Foreword: Manufacturing is going through a revolution with 3D printing and injection molding. 3D printing and injection molding are both used to make physical products, but they work in very different ways and have different benefits. So, 3D printing can’t replace injection molding completely.

What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, is a way to make things by building them layer by layer. It’s like building a house out of Lego bricks, but instead of using your hands, a machine does all the work. The machine reads a computer file that tells it what to do, and then it makes the thing you want out of plastic, metal, or other materials.

One of the best things about 3D printing is that you can make things that are really hard or even impossible to make with other kinds of machines. This means that you can make all kinds of new things that you couldn’t make before. You can also make things really fast and really cheap, because you don’t have to spend a lot of money to make a special tool or a mold.

What is Injection Molding ?
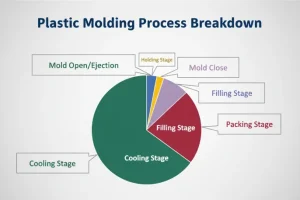
Injection molding is a method where you heat up some stuff, melt it, and then shoot it into a mold. You do this by pushing it in with a lot of pressure. Then you let it cool down and harden. When it’s done, you have a thing. This is a good way to make a lot of things that are hard to make. It’s one of the ways we make things.

So, here’s how injection molding works: you melt plastic pellets and then shoot them into a mold under high pressure. The mold is the shape of the thing you want to make. As the plastic cools and hardens, it takes the shape of the mold, and then you pop the part out.

The good things about injection molding are that it’s efficient and you can make a lot of stuff. Once you pay for the mold, the cost of making each part is pretty low, especially if you make a lot of them. Plus, you can make all kinds of shapes with all kinds of plastics.

Advantages of Injection Molding
Injection molding is famous for its unmatched efficiency in mass production, giving you a fast, consistent, and cost-effective way to make your products. It’s great for making parts with complex shapes, and it keeps the accuracy and consistency high when you’re making a lot of parts. You can also use lots of different materials and colors to meet the needs of different industries.

Suitable for Producing Complex and Precision Products
One of the main advantages of plastic injection molding is that it’s easy to design complex plastic precision parts and assemblies. Injection molding has tight tolerances compared to other technologies. That’s why it’s also widely used in the production of automobile parts.

Choose Freely From a Variety of Materials
There are a ton of plastic materials that can be used in the plastic injection molding process. There are materials such as antistatic plastics, thermoplastic rubbers, chemical-resistant plastics, and biocompostable materials that come in color matching or masterbatch colorings.

Automated Processes That Reduce Manufacturing Costs
Injection molding is an automated process. In fact, most injection molding processes are performed using machines and robots. Since automation reduces manufacturing costs, overhead costs are also reduced. Additionally, as labor is reduced, the overall cost of manufacturing the product is also reduced.

Highly Efficient Production Methods
Once the injection mold is designed according to the specifications given by the customer and the injection molding machine is pre-programmed, the actual molding process used to produce the part becomes very fast. Therefore, one mold can produce more products. High productivity makes plastic injection molding efficient and cost-effective as well.

Produce Less Waste and be Green
For injection molding, the part repeatability factor is very high. Even sprues and runners (i.e., the residual plastic fragments created by the tunnel plastic, from which they reach the actual mold) can be regrinded for material reuse.

Disadvantages of 3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has changed the way we think about design and production. While it offers unparalleled flexibility and customization, it also has limitations. The process is generally slower than traditional manufacturing methods, making it less suitable for high-volume production.

Not Strong Enough
Compared with traditional manufacturing materials, most current 3D printing materials aren’t strong enough. Although some high-strength and wear-resistant materials have been developed, they’re still not as strong as metal. This limits some applications that need to be really strong.
Manufacturing Speed is Relatively Slow
Compared to traditional manufacturing processes, 3D printing is slow. It takes a long time to print large items because 3D printing builds things up layer by layer. Even though people have tried to make 3D printing faster, it still can’t compete with traditional manufacturing speeds.
Materials are Expensive
Right now, the materials used in 3D printing are expensive. Some of the special materials for 3D printing are really expensive. This makes it hard to use 3D printing for big things, especially when the materials cost more than traditional manufacturing.

Defect Detection is a Problem
Because of the complex control of the 3D printing manufacturing process, which uses layered manufacturing and layer-by-layer manufacturing processes, the quality of the joints between layers cannot be as uniform as precision forged parts. 3D printing technology is limited by its inherent forming principles.

Parts made by 3D printing technology, especially metal parts, have internal manufacturing defects, mainly including voids, micro-cracks, poor melting, and other defects. The size of these defects is generally less than 20 μm, less than the threshold of general non-destructive testing methods, and these defects are sources of crack initiation, seriously affecting the fatigue performance of the structure.

Difficulty in Precise Control
In the 3D printing process, from the software and hardware of the equipment itself to the forming materials and forming processes, there are multiple factors that affect the processing quality in each link. Engineering practice shows that the key factors affecting 3D printing accuracy are mechanical control, model data processing, material characteristics and forming parameter control.

