacturing efficiency, underlining the critical role these components play in the vast world of plastic injection molding.