These factors control the amount of material added, the size of the 3D printing unit, and the accuracy of system motion, which determine the accuracy of the part in the accumulation direction and the minimum feature manufacturing capability of the part.

Improving 3D printing accuracy requires reducing the amount of material added, controlling the size of the 3D printing unit, and improving system movement accuracy. However, these capabilities are difficult to further improve in short-term research.

What are the Main Differences Between 3D Printing and Injection Molding?
3D printing and injection molding are often seen as competing technologies, each with their own advantages and applications.

While 3D printing offers customization and flexibility, injection molding is great for high-volume production efficiency and lower costs.

Let’s Compare the Differences Between 3D Printing and Injection Molding.
Lnitial Setup Costs
Injection molding has high initial setup costs due to mold manufacturing (e.g., $10,000 – $50,000), while 3D printing has relatively low initial setup costs because no molds are required.

Cost Per Unit
Injection molding is low in high volume and costs decrease with scale, 3D printing is generally higher, especially for one-offs or small batches.

Speed
Injection molding is fast, seconds to minutes per part, ideal for mass production. 3D printing is slower, taking several hours per part, varying by complexity and size.

Materials
Injection molding is available in a wide range of materials, including various plastics and metals, and is suitable for high-stress applications. 3D printing is available in a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and resins, but suitability varies by application.

Volume
Injection molding is highly efficient in mass production, with output ranging from thousands to millions of pieces. 3D printing is best suited for small batches, prototypes, and customized products.

Customization
Injection molding mold replacement is costly and time-consuming. 3D printing is highly .

Flexible and Easy to Modify Designs Digitally
Strength and Durability
Injection molding is generally stronger and better for functional parts, 3D printing can vary depending on the technology and materials used.

Precision and Consistency
Injection molding is extremely precise with tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.005 inches), 3D printing is accurate but can vary (e.g., ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm).

Environmental Lmpact
Injection molding has a high impact due to material waste and energy used in the process, 3D printing has the potential for lower impact with less waste and more sustainable materials.

Design Complexity Capabilities
Injection molding can handle complex designs but is limited by the constraints of the mold, 3D printing is great for complex shapes and intricate details.

Tolerances and Surface Quality
Injection molding has tight tolerances and a good finish without additional processing, 3D printing tolerances may not be as tight and the surface finish may require post-processing.

Material Suitability for End Use
Injection molding is great and good for functional parts and final products, 3D printing is good for prototypes and non-functional parts, but it depends on what you’re making.

When to Use Injection Molding for Plastic Parts?
Injection molding is the way to go for certain manufacturing needs. It’s the best method for projects where volume, cost, and precision are important.

Mass Production
When you need to make a lot of parts, injection molding is the way to go. It’s perfect for mass production because it can make a ton of parts quickly and consistently. The cost to set up the mold is offset by the lower cost per part, which saves you a lot of money when you’re making a lot of parts. Injection molding is the fastest and most efficient way to make thousands to millions of the same thing, so it’s the best choice for high-volume needs.

Consistency and Precision in Production
Injection molding is known for its ability to produce parts with high precision and uniformity. This is the way to go if you need parts with tight tolerances and consistent quality. The precision of injection molding means that each part is a copy of the last, which is important in industries where consistency is key, like automotive and medical device manufacturing.

Complex Part Design and Detail Design
When you’re dealing with complex part designs or need intricate details, injection molding is often the best choice. The process can handle complex geometries and fine details that might be difficult or impossible with 3D printing. Injection molds can be designed to produce complex shapes with high precision, making this method great for parts with detailed features or specific functional requirements.

Materials and Durability
If you need to make parts out of a specific material or with certain physical properties, injection molding gives you a lot of options. You can use all kinds of plastics and composites to make sure your final product is strong enough, flexible enough, or heat resistant enough. This is especially important if you’re making parts that have to stand up to a lot of mechanical stress or environmental factors.

Cost-Effective for Big Orders
When you’re making a lot of parts, the cost benefits of injection molding really start to show. Even though you have to spend more money up front to design the mold and set up the machine, the cost per part goes way down as you make more parts.

Great Surface Finish and Looks Good
Parts made by injection molding have a great surface finish and usually don’t need any more work. It’s important for consumer products that they look as good as they work. Injection molding is the best way to make parts that look good, have the same color and feel the same. That’s why people who make things like phones and toasters use injection molding.

When to Use 3D Printing?
3D printing is great for some things and has some advantages over other ways of making stuff like injection molding.

You Can Make Stuff Fast and Change It Fast
When you’re starting to make something, 3D printing is amazing. It lets you make a thing, try it out, and make it better. You can make stuff fast and change it fast. 3D printing is really good at making stuff fast and easy, making stuff when you need it, and trying out new ideas.

Making Custom Parts
3D printing is great for making custom or personalized parts. Whether it’s custom medical devices, custom car parts, or unique architectural models, this method allows for a lot of customization without the high cost of custom molds for injection molding.

Complex Shapes and Designs
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is that it can handle complex shapes and designs that would be hard or impossible to do with injection molding. This means you can do things that were never possible before, like making parts with internal shapes, undercuts, and weird shapes.

Small-Batch and Limited-Run Production
3D printing is perfect for making small quantities and limited runs. It’s a cost-effective alternative for projects where you don’t need a lot of parts, so you don’t have to spend a ton of money on injection molds. This is especially good for startups and small businesses that don’t have a lot of products.

Less Waste and Sustainable Manufacturing
Sustainability is a big deal in manufacturing, and 3D printing is a greener option. Instead of cutting away material to make a shape, like traditional methods, it only uses the material it needs to build the part. That means less waste.

Application Differences Between 3D Printing and Injection Molding
When it comes to 3D printing vs. injection molding, the choice often depends on the application. Each has its own strengths and is better suited for different production needs.

3D printing is great for customization and complex designs, while injection molding is the preferred choice for high-volume, cost-effective production. Let’s take a closer look at where each is commonly used in various industries.

Prototypes
3D printing allows for rapid design changes and the ability to test multiple iterations quickly. Injection molding is great for final-stage prototypes that need to look and feel like the actual product.

Custom parts: 3D printing is great for custom products or custom components with unique requirements. Injection molding is cost-effective for high-volume custom parts, but each design requires a mold.

Complex Designs
3D printing can make complex details and complex shapes that you can’t make with other methods. Injection molding is limited by mold complexity and is better for simple shapes.

Small batch production
3D printing is cheap for small batches and doesn’t need a big upfront investment. Injection molding is expensive because you have to pay for the mold and the setup.

Mass Production
3D printing is not suitable for mass production due to its slow speed and high cost per unit. Injection molding is highly efficient and significantly reduces the cost per unit in mass production.

Medical devices
3D printing is suitable for custom medical implants and prosthetics, while injection molding is used for mass production of medical supplies such as syringes and vials.

Aerospace Parts
3D printing is suitable for lightweight, complex components, while injection molding is suitable for high-volume items such as cabin parts.

Automotive Parts
3D printing is limited to prototyping and specialty components, while injection molding is suitable for high-volume items such as cabin parts.

Automotive Parts
3D printing is limited to prototype design and professional groups, while injection molding dominates the production of high-volume standard parts.

Consumer Goods
3D printing is great for custom or limited-edition stuff, and injection molding is great for making a lot of stuff like toys and homewares.

Education/Research
3D printing is good for learning and experimenting, injection molding is not typically used because it costs a lot to set up,

Why 3D Printing Cannot Completely Replace Injection Molding ?
Price
Both FDM and injection molding use ABS material. ABS for injection molding costs 10,000 yuan per ton, which is 10 yuan. One kilogram, plus a few cents of toner, the raw material cost is just like this. Looking back, FDM uses ABS filament, which costs about 50 per kilogram. The material cost difference is almost 5 times.

Material Utilization
It is said that 3D printing is additive manufacturing and saves materials. However, many people may not know that injection molding actually saves materials. Injection molding has a very mature waste recycling and reuse process, and the nozzle material can be re-invested without even landing on the ground. Returned to the hopper for reuse, a 25kg bag of raw materials is almost equivalent to 25kg of product.

Speed
Generally speaking, it is not a big problem to process two molds in one minute for injection molding to ensure good product quality. FDM and FDM printing should be recorded in hours.

Product Strength and Molding Accuracy
The word injection molding has made it very clear. After the plastic raw material is melted, it is injected into the mold with a certain pressure. The pressure will still be maintained for a period of time after the raw material fills the mold, and then after a period of time After cooling, it can be removed from the mold.

This process ensures that the product has sufficient strength and precision. Lego bricks, the Lego bricks produced 10 years ago, and the Lego bricks produced today can all fit together well. If FDM is used to make Lego bricks, it is difficult to control the accuracy to this level.

In addition, FDM is printed layer by layer. This method cannot guarantee that the product will be smooth.With enough strength, the same Lego brick can be picked up and used if it is dropped and stepped on, but cannot be used again if it is FDM printed.

In conclusion, injection molding has its advantages as it has evolved. These advantages prevent me from seeing the possibility of being replaced by 3D printing. 3D printing has its advantages as a specialized and customized processing method, but I want to replace injection molding. I think it is still difficult to form.

Conclusion
When it comes to choosing between 3D printing and injection molding, there are a few things to consider. These include throughput, design complexity, cost, and the intended application. 3D printing is great because it’s super flexible. You can use it for rapid prototyping, customization, and creating complex designs. It’s perfect for low-volume production, especially when you need unique or complex parts.

On the other hand, injection molding is great for high-volume production. It’s cost-effective, precise, and consistent. It’s the way to go when you need to make a lot of the same part. It’s especially good when you need parts that are strong and durable. So, when it comes to 3D printing vs. injection molding, each has its own advantages. You need to look at your project and decide which one is right for you